[Updated: July 6, 2022]
Noise
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- What Is Occupational Noise?
- Basic Qualities of Sound
- How We Hear
- Hearing Loss
- Effects of Excessive Occupational Noise Exposure
- Impulsive/Impact Noise
- Ultrasound
- Ototoxicity and Synergistic Effects with Noise
- Affected Industries and Workers
- Regulations and Standards
- Workplace Hazard Analysis
- Noise Exposure Controls - Overview
- Training
- Hearing Conservation Programs (HCPs)
- Measurements
- Investigation Guidelines
- Hazard Abatement and Control
- References
- Resources
List of Appendices:
Appendix A – Glossary
Appendix B – Sample Equations and Calculations
Appendix C – Ultrasound
Appendix D – Combined Exposure to Noise and Ototoxic Substances
Appendix E – Historical Analysis of Affected Industries and Jobs
Appendix F – Noise Reduction Rating
Appendix G – Evaluating Noise Exposure of Workers Wearing Sound-Generating Headsets
Appendix H – Economic Feasibility Analysis of Noise Engineering Controls
Appendix I – Reviewing Audiograms
Appendix J – Three Ways to Jump-Start a Noise-Control Program
I. Introduction
Hazardous noise is one of the most common occupational hazards in American workplaces. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC)/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) estimates that 22 million workers in the United States are exposed to hazardous noise. Exposure to high levels of noise may cause hearing loss, create physical and psychological stress, reduce productivity, interfere with communication, and contribute to accidents and injuries.
This chapter provides technical information and guidance to help Compliance Safety and Health Officers (CSHOs) evaluate noise hazards in the workplace. The content is based on currently available research publications, OSHA standards, and consensus standards.
The chapter is divided into seven main sections. Following this introduction, the second section provides background information about noise and noise regulations and an overview of available noise controls. The third section describes worksite noise evaluations, including noise measurement equipment, noise evaluation procedures, and noise sampling procedures. The fourth section offers investigative guidelines (including methods for preparing for an investigation) and outlines a strategy for conducting noise evaluations. The fifth section provides a more detailed description of noise hazard abatement and control, including engineering and administrative controls, hearing protection, hearing conservation programs (HCPs), cost comparisons between noise hazard abatement options, and case studies. The final two sections provide references used to produce this chapter and resources for obtaining additional information. Following the main sections, the appendices provide a glossary of terms, sample calculations, and expanded discussion of certain topics introduced in the chapter.
II. Background Information
A. What Is Occupational Noise?
Occupational noise can be any sound in any work environment.
A textbook definition of sound is "a rapid variation of atmospheric pressure caused by some disturbance of the air." Sound propagates as a wave of positive pressure disturbances (compressions) and negative pressure disturbances (rarefactions), as shown in Figure 1. Sound can travel through any elastic medium (e.g., air, water, wood, metal).
Figure 1. Sound Waves
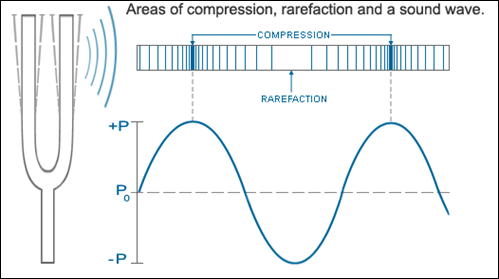
When air molecules are set to vibrate, the ear perceives the variations in pressure as sound (OTM/Driscoll). The vibrations are converted into mechanical energy by the middle ear, subsequently moving tiny membranes across microscopic cilia (hair cells) in the inner ear, which in turn convert the sound waves into nerve impulses. If the vibrations are too intense, over time the cilia can be damaged, causing hearing loss. In the workplace, sound that is intense enough to damage hearing is a hazard that must be addressed by employers.
Several key terms describe the qualities of sound. These qualities influence how it affects hearing and health, how it is measured, and how it can be controlled. Effective occupational noise investigations require the investigator to understand these basic terms.
B. Basic Qualities of Sound
-
Wavelength
The wavelength (λ) is the distance traveled by a sound wave during one sound pressure cycle, as shown in Figure 2. The wavelength of sound is usually measured in meters or feet. Wavelength is important for designing engineering controls. For example, a sound-absorbing material will perform most effectively if its thickness is at least one-quarter the wavelength.
Figure 2. Wavelength

-
Frequency
Frequency, f, is a measure of the number of vibrations (i.e., sound pressure cycles) that occur per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), where one Hz is equal to one cycle per second.
Sound frequency is perceived as pitch (i.e., how high or low a tone is). The frequency range sensed by the ear varies considerably among individuals. A young person with normal hearing can hear frequencies between approximately 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz. As a person ages, the highest frequency that they can detect tends to decrease.
Human speech frequencies are in the range of 500 Hz to 4,000 Hz. This is significant because hearing loss in this range will interfere with conversational speech. The portions of the ear that detect frequencies between 3,000 Hz and 4,000 Hz are the earliest to be affected by exposure to noise. Audiograms often display a 4,000-Hz "Notch" in patients who are developing the beginning stages of sensorineural hearing loss (hearing loss due to damage to the inner ear cilia or the auditory nerve).
-
Speed
The speed at which sound travels, c, is determined primarily by the density and the compressibility of the medium through which it is traveling. The speed of sound is typically measured in meters per second or feet per second.
Speed increases as the density of the medium increases and its elasticity decreases. For example:
-
In air, the speed of sound is approximately 344 meters per second (1,130 feet per second) at standard temperature and pressure.
-
In liquids and solids, the speed of sound is much higher. The speed of sound is about 1,500 meters per second in water and 5,000 meters per second in steel.
The frequency, wavelength, and speed of a sound wave are related by the equation
c = f λ
Where c = speed of sound in meters or feet per second, f = frequency in Hz, and λ = wavelength in meters or feet.
-
-
Sound Pressure
The vibrations associated with sound are detected as slight variations in pressure. The range of sound pressures perceived as sound is extremely large, beginning with a very weak pressure causing faint sounds and increasing to noise so loud that it causes pain.
The threshold of hearing is the quietest sound that can typically be heard by a young person with undamaged hearing. This varies somewhat among individuals but is typically in the micropascal range. The reference sound pressure is the standardized threshold of hearing and is defined as 20 micropascals (0.0002 microbars) at 1,000 Hz.
The threshold of pain, or the greatest sound pressure that can be perceived without pain, is approximately 10 million times greater than the threshold of hearing. It is, therefore, more convenient to use a relative (e.g., logarithmic) scale of sound pressure rather than an absolute scale (OTM/Driscoll).
-
Decibels
Noise is measured in units of sound pressure called decibels (dB), named after Alexander Graham Bell. The decibel notation is implied any time a "sound level" or "sound pressure level" is mentioned.
Figure 3. Decibel Scale

Decibel Scale - Typical Sound Levels (dBA) - From bottom to top (blue to red in color): Noise, 0 - Threshold of Hearing (1000hz), 10, 20 - Silent Study Room, 30, North Rim of Grand Cayon, 40 - Soft Whisper (5 ft. away), 50 - Urban Residence, 60 - Conversation (3 ft. away), 70 - Classroom Chatter, 80 - Freight Train (100 ft. away), 90 - Boiler Room, 100 - Construction Site, 110 - Night Club (w/ music), 120 - Operating Heavy Equipment, 130 - Jet Taking Off (200 ft. away), 140 - Threshold of Pain.
Decibels are measured on a logarithmic scale: a small change in the number of decibels indicates a huge change in the amount of sound pressure and correspondingly the potential for damage to a person's hearing.
The decibel scale is convenient because it compresses sound pressures important to human hearing into a manageable scale. By definition, 0 dB is set at the reference sound pressure (20 micropascals at 1,000 Hz, as stated earlier). At the upper end of human hearing, noise causes pain, which occurs at sound pressures of about 10 million times that of the threshold of hearing. On the decibel scale, the threshold of pain occurs at 140 dB. This range of 0 dB to 140 dB is not the entire range of sound, but is the range relevant to human hearing (Figure 3).
Decibels are logarithmic values, so it is not correct to sum multiple sound values using arithmetic addition. See Appendix B.3 for information on the cumulative effects of multiple sound sources on the decibel level.
The decibel is a dimensionless unit; however, the concepts of distance and three-dimensional space are important to understanding how noise spreads through an environment and how it can be controlled. Sound fields and sound power are terms used in describing these concepts.
-
Sound Fields
Many noise-control problems require a practical knowledge of the relationships between:
- A sound field (a region in which sound is propagating) and two related concepts.
- Sound pressure (influenced by the energy [in terms of pressure] emitted from the sound source, the distance from the sound source, and the surrounding environment) (OTM/Driscoll).
-
Sound power (sound energy emitted from a sound source and not influenced by the surrounding environment).
Sound fields are categorized as near field or far field, a distinction that is important to the reliability of measurements. The near field is the space immediately around the noise source, sometimes defined as within the wavelength of the lowest frequency component (e.g., a little more than 4 feet for a 25-Hz tone, about 1 foot for a 1,000-Hz tone, and less than 7 inches for a 2,000-Hz tone). Sound pressure measurements obtained with standard instruments within the near field are not reliable because small changes in position can result in big differences in the readings.
The far field is the space outside the near field, meaning that the far field begins at a point at least one wavelength distance from the noise source. Standard sound level meters (i.e., type I and type II) are reliable in this field, but the measurements are influenced by whether the noise is simply originating from a source (free field) or being reflected back from surrounding surfaces (reverberant field).
A free field is a region in which there are no reflected sound waves. In a free field, sound radiates into space from a source uniformly in all directions. The sound pressure produced by the source is the same in every direction at equal distances from the point source. As a principle of physics, the sound pressure level decreases 6 dB, on a Z-weighted (i.e., unweighted) scale, each time the distance from the point source is doubled. This is a common way of expressing the inverse-square law in acoustics and is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Sound Pressure Levels in a Free Field

If a point source in a free field produces a sound pressure level of 90 dB at a distance of 1 meter, the sound pressure level is 84 dB at 2 meters, 78 dB at 4 meters, and so forth. This principle holds true regardless of the units used to measure distance.
Free field conditions are necessary for certain tests, where outdoor measurements are often impractical. Some tests need to be performed in special rooms called free field or anechoic (echo-free) chambers, which have sound-absorbing walls, floors, and ceilings that reflect practically no sound.
In spaces defined by walls, however, sound fields are more complex. When sound-reflecting objects such as walls or machinery are introduced into the sound field, the wave picture changes completely. Sound reverberates, reflecting back into the room rather than continuing to spread away from the source. Most industrial operations and many construction tasks occur under these conditions. Figure 5 diagrams sound radiating from a sound source and shows how reflected sound (dashed lines) complicates the situation.
Figure 5. Original and Reflected Sound Waves

The net result is a change in the intensity of the sound. The sound pressure does not decrease as rapidly as it would in a free field. In other words, it decreases by less than 6 dB each time the distance from the sound source doubles.
Far from the noise source--unless the boundaries are very absorbing--the reflected sound dominates. This region is called the reverberant field. If the sound pressure levels in a reverberant field are uniform throughout the room, and the sound waves travel in all directions with equal probability, the sound is said to be diffuse.
In actual practice, however, perfectly free fields and reverberant fields rarely exist--most sound fields are something in between.
-
Sound Power
Up to this point, this discussion has focused on sound pressure. Sound power, however, is an equally important concept. Sound power, usually measured in watts, is the amount of energy per unit of time that radiates from a source in the form of an acoustic wave. Generally, sound power cannot be measured directly, but modern instruments make it possible to measure the output at a point that is a known distance from the source.
Understanding the relationship between sound pressure and sound power is essential to predicting what noise problems will be created when particular sound sources are placed in working environments. An important consideration might be how close workers will be working to the source of sound. As a general rule, doubling the sound power increases the noise level by 3 dB.
As sound power radiates from a point source in free space, it is distributed over a spherical surface so that at any given point, there exists a certain sound power per unit area. This is designated as intensity, I, and is expressed in units of watts per square meter.
Sound intensity is heard as loudness, which can be perceived differently depending on the individual and their distance from the source and the characteristics of the surrounding space. As the distance from the sound source increases, the sound intensity decreases. The sound power coming from the source remains constant, but the spherical surface over which the power is spread increases--so the power is less intense. In other words, the sound power level of a source is independent of the environment. However, the sound pressure level at some distance, r, from the source depends on that distance and the sound-absorbing characteristics of the environment (OTM/Driscoll).
-
Filtering
Most noise is not a pure tone, but rather consists of many frequencies simultaneously emitted from the source. To effectively evaluate the total noise of a most sources, it is usually necessary to measure it across its frequency spectrum. One reason for this is that people react differently to low, mid, and high-frequency sounds. Additionally, for the same sound pressure level, high-frequency noise is much more disturbing and more capable of producing hearing loss than low-frequency noise. Furthermore, engineering solutions to reduce or control noise are different depending on the predominant frequency of the noise. As a general guideline, low-frequency noise is more difficult to control.
Certain instruments that measure sound pressure level can determine the frequency distribution of a sound by passing that sound successively through several different electronic filters that separate the sound into nine octaves on a frequency scale. Two of the most common reasons for filtering a sound include 1) determining its most prevalent frequencies (or octaves) to help determine how to best control the sound and 2) adjusting the sound level reading using one of several available weighting methods. These weighting methods (e.g., the A-weighted network, or scale) are intended to indicate perceived loudness across octaves and provide a rating of industrial noise that indicates the impact that particular noise has on human hearing. The following paragraphs provide more detailed information.
-
Octave Bands (Frequency Bands)
Octave bands, a type of frequency band, are a convenient way to measure and describe the various frequencies that are part of a sound. A frequency band is said to be an octave in width when its upper band-edge frequency, f2, is twice the lower band-edge frequency, f1: f2 = 2 f1.
Each octave band is named for its center frequency (geometric mean), calculated as follows: fc = (f1f2)1/2, where fc = center frequency and f1 and f2 are the lower and upper frequency band limits, respectively. The center, lower, and upper frequencies for the commonly used octave bands are listed in Table II-1.
Table II-1. Octave Band Filters and Frequency Range Lower Band Limit (Hz)
Band Center Frequency
(Geometric Mean in Hz)Upper Band Limit (Hz)
22
31.5
44
44
63
88
88
125
177
177
250
354
354
500
707
707
1,000
1,414
1,414
2,000
2,828
2,828
4,000
5,656
5,656
8,000
11,312
11,312
16,000
22,624
Each octave band is named for its center frequency.
The width of a full octave band (its bandwidth) is equal to the upper band limit minus the lower band limit (bandwidth = f2 - f1). For more detailed frequency analysis, the octaves can be divided into one-third octave bands; however, this level of detail is not typically required for evaluation and control of workplace noise.
Electronic instruments called octave band analyzers (OBA) filter sound to measure the sound pressure (as dB) contributed by each octave band. These analyzers either attach to a type 1 sound level meter or are integral to the meter. Both the analyzers and sound level meters are discussed further in Section III.
-
Loudness and Weighting Networks
Loudness is the subjective human response to sound. It depends primarily on sound pressure but is also influenced by frequency.
Three different internationally standardized characteristics are used for sound measurement: weighting networks A, C, and Z (or "zero" weighting). The A and C weighting networks are the sound level meter's means of responding to some frequencies more than others. The very low frequencies are discriminated against (attenuated) quite severely by the A-network and hardly attenuated at all by the C-network. Sound levels (dB) measured using these weighting scales are designated by the appropriate letter (i.e., dBA or dBC).
The A-weighted sound pressure level measurement is thought to provide a rating of noise that predicts the injurious effects the noise has on human hearing and has been adopted by OSHA in its noise standards (OTM/Driscoll). In contrast, the Z-weighted measurement is an unweighted scale (introduced as an international standard in 2003), which provides a flat response across the entire frequency spectrum from 10 Hz to 20,000 Hz. The C-weighted scale is used as an alternative to the Z-weighted measurement (on older sound level meters on which Z-weighting is not an option). It can be used to evaluate hearing protection and for characterizing low-frequency sounds capable of inducing vibrations in buildings or other structures. Some references may mention the B-weighted scale, but note that this scale is no longer used.
The networks evolved from experiments designed to determine the response of the human ear to sound, reported in 1933 by a pair of investigators named Fletcher and Munson. Their study presented a 1,000-Hz reference tone and a test tone alternately to the test subjects (young men), who were asked to adjust the level of the test tone until it sounded as loud as the reference tone. The results of these experiments yielded the frequently cited Fletcher-Munson, or "equal-loudness," contours, which are displayed in Figure 6.
Figure 6. The Fletcher-Munson Contours

These contours represent the sound pressure level necessary at each frequency to produce the same loudness response in the average listener. The nonlinearity of the ear's response is represented by the changing contour shapes as the sound pressure level is increased (a phenomenon that is particularly noticeable at low frequencies). The lower, dashed curve indicates the threshold of hearing and represents the sound-pressure level necessary to trigger the sensation of hearing in the average listener. Among healthy individuals, the actual threshold may vary by as much as 10 decibels in either direction.
Ultrasound is not listed in Figure 6 because it has a frequency that is too high to be audible to the human ear. See Appendix C for more information about ultrasound and its potential health effects and threshold limit values.
C. How We Hear
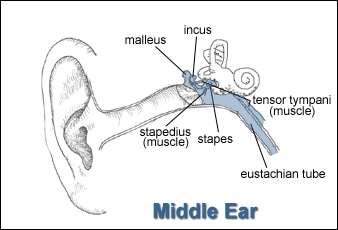
The ear is the organ that makes hearing possible. It can be divided into three sections: the external or outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Figure 7 shows the parts of the ear.
Figure 7. Anatomy of the Human Ear
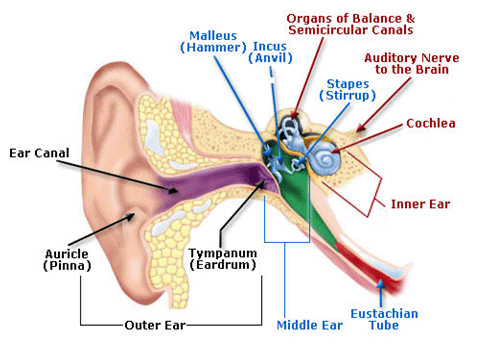
Anatomy of the Human Ear illustration includes Outer Ear - Auricle (Pinna), Ear Canal, and Tympanum (Eardrum), Middle Ear - Malleus (Hammer), Incus (Anvil), Stapes (Stirrup) and Eustachian Tube, Inner Ear - Organs of Balance & Semicircular Canals, Auditory Nerve to the Brain, and Cochlea.
The function of the ear is to gather, transmit, and perceive sounds from the environment. This involves three stages:
-
Stage 1: Modification of the acoustic wave by the outer ear, which receives the wave and directs it to the eardrum. Sound reaches the eardrum as variations in air pressure.
-
Stage 2: Conversion and amplification of the modified acoustic wave to a vibration of the eardrum. These vibrations are amplified by the ossicles, small bones (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) located in the middle ear that relay vibration to the inner ear. The vibrations are then transmitted as wave energy through the liquid of the inner ear (the cochlea).
-
Stage 3: Transformation of the mechanical movement of the wave into nerve impulses that will travel to the brain, which then perceives and interprets the impulse as sound. The cilia of nerve cells in the inner ear respond to the location of movement of the basilar membrane and, depending on their position in the decreasing radius of the spiral-shaped cochlea, activate the auditory nerve to transmit information that the brain can interpret as pitch and loudness.
Impaired function at any of these stages will affect hearing.
Additional information on the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear is available on OSHA's Occupational Noise Exposure Safety and Health Topics Page.
D. Hearing Loss
To categorize different types of hearing loss, the impairment is often described as either conductive or sensorineural, or a combination of the two.
Conductive hearing loss results from any condition in the outer or middle ear that interferes with sound passing to the inner ear. Excessive wax in the auditory canal, a ruptured eardrum, and other conditions of the outer or middle ear can produce conductive hearing loss. Although work-related conductive hearing loss is not common, it can occur when an accident results in a head injury or penetration of the eardrum by a sharp object, or by any event that ruptures the eardrum or breaks the ossicular chain formed by the small bones in the middle ear (e.g., impulsive noise caused by explosions or firearms). Conductive hearing loss may be reversible through medical interventions such as hearing amplification (e.g. hearing aids) or surgical treatment. It is characterized by relatively uniformly reduced hearing across all frequencies in audiometric tests of the ear, with no reduction using hearing tests that transmit sound through bone conduction.
Sensorineural hearing loss tends to be a permanent condition that is often associated with irreversible damage to the inner ear. The normal aging process and excessive noise exposure are both notable causes of sensorineural hearing loss. Studies show that exposure to noise damages the sensory cilia that line the cochlea. Even moderate noise can cause twisting and swelling of the cilia and biochemical changes that reduce cilia sensitivity to mechanical motion, resulting in auditory fatigue. As the severity of the noise exposure increases or if the noise exposure is chronic, the cilia and supporting cells disintegrate and the associated nerve fibers eventually disappear. Occupational noise exposure is a significant cause of sensorineural hearing loss, which appears on sequential audiograms as declining sensitivity to sound, typically first at high frequencies (4,000 Hz), and then lower frequencies as damage continues. Often the audiogram of a person with sensorineural hearing loss will show a "Notch" between 3,000 Hz and 6,000 Hz, and most commonly at 4,000 Hz. This is a dip in the person's hearing level at 4,000 Hz and is an early indicator of sensorineural hearing loss due to noise. Results are the same for audiometric hearing tests and bone conduction testing. Sensorineural hearing loss can also result from other causes, such as viruses (e.g., mumps), congenital defects, and some medications. Modern hearing aids, though expensive, are able to adjust background sounds, changing signal-to-noise ratios, and support hearing and speech discrimination despite the diffuse nature of sensorineural hearing loss. The role of cochlear implants remains unclear.
Figure 8 shows the typical audiogram patterns for people with conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Figure 8. Audiograms
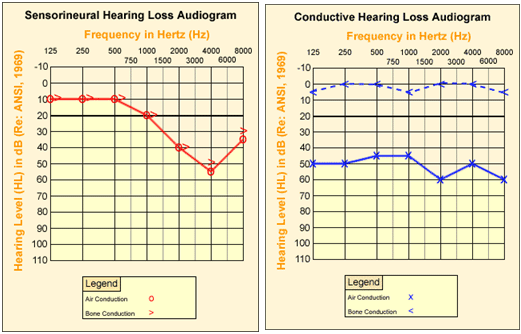
Download the NIOSH "Hearing Loss Simulator" to understand more about the effects of noise exposure and age on hearing.
Presbycusis is a gradual sensorineural hearing loss associated with aging. The onset and the degree of hearing loss can vary considerably and is related to genetics, other impacts such as an accumulation of diseases, medications, and the cumulative effect of noise in the modern environment. Presbycusis and noise induced hearing loss appear to be additive and both can contribute to hearing loss in older people. Both types of hearing loss affect the upper range of an audiogram. A sloping audiogram with tapering to the lowest levels at 8,000 Hz often indicates that the hearing loss is aged-related, but after years of exposure, noise-induced hearing loss can have the same pattern. As humans begin losing their hearing, they often first lose the ability to detect quiet sounds in the high frequency range. This progresses to difficulty understanding conversations in noisy environments, even when amplified by hearing aids.
Mixed hearing loss is any combination of conductive and sensorineural loss. For example, a middle ear infection combined with noise-induced hearing loss.
E. Effects of Excessive Occupational Noise Exposure
Workplace noise affects the human body in various ways. The most well-known is hearing loss, but work in a noisy environment also can have other effects.
-
Auditory Effects
Although noise-induced hearing loss is one of the most common occupational illnesses, it is often ignored because there are no visible effects. It usually develops over a long period of time, and is typically painless. Employees experience a progressive loss of communication, socialization, and responsiveness to the environment. In its early stages (when hearing loss is above 2,000 Hz), it affects the ability to understand or discriminate speech. As it progresses, it begins to affect the ability to hear sounds in general.
The primary effects of workplace noise exposure include noise-induced temporary threshold shift, noise-induced permanent threshold shift, acoustic trauma, and tinnitus. A noise-induced temporary threshold shift is a short-term decrease in hearing sensitivity that displays as a downward shift in the audiogram output. It returns to the pre-exposed level in a matter of hours or days, assuming there is not continued exposure to excessive noise.
If noise exposure continues, the shift can become a noise-induced permanent threshold shift, which is a decrease in hearing sensitivity that is not expected to improve over time. A standard threshold shift (STS), as defined by OSHA, is a change in hearing thresholds of an average of 10 dB or more at 2,000, 3,000, and 4,000 Hz in either ear when compared to a baseline audiogram. Employers can conduct a follow-up audiogram within 30 days to confirm whether the STS is permanent. Under 29 CFR 1910.95(g)(8), if workers experience an STS, employers are required to fit or refit the workers with hearing protectors, train them in the use of the hearing protectors, and require the workers to use them. Recording criteria for cases involving occupational hearing loss can be found in 29 CFR 1904.10; also see information and examples in Appendix I.
The effects of excessive noise exposure worsen when workers have extended shifts (longer than 8 hours). With extended shifts, the duration of the noise exposure is longer and the amount of time between shifts is shorter. This means that the ears have less time to recover between noisy shifts. As a result, short-term effects, such as temporary threshold shifts, can become permanent more quickly than would occur with standard 8-hour workdays.
Tinnitus, or "ringing in the ears," is a common byproduct of overexposure to noise and can occur after long-term exposure to high sound levels, or sometimes from short-term exposure to very high sound levels, such as gunshots. Other physical and physiological conditions are also known to cause tinnitus. Regardless of the cause, this condition is actually a disturbance produced by the inner ear and interpreted by the brain as sound. Individuals with tinnitus describe it as a hum, buzz, roar, ring, or whistle, which can be short term or permanent. Noise-exposed workers may not associate tinnitus with noise exposure or be aware that tinnitus may be an early indicator of overexposure to noise. Hearing conservation training is often focused on noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) and may not address tinnitus awareness and prevention adequately.
Acoustic trauma refers to a temporary or permanent hearing loss due to a sudden, intense acoustic or noise event, such as an explosion.
-
Worker Illness and Injury Reports
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) publishes annual statistics for occupational injuries and illnesses (including hearing loss) reported by employers as part of required recordkeeping. The BLS data shows, that in private, state government, and local government establishments, hearing loss represented 9.9% of the occupational illnesses reported in 2019, or a total of 16,900 cases (BLS table SNR07.xlsx). For private establishments, hearing loss represented 11.4% of the occupational illnesses during the same year (see Figure 9 below). Between 2014 and 2019, the rate declined from 1.9 to 1.4 cases per 10,000 full-time workers. Although there was a decline in rate during this period, the number of cases is still significant and hearing loss remains as a hazard that must be continuously addressed.
Figure 9. Distribution of Occupational Injury and Illness Cases Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, 2019

- Other Effects
As a general guideline, the work area is too noisy if a worker cannot make themselves understood without raising their voice while talking to a co-worker 3 feet away.
Other consequences of excessive workplace noise exposure include interference with communications and performance. Workers might find it difficult to understand speech or auditory signals in areas with high noise levels. Noisy environments also lead to a sense of isolation, annoyance, difficulty concentrating, lowered morale, reduced efficiency, absenteeism, and accidents.
In some individuals, excessive noise exposure can contribute to other physical effects. These can include muscle tension and increased blood pressure (hypertension). Noise exposure can also cause a stress reaction, interfere with sleep, and cause fatigue.
F. Impulsive/Impact Noise
Impulsive/impact noise is typically generated by the rapid release of compressed gases (impulse) or the collision of solid objects (impact) and is defined as the instantaneous change in sound pressure over a short period of time. Examples may include the impact of two metal objects, or the shooting of a firearm. The standard states that exposure to impulsive or impact noise should not exceed a 140-dB peak sound pressure level. Impulsive or impact noises are considered to be much more harmful to hearing than continuous noises. In construction, most of the 500,000 workers who are exposed to hazardous noise levels are also exposed to impulsive and impact noise sources on worksites. Impulsive and impact noise is typified by a sound that rapidly rises to a sharp peak and then quickly fades. Both are transient noises of brief duration and high intensity. The sound may or may not have a "ringing" quality (such as a striking a hammer on a metal plate or a gunshot in a reverberant room). Impulsive noise can be repetitive or a single event (like a sonic boom); if impulses occur in very rapid succession (such as with some jack hammers), it is not described as impulsive or impact noise.
G. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is high-frequency sound that is inaudible (i.e., cannot be heard) by the human ear. However, it still might affect hearing and produce other health effects. For more information, see Appendix C.
Factors to consider regarding ultrasound include:
-
The upper frequency of audibility of the human ear is approximately 15 to 20 kilohertz (kHz). This is not a set limit: some individuals may have higher or lower (usually lower) limits. The frequency limit normally declines with age.
-
Most of the audible noise associated with ultrasonic sources, such as ultrasonic welders or ultrasonic cleaners, consists of subharmonics of the machine's major ultrasonic frequencies.
Example: Many ultrasonic welders have a fundamental operating frequency of 20 kHz, a sound that is at the upper frequency of audibility of the human ear. However, a good deal of noise may be present at 10 kHz, the first subharmonic frequency of the 20-kHz operating frequency, which is audible to most people.
H. Ototoxicity and Synergistic Effects with Noise
Ototoxicity is the property of being toxic to the ear (oto-), specifically the cochlea or auditory nerve. Ototoxic agents (ototoxins) have adverse effects on organs or nerves involved in hearing or balance and may be physical (e.g., noise), biological, or chemical. Substances including pesticides, solvents, pharmaceuticals, asphyxiants, nitriles, and metal compounds that contain ototoxicants may expose workers via inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. Severity of health effects caused by ototoxicants vary depending on compound characteristics and properties; exposure route; exposure concentration, frequency, and duration; exposures to other hazards, and individual characteristics such as age.
Animal and epidemiological studies have demonstrated that combined exposure to noise and some chemicals (e.g., solvents) induces synergistic adverse effects on hearing. Experimental studies have explored specific substances, including toluene, styrene, ethylbenzene, and trichloroethylene. A 2019 study found that organic solvents benzene, ethylbenzene, and toluene were significantly associated with increased adjusted odds of high-frequency hearing loss (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30806784/).
Evidence from epidemiological studies strongly suggests that combined exposure to noise and ototoxic substances can have interactive effects (either additive or synergistic), in which they exacerbate noise-induced impairments even though the noise intensity is below the permissible limit value. Synergistic ototoxic effects with noise have also been reported with asphyxiants (such as carbon monoxide) and metals (such as lead).
While an estimated 22 million workers in the United States are affected by noise exposures, estimates of the number of workers exposed to combinations of noise and ototoxic organic solvents are between 5 and 10 million. Reviewing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for ototoxic chemicals or ingredients is one way to identify ototoxicant chemicals in the workplace. A combination of interventions based on the hierarchy of control (elimination; engineering, administrative, and work practice controls; and personal protective equipment (PPE)) can be used to prevent/minimize exposure to ototoxic chemicals. In 2018, OSHA and NIOSH published a Safety and Health Information Bulletin (SHIB) “Preventing Hearing Loss Caused by Chemical (Ototoxicity) and Noise Exposure” (SHIB 03-08-2018). See Appendix D for additional information and additional sources of information on this topic.
I. Affected Industries and Workers
Workplace noise exposure is widespread. A 2019 review of occupational noise exposure notes that while the Mining, Construction, and Manufacturing sectors typically have the highest prevalence of noise exposure and hearing loss, there are noise-exposed workers in every sector and every sector has workers with hearing loss (https://doi.org/10.1121/1.5134465). For example, a 2020 study of the Services sector that examined audiograms for 1.9 million workers (158,436 within Services) from 2006 to 2015, found that the prevalence of hearing loss within the Services sector was 17% compared to 16% for all industries combined. However, many sub-sectors greatly exceeded the overall prevalence (10–33% greater) and/or had adjusted risks significantly higher than the reference industry. Workers in Administration of Urban Planning and Community and Rural Development had the highest prevalence (50%), and workers in Solid Waste Combustors and Incinerators had more than double the risk, the highest of any sub-sector (https://doi.org/10.1080/14992027.2020.1780485). A 2015 review of audiograms for 1.8 million workers from 1981–2010 evaluated trends for worker hearing loss by industry and found that in addition to the prevalence being consistently high for Mining and Construction workers, the risk also remained high for workers in Healthcare and Social Assistance (https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.22429).
Occupational hearing loss surveillance performed by NIOSH indicated the highest percentage of workers exposed to hazardous noise occurred in the construction, manufacturing, and mining/oil and gas extraction industries. These same industries had the highest percentage of workers with material hearing impairment. A summary of this data is shown in Table II-2 below.
|
Industry |
Workers Exposed to Hazardous Noise |
Workers with Hearing Difficulty |
Workers with Tinnitus |
Workers (tested) with Material Hearing Impairment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Industries |
25% |
12% |
8% |
16% |
|
Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing, and Hunting |
37% |
14% |
13% |
15% |
|
Construction |
51% |
14% |
7% |
25% |
|
Healthcare and Social Assistance |
13% |
10% |
7% |
19% |
|
Manufacturing |
46% |
18% |
11% |
20% |
|
Mining and Oil and Gas Extraction |
61% |
23% |
11% |
24% (mining) |
|
Services (including Public Safety) |
11-34% |
8-15% |
6-10% |
17% |
|
Transportation (T), Warehousing (W), and Utilities (U) |
40% (T,W) |
13% (T,W) |
7% (T,W) |
12% (T,W,U) |
|
Wholesale (W) and Retail (R) Trade |
28% (W) |
9% (W) |
6% (W) |
20% (W,R) |
A previous historical analysis of OSHA’s Integrated Management Information System (IMIS) data for 1979-2006 showed that workers were exposed to hazardous noise levels in every major industry sector. A summary of this analysis is contained in Appendix E.
J. Regulations and Standards
- Brief History of Occupational Noise Standards
The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act) of 1970 built upon earlier attempts in the United States to regulate noise hazards associated with occupational hearing loss. In 1969, the Walsh-Healey Public Contract Act added the Occupational Noise Exposure Standard as an amendment, basing it on the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) noise threshold limit value (TLV) in effect at that time. This set an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) of 90 dBA, a 90 dBA sampling threshold, and a 5-dBA exchange rate for any company with a federal contract worth more than $10,000. This effort to reduce occupational noise hazards was not far-reaching but was a first attempt to regulate noise hazards. Adopted into the OSH Act in 1970, it served as the basis for OSHA's noise standard. The same 8-hour TWA, threshold, and exchange rate are still used by OSHA today.
Also in 1969, the Bureau of Labor Standards promulgated an occupational construction noise standard under the Construction Safety Act, which was later adopted by OSHA in 1971. Soon after, in 1972, NIOSH published recommendations for an OSHA occupational noise standard, which included a recommended 8-hour TWA exposure limit of 85 dBA, an 80 dBA sampling threshold, and a 5-dBA exchange rate. However, in 1973, OSHA's Standards Advisory Committee maintained the 90-dBA 8-hour TWA, 90 dBA sampling threshold, and 5-dBA exchange rate. Even though noise energy exposure doubles every 3 dB, OSHA thought it important to account for the time during the workday that a worker was not exposed to noise hazards. At the time, using a 5-dB exchange rate was viewed as a sufficient way to account for this.
In 1974, OSHA published a proposed occupational noise standard, which included a requirement for employers to provide a hearing conservation program for workers exposed to an 8-hour TWA of 85 dBA or more using an 80 dBA sampling threshold and 5 dBA exchange rate. This provision was adopted as part of the amendments of 1981 and 1983. The 8-hour TWA for OSHA's noise standard remained at 90 dBA, 90 dBA sampling threshold, and 5-dBA exchange rate and included a requirement for a hearing conservation program for workers exposed to an 8-hour TWA of at least 85 dBA, 80 dBA sampling threshold, and a 5 dBA exchange rate. More recently, in the 2002 recordkeeping standard (29 CFR Part 1904), OSHA clarified the criteria for reporting cases involving occupational hearing loss.
While OSHA provided requirements for hearing conservation programs in general industry under the 1983 Hearing Conservation Amendment (HCA), the construction industry standard remained less specific in that regard. In 2002, an advance notice of proposed rulemaking (ANPR) was published in the Federal Register, 67:50610-50618, considering rulemaking to revise the construction noise standards to include a hearing conservation component for the construction industry that provides a similar level of protection to that afforded to workers in general industry. However, the rulemaking did not proceed and the occupational noise standard for construction remained unchanged.
In 1979, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) developed labeling requirements for hearing protectors, which required hearing protector manufacturers to measure the ability of their products to reduce noise exposure--called the noise reduction rating (NRR). OSHA adopted the NRR but later recognized that the NRR listed on hearing protectors often did not reflect the actual level of protection. The actual level of protection is likely lower than indicated on the label because most workers are not provided with fit-testing, and donning methods in a controlled laboratory setting are not representative of the donning methods that workers used in the field. EPA is considering options for updating this rule. See Appendix F for current information on NRRs and hearing protection labeling requirements. In special cases, noise exposure originates from noise-generating headsets. See Appendix G for a discussion of the techniques used to evaluate the noise exposure levels of these workers.
In 1998 NIOSH published Criteria for a Recommended Standard: Occupational Noise Exposure (DHHS 98-126). That publication recommends a 3 dB rather than a 5 dB exchange rate. Although OSHA enforces its own standard, the Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation (CAOHC), which trains and certifies clinicians in managing audiometric programs, expects clinicians to understand how the different exchange rates influence estimates of noise dose and therefore affect attribution to hearing loss.
- OSHA Noise Standards
General Industry: 29 CFR 1910.95, "Occupational Noise Exposure." This standard is designed to protect general industry workers, such as those working in the manufacturing, utilities, and service sectors. The general industry standard establishes permissible noise exposures, requires the use of engineering and administrative controls, and sets out the requirements of a hearing conservation program. Paragraphs (c) through (n) of the general industry standard do not apply to the oil and gas well-drilling and servicing operations; however, paragraphs (a) and (b) do apply.
The general industry noise standard contains two noise exposure limit tables. Each table serves a different purpose:
-
Table G-16: This table applies to the engineering and administrative controls section, which provides a 90-dBA criterion for an 8-hour TWA PEL and is measured using a 90-dBA threshold (i.e., noise below 90 dBA is not integrated into the TWA). This table limits short-term noise exposure to a level not greater than 115 dBA (for up to 15 minutes).
-
Table G-16A: This table, presented in Appendix A of 29 CFR 1910.95, provides information (e.g., reference durations) useful for calculating TWA exposures when the workshift noise exposure is composed of two or more periods of noise at different levels. Although this table lists noise levels exceeding 115 dBA, these listings are only intended as aids in calculating TWA exposure levels; the listings for higher noise exposure levels do not imply that these noise levels are acceptable.
Additional information on the general industry standard is also available on the Safety and Health Topics, Occupational Noise Exposure-Standards page.
Construction Industry: Noise in construction is covered under 29 CFR 1926.52, "Occupational Noise Exposure," and 29 CFR 1926.101, "Hearing Protection." Under 29 CFR 1926.52, employers are required to use feasible engineering or workplace controls when workers are exposed to noise at or above permissible noise exposures, which are listed in Table D-2 [1926.52(d)(1)]. The PEL of 90 dBA for an 8-hour TWA is measured using a 90-dBA threshold (this is the only threshold used for the construction industry noise standards). 29 CFR 1926.101 requires employers to provide hearing protectors that have been individually fitted (or determined to fit) by a competent person if it is not feasible to reduce noise exposure below permissible levels using engineering or workplace controls.
The requirements for permissible noise exposures and controls under the construction standard are the same as those under the general industry standard (1910.95), though other requirements differ. Continuing, effective hearing conservation programs are required in all cases where the sound levels exceed the values shown in Table D-2 (1926.52(d)(1)). When a hearing conservation program is required, employers must incorporate as many elements listed in the Standard Interpretation titled "Effective Hearing Conservation Program Elements for Construction Industry" (08/04/1992) into their program as feasible.
Agricultural Worksites: Although there is no standard for occupational noise exposure in agriculture, the evaluation and control methods discussed in this chapter are still valid. For any potential citations, CSHOs must use the guidance in the Field Operations Manual.
Maritime Worksites: Noise in marine terminals and longshoring operations fall under the requirements of the general industry noise standard; therefore, employers in such operations must meet the elements of the general industry Hearing Conservation Amendment, 29 CFR 1910.95(c) through (o).
-
K. Workplace Hazard Analysis
OSHA considers incorporating workplace hazard analyses (sometimes referred to as job hazard analyses) into a Safety and Health Program (SHP) as a best practice and as one component of the employer’s larger commitment to ensuring a safe and healthful workplace for its workers. (See OSHA Recommended Practices for Safety and Health Programs for more information).
The first step in doing a workplace hazard analysis is identifying the hazards; this is done to obtain a comprehensive overall picture of what hazards are or may be present in the workplace environment, including how the hazards may vary by specific job tasks. The workplace hazard analysis focuses on the relationship between the worker, the task, the tools, and the work environment. Workplace hazard analysis should include a comprehensive noise hazard evaluation to identify workers’ exposure to impact/impulsive noise, ultrasound, and mixed hazards with the potential for additive or synergistic negative effects (e.g., ototoxic chemicals and noise). Negative outcomes of excess workplace noise exposure include noise-induced temporary threshold shift, noise-induced permanent threshold shift, high-frequency hearing loss, acoustic trauma, tinnitus, loss of communication, and potential increases in workplace injuries due to that loss in communication. A review of previous audiograms and illness logs to identify trends of workplace noise induced hearing loss should also be included in the workplace hazard analysis for noise.
The second step in doing a workplace hazard analysis is identifying measures to adequately control the hazards. This is necessary in order to gain a comprehensive picture of the measures that can be used to eliminate or reduce exposures to the workplace hazards.
The third step in doing a workplace hazard analysis is making an assessment of whether the combination of measures control the hazards to an acceptable level. Hazard abatement and control includes following the hierarchy of controls and prioritizing engineering controls as a top option. Ideally, the use of engineering controls should reduce noise exposure to the point where the risk to hearing is significantly reduced or eliminated. If engineering controls alone are not sufficient, a combination of controls including engineering, administrative, work practice, PPE, training, and development and implementation of a hearing conservation program should be tailored to adequately protect workers at that specific workplace. More detailed information on abatement and control is provided in Section V.
L. Noise Exposure Controls - Overview
Noise controls should minimize or eliminate sources of noise; prevent the propagation, amplification, and reverberation of noise; and protect workers from excessive noise exposure. Ideally, the use of engineering controls should reduce noise exposure to the point where the risk to hearing is significantly reduced or eliminated. This section provides an overview of noise control concepts; for more detailed information refer to Section V.
Engineering and administrative controls are essential to an effective hearing loss prevention program. They are technologically feasible for most noise sources, but their economic feasibility must be determined on an individual basis. In some instances, the application of a relatively simple noise-control solution reduces the hazard to the extent that the other elements of the program, such as audiometric testing and the use of hearing protection devices, are no longer necessary. In other cases, the noise reduction process may be more complex and must be accomplished in stages over a period of time. Even so, with each reduction of a few decibels, the risk of hearing loss is reduced, communication is improved, and noise-related annoyance is reduced.
The first step in noise control is to identify the noise sources and their relative importance. This can be difficult in an industrial setting with many noise sources. It can be accomplished through several methods used together: obtain a frequency spectrum from an octave band analyzer, turn various components in the factory on and off or use temporary mufflers or enclosures to isolate noise sources, and probe areas close to equipment with a sound level meter to pinpoint areas where sound is dominant. These measures will aid in identifying the sound sources that affect workers the most and should be prioritized when implementing noise controls. Once the noise sources have been identified, it is possible to proceed in choosing an engineering control, administrative or work practice control, or a form of PPE to reduce the noise level if noise exposure is too high (Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control).
-
Hierarchy of Controls for Noise
The hierarchy of controls for noise can be summarized as: 1) eliminate or minimize noise exposure by installing equipment that produces less noise (e.g., buy-quiet programs), 2) prevent or contain the escape of noise at its source (engineering controls), 3) control exposure by changing work schedules to reduce the amount of time any one worker spends in the high noise area (administrative controls) or by changing practices such as distancing from noise-producing equipment (work practice controls), and 4) control the exposure with hearing protection. This hierarchy highlights the principle that the best prevention strategy is to eliminate exposure to hazards that can lead to hearing loss. Corporations that have started buy-quiet programs are moving toward workplaces where no harmful noise will exist. Many companies are automating equipment or setting up procedures that can be managed by workers from a quiet control room free from harmful noise. When it is not possible to eliminate the noise hazard or relocate the worker to a safe area, the worker must be protected with PPE.
Note: Refer to the OSHA Field Operations Manual (FOM) for current citation policy when addressing engineering/administrative and work practice controls versus hearing conservation program.
-
Noise-Control Engineering--Concepts and Options
The rest of this section, until the discussion of administrative and work practice controls, presents information adapted from material developed under contract for the Noise eTool by Dennis Driscoll in 2002.
Much industrial noise can be controlled through simple solutions. It is important, however, that all individuals administering abatement projects have a good understanding of the principles of noise control and proper use of acoustical materials. Industrial hygienists, safety professionals, facility engineers, and others can make significant progress in reducing equipment noise levels and worker noise exposures by combining their knowledge of acoustics with an understanding of the manufacturing equipment and/or processes.
Reducing excessive equipment noise can be accomplished by treating the source, the sound transmission path, the receiver, or any combination of these options. Descriptions of these control measures follow.
-
Source Treatment
The best long-term solution to noise control is to treat the root cause of the noise problem. For source treatment to be effective, however, a comprehensive noise-control survey usually needs to be conducted to clearly identify the source and determine its relative contribution to the area noise level and worker noise exposure. At least four methods exist for treating the source: modification, retrofit, substitution, and relocation.
Modification
For the most part, industrial noise is caused by mechanical impacts, high-velocity fluid flow, high-velocity air flow, vibrating surface areas of machines, and vibrations of the product being manufactured.
Mechanical Impacts
To reduce noise caused by mechanical impacts, the modifications outlined below should be considered. For any of these options to be practical, however, they should not adversely affect production:
- Reduce excessive power or energy of items in motion (driving forces).
- Reduce or optimize speed.
- Minimize distance between impacting parts.
- Dynamically balance rotating equipment.
- Maintain equipment in good working order.
-
Use vibration isolation when applicable.
High-Velocity Fluid Flow
High-velocity fluid flow can often create excessive noise as the transported medium passes through control valves or simply passes through the piping. Frequently, noise is carried downstream by the fluid, and/or vibratory energy is transferred to the pipe wall. A comprehensive acoustical survey can isolate the actual noise source so that the appropriate noise-control measures can be identified. When deemed practical, some effective modifications for high-velocity fluid-flow noise include:
- Locate control valves in straight runs of pipe.
- Locate all L's and T's at least 10 pipe diameters downstream of a valve.
- Ensure that all pipe cross-section reducers and expanders are at an included angle of 15 to 20 degrees.
- Eliminate sudden changes of direction and influx of one stream into another.
- Limit the fluid-flow velocity to a maximum of 30 feet per second for liquids.
- Maintain laminar flow for liquids (keep the Reynolds Number less than 2,000).
- When vibratory energy is transferred to the pipe wall, use flex connectors and/or vibration isolation for the piping system and/or acoustical insulation.
-
When excessive noise in the fluid cannot be controlled by any of the options above, install an in-line silencer.
High-Velocity Air Flow (Pneumatic or Compressed Air Systems)
One of the most common noise sources within manufacturing equipment is pneumatic- or compressed-air-driven devices such as air valves, cylinders, and solenoid valves. High-velocity air is also a major contributor to worker noise exposure where hand-held air wands or guns are used to remove debris from work areas. Finally, compressed air nozzles are often used to eject parts from a machine or conveyor line. All these forms of pneumatic systems generate undesirable noise as the high-velocity air mixes with the atmospheric air, creating excessive turbulence and particle separation. It is important to note that the intensity of sound is proportional to the air flow velocity raised to the 8th power. Therefore, as a source modification, it is recommended that the air-pressure setting for all pneumatic devices be reduced or optimized to as low a value as practical. As a general guideline, the sound pressure level can be reduced by approximately 6 dBA for each 30% reduction in air velocity. Additional noise controls for high-velocity air are presented in the retrofit and relocation sections below.
Surface- or Panel-Radiated Noise
Machine casings or panels can be a source of noise when sufficient vibratory energy is transferred into the metal structure and the panel is an efficient radiator of sound. Typically, machine casings or large metal surface areas have the potential to radiate sound when at least one dimension of the panel is longer than one-quarter of the sound's wavelength. Conducting a thorough noise-control survey will help identify the source of vibration and the existence of any surface-radiated sound. When a machine casing or panel is a primary noise source, the most effective modification is to reduce its radiation efficiency. The following noise-control measures should be considered:
- Divide vibrating surface areas into smaller sections.
- Add stiffeners to large unsupported metal panels such as rectangular ducts or large machine casing sections.
- Add small openings or perforations to large, solid surfaces.
- Use expanded metal, when practical, in place of thin metal panels.
-
Add vibration damping material.
Retrofit Products and Applications
A variety of commercially available acoustical products and applications can be applied on or relatively close to noise sources to minimize noise. The Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide should be consulted for a partial list of the manufacturers of these products and applications. Specific retrofit materials and/or applications include the following:
Vibration Damping
Just because a surface area vibrates, it is not correct to assume it is radiating significant noise. In fact, probably less than 5% of all vibrating panels produce sufficient airborne noise to be of concern in an occupational setting. However, vibration damping materials can be an effective retrofit for controlling resonant tones radiated by vibrating metal panels or surface areas. In addition, this application can minimize the transfer of high-frequency sound energy through a panel. The two basic damping applications are free-layer and constrained-layer damping. Free-layer damping, also known as extensional damping, consists of attaching an energy-dissipating material on one or both sides of a relatively thin metal panel. As a guide, free-layer damping works best on panels less than ¼-inch thick. For thicker machine casings or structures, the best application is constrained-layer damping, which consists of damping material bonded to the metal surface covered by an outer metal constraining layer, forming a laminated construction. Each application can provide up to 30 dB of noise reduction.
It is important to note that the noise reduction capabilities of the damping application are essentially equal, regardless of which side it is applied to on a panel or structure. Also, for practical purposes, it is not necessary to cover 100% of a panel to achieve a significant noise reduction. For example, 50% coverage of a surface area can provide a noise reduction that is roughly 3 dB less than 100% coverage. In other words, assuming that 100% coverage results in 26 dB of attenuation, 50% coverage could provide approximately 23 dB of reduction, 25% coverage could produce a 20-dB decrease, etc. For free-layer damping treatments, it is recommended that the application material be at least as thick as the panel or base layer to which it is applied. For constrained-layer damping, the damping material again should be the same thickness as the panel; however, the outer metal constraining layer may be half the thickness of the base layer.
For damping materials to be successful, at a minimum, the two following conditions must be satisfied (determine by a comprehensive noise-control survey):
- The panel being treated must be capable of creating high noise levels in the first place.
-
The structure must be vibrating at one of its natural frequencies or normal modes of vibration.
When selecting the right type of damping material, it is recommended that the person making the decision refer to the expertise of the product manufacturer or their designated representative(s). Typically, the supplier will need to obtain specific information from the buyer, such as the temperature and size of the surface area to be treated and the substrate thickness. Consideration must also be given to ensure that damping materials are compatible with the work environment where they will be installed (i.e., they should not create any flammability issues or other hazards). The supplier will then use the input data to select the most effective product for the particular application. The vendor can also provide the buyer with estimates of noise reduction and costs for procuring the material.
Some common applications for vibration damping include:
- Hopper bins and product chutes
- Resin pellet transfer lines (provided they are metal pipe)
- Thin metal machine casings or panels that radiate resonant tones
- Metal panels being impacted by production parts (e.g., drop bins)
- Metal enclosure walls
- Fan and blower housings
-
Gear box casings (constrained-layer damping required for thick substrates)
Vibration Isolation
Most industrial equipment vibrates to some extent. Determining whether or not the vibrating forces are severe enough to cause a problem is accomplished through a comprehensive noise and/or vibration survey. As machines operate, they produce either harmonic forces associated with unbalanced rotating components or impulsive forces attributed to impacts such as punch presses, forging hammers, and shearing actions. Excessive noise can be one result of the vibratory energy produced; however, potential damage to the equipment itself, the building, and/or the product being manufactured is more likely. Quite often, vibration problems are clearly identified by predictive-maintenance programs that exist within most industrial plants.
Assuming that the root cause or source cannot be effectively modified, the next option for controlling undesirable vibration is to install vibration isolation. Isolators come in the form of metal springs, elastomeric mounts, and resilient pads. These devices serve to decouple the relatively "solid" connection between the source and the recipient of the vibration. As a result, instead of the vibratory forces being transmitted to other machine components or the building, they are readily absorbed and dissipated by the isolators.
When selecting the appropriate isolation device(s), consider the expertise of trained professionals. It is critical to note that improper selection and installation of isolators can actually make a noise and vibration problem worse. Many manufacturers of vibration isolation equipment have useful websites for troubleshooting problems and finding solutions (see the Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide for a partial list of manufacturers).
Some common applications for vibration isolation are:
- Pipe hangers
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment
- Flex connectors for piping systems
- Rotating machinery mounts and bases for electric motors, compressors, turbines, fans, pumps, and other similar equipment
- Impact equipment such as punch presses, forging hammers or hammer mills, and shearing presses
-
Enclosure isolation
Silencers
Silencers are devices inserted in the path of a flowing medium, such as a pipeline or duct, to reduce the downstream sound level. For industrial applications, the medium typically is air. There are basically four types of silencers: dissipative (absorptive), reactive (reflective), combination of dissipative and reactive, and pneumatic or compressed air devices. This section will address the absorptive and reflective type; a separate section will discuss the pneumatic or compressed air silencers. The type of silencer required will depend on the frequency spectrum of the noise source and operational conditions of the source itself.
Dissipative silencers use sound-absorbing materials to surround or encompass the primary airflow passage. These silencers' principal method of sound attenuation is by absorption. The advantages and disadvantages of dissipative silencers include:
Advantages:
- Very good medium-frequency (500-2,000 Hz) to high-frequency (>2,000 Hz) attenuation.
- Low-to-medium pressure loss.
-
They are a standard design.
Disadvantages:
- Poor low-frequency (<500 Hz) attenuation.
- Very sensitive to moisture and particulates in the air stream.
-
They can be a difficult retrofit.
Reactive silencers use sound reflections and large area variations (impedance changes) to reduce noise in the airflow. The principal method of attenuation is through sound reflection, which cancels and interferes with the oncoming sound waves. The advantages and disadvantages of reactive silencers include:
Advantages:
- Good low-frequency attenuation.
- Can be designed to minimize pure tones.
-
Can be used in high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Disadvantages:
- Usually there is a high cost when fabricated from corrosion-resistant materials.
- Sensitive to particulate and moisture contamination.
- Relatively narrow range of attenuation.
- High-to-medium pressure loss.
- They can be a difficult retrofit.
-
They can be expensive because they are typically a custom design.
The combination dissipative and reactive silencer is essentially a reactive silencer with sound-absorption added to provide high-frequency attenuation capabilities. The advantages and disadvantages are similar to those listed for each type.
To determine which type of silencer is best for a particular application, a trained professional should be consulted. The manufacturer or a designated representative will need to work closely with the facility engineering representative(s) to clearly identify all operational and physical constraints. The Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide contains a partial list of silencer manufacturers and their websites.
Typical applications for silencers include:
- High-pressure gas pressure regulators, air vents, and blow downs
- Internal combustion engines
- Reciprocating compressors
- Centrifugal compressors
- Rotary positive displacement blowers
- Rotary vacuum pumps and separators
- Industrial fans
- HVAC systems
- Totally enclosed, fan-cooled electric motors
-
Gas turbines
Pneumatic or Compressed Air Silencers
In the earlier High-Velocity Air Flow section, it was mentioned that pneumatic or compressed air is a very common noise source in manufacturing plants. Assuming sufficient noise reduction cannot be achieved by optimizing the air-pressure setting, the second step for controlling this class of noise source is to use commercially available silencers.
For retrofitting pneumatic devices, selecting the appropriate silencer type is critical for this control measure to succeed over time. If the source is a solenoid valve, air cylinder, air motor, or some other device that simply exhausts compressed air to the atmosphere, then a simple diffuser-type silencer will suffice. The disadvantage of these types of devices is that they can cause unacceptable back pressure. Therefore, when selecting a diffuser silencer, it is important that the pressure-loss constraints for the particular application be satisfied. Diffuser silencers can provide 15-30 dB of noise reduction.
For compressed air systems that perform a service or specific task, such as ejecting parts or blowing off debris, a number of devices are available for retrofit at the point of discharge. Another typical application for compressed air is in blow-off guns or air wands. These tools come in a variety of sizes and shapes, and depending on the velocity of the air and the surface area they contact, can generate noise levels of 90 dBA to 115 dBA, depending on the velocity of the air and the surface area they contact. It is recommended that the Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide be consulted for a list of available suppliers. Usually, the manufacturer websites provide sufficient information and self-help guidance to enable selection of the most appropriate device for retrofit.
It should be noted that silencers for pneumatic or compressed air systems normally require routine inspection, maintenance, and/or replacement, as these silencers will plug up with debris, be removed by operators, or occasionally become damaged over time. If these devices are kept in good working order, however, excessive high-velocity air noise in manufacturing facilities should not be an issue.
The major problem with air guns is that, like other pneumatic or compressed air systems used to drive and motivate machinery, equipment operators will often increase the air pressure in an attempt to create more blow-off power. Earlier, in the High-Velocity Air Flow section, it was noted that the intensity of noise is proportional to the 8th power of the air velocity. Consequently, a higher pressure setting will significantly increase the noise level. In addition, when a compressed air silencer is installed on machines, many operators will remove or suppress this device to maintain the perception of having the higher level of power to which they are accustomed, which is based on their subjective assessment of the sound level. To prevent unnecessary or unauthorized air adjustments by the process or equipment operators, air-pressure regulators should be set and locked to ensure that they cannot be modified without a supervisor's consent, and operators should be educated and trained in determining whether the power is adequate.
Substitute for the Source
Another source treatment involves using alternative equipment or materials that are inherently quieter yet still meet the production needs. This option is called substitution for the source. Often, equipment manufacturers have alternative devices that perform the same function at lower noise levels. These quieter devices typically cost more, however, as they require tighter tolerances and more precision as they are manufactured. Therefore, when applicable, it will be necessary for the user to determine if the noise reduction benefit justifies the additional cost. The supplier's or the manufacturer's website should be consulted to learn if quieter equipment is available and at what additional cost. Examples where alternative and quieter equipment may exist include:
- Gears
- Bearings
- Fans or blowers
- Control valves
- Air compressors
- Conveyors
- Electric motors
- Pumps
There might also be opportunities to replace equipment with different devices or materials. Here, the user should investigate whether alternative and quieter ways exist to accomplish the task or intended service. Where practical, examples of source substitution include:
- Using belt drives over gears.
- Using belt conveyors instead of rollers.
- Employing mechanical parts ejectors or pickups over compressed air.
- Substituting quiet air nozzles for open-ended pipe or air lines.
- Replacing omnidirectional fans on electric motors with unidirectional aerodynamic fans.
- Substituting metal or steel parts with materials having high internal-damping properties, such as wood, nylon, or stiff plastic components.
-
Using perforated or mesh panels in place of solid panels.
Relocation of the Source
Controlling noise by locating or relocating the source should be considered for the design and equipment layout of new plant areas and for reconfiguring existing production areas. A simple rule to follow is to keep machines, processes, and work areas of approximately equal noise level together, and separate particularly noisy and quiet areas by buffer zones having intermediate noise levels. In addition, a single noisy machine should not be placed in a relatively quiet, populated area. Reasonable attention to equipment layout from an acoustical standpoint will not eliminate all noise problems, but it will help minimize the overall background noise level and provide more favorable working conditions.
Here are some examples of source relocation:
- Rerouting all pneumatic or compressed air discharge ports from outside to the inside of machine cabinets.
- Using pipe extensions to relocate pneumatic exhausts away from the immediate area and into unoccupied spaces.
- Locating blowers (e.g., dust collectors, vacuum pumps) on the building roof or in routinely unoccupied areas, and using extended ductwork to service the process or equipment of concern.
-
Conducting reclaim or material scrap grinding in routinely unoccupied areas.
-
Path Treatment
Assuming that all available options for controlling noise at the source have been exhausted, the next step in the noise-control hierarchy is to determine ways to treat the sound transmission path. Typical path treatments include adding sound-absorption materials to the room or equipment surfaces, installing sound transmission loss materials between the source and receiver(s), using acoustical enclosures or barriers, or any combination of these treatments. A description of each treatment option follows.
Sound-Absorption Materials
Sound-absorption materials are used to reduce the buildup of sound in the reverberant field. The reverberant field exists at all locations where sound waves reflect off relatively hard surfaces, such as walls, ceilings, or inside enclosures, and then combine with the sound waves propagating directly from the noise source. The added effect produces a higher noise level than the level that would have existed in the absence of any reflecting surfaces.
Keep in mind that adding sound absorption to decrease the reflected or reverberant noise in a room will do nothing to reduce the acoustical energy propagating by direct line of sight from the source. Therefore, it is helpful for the user to estimate what portion of a worker's noise exposure comes from the direct sound field and what percentage results from reverberant sound. When reverberant noise is a major contributor to a worker's daily noise exposure, then adding sound-absorbing materials may be beneficial.
A user must understand and apply the principles of room acoustics when adding sound-absorbing materials to the walls and ceiling to reduce the noise levels throughout the room. If a user installs sound absorption in a room without putting any science behind the decision, then the likelihood of success will be tenuous at best.
Using sound absorption on a room's surfaces has both advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Provides a significant reduction in the reverberant sound buildup, especially in pre-existing hard surface spaces.
- Works best in relatively small volume rooms or spaces (<10,000 ft2).
- Requires minimal maintenance after initial installation.
- Can be purchased and installed at a reasonable cost.
-
Works best on middle-to high-frequency noise.
Disadvantages:
- Room treatment does nothing to address the root cause of the noise problem.
- Does not reduce noise resulting from direct sound propagation.
- The absorption can deteriorate over several years and may need periodic replacement (perhaps every 7 to 10 years).
-
Rarely does this form of treatment eliminate the need for hearing protection.
Sound Transmission Loss (TL) Materials
Sound TL materials are used to block or attenuate noise propagating through a structure, such as the walls of an enclosure or room. These materials are typically heavy and dense, with poor sound transmission properties. Common applications include barriers, enclosure panels, windows, doors, and building materials for room construction.
All products sold for noise control should have a TL rating that is determined by ASTM standard. It is important to note that TL rating varies with frequency. TL values generally range from 20 to 60 dB, with the higher number indicating superior attenuation properties. For TL values of common building materials, consult Table 9.12 in The Noise Manual (AIHA, 2003, or latest edition).
Acoustical Enclosures
The acoustical enclosure is the most common path of treatment. Quite often enclosures are used to address multiple noise sources all at once or when there are no feasible control measures for the source. However, there are a number of advantages and disadvantages associated with solid enclosures (no acoustical leaks) that must be considered by the user.
Advantages:
- Can provide 20 to 40 dB of noise reduction.
- Can be installed in a relatively short time frame.
- Can be purchased and installed at a reasonable cost.
-
Provides significant noise reduction across a wide range of frequencies.
Disadvantages:
- Worker visual and physical access to equipment is restricted.
- Repeated disassembly and reassembly of the enclosure often results in the creation of significant open and direct paths via small gaps and openings along the panel joints (sound flanking).
- Heat buildup inside the enclosure can be problematic.
- Internal lighting and fire suppression may need to be incorporated into the design.
- The long-term potential for internal surface contamination from oil mist or other airborne particulates is high.
- The panels become damaged or the internal absorption material simply deteriorates over time.
-
Enclosures require periodic maintenance, such as replacement of seals and gasket material, to keep the acoustical integrity at a high attenuation value.
Enclosures, both off-the-shelf and custom-design, are available from a number of manufacturers listed in the Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide. It can also be more cost-effective to build enclosures in-house by following the Guidelines for Building Enclosures.
Acoustical Barriers
An acoustical barrier is a partial partition inserted between the noise source and receiver, which helps block or shield the receiver from the direct sound transmission path. For a partial barrier to be effective, it is critical that the receiver be in the direct field, not the reverberant field. Should the worker's location be primarily in the reverberant field, then the benefit of the barrier will be negligible.
The noise reduction provided by a barrier is a direct function of its relative location to the source and receiver, its effective dimensions, and the frequency spectrum of the noise source. The practical limits of barrier attenuation will range from 15 to 20 dB. For additional details on calculating barrier insertion loss or attenuation, the user should review some of the references, particularly The Noise Manual (AIHA, 2003; or latest edition). Recommendations for acoustical barrier design and location to maximize noise reduction capabilities include:
- The barrier should be located as close as practical to either or both the source and receiver.
- The width of the barrier on either side of the noise source should be at least twice its height (the wider the better).
- The height should be as tall as practical.
- The sound transmission loss of the panel should be at least 10 dB greater than the estimated noise reduction of the barrier.
- The barrier should be solid and not contain any gaps or openings.
-
The worker(s) being protected by the barrier should work primarily in the direct sound field.
-
Receiver Treatment
The final control option involves reducing noise at the receiver. When deemed practical, personnel shelters can be installed or the receiver can be relocated to a relatively quiet area. It is important to keep in mind that worker noise exposure is a function of both the magnitude of noise and duration of exposure. Therefore, receiver treatment works best in areas with high noise for those job activities that are fairly stationary or confined to a relatively small area, and where significant time is spent throughout the workday.
Worker Enclosures
Enclosures, or personnel shelters, can provide a cost-effective means for lowering worker noise exposure instead of lowering equipment noise levels. Control booths or rooms are commercially available from a number of manufacturers, many of which are listed in the Noise and Vibration Control Product Manufacturer Guide (see Section VII-Resources). The cost for these units typically ranges from $5,000 to $35,000 depending on the size and sophistication of their design and their need for electronic controls, video monitoring, number of observation windows, and other features. Any of the vendors listed in the manufacturer's guide can provide a cost estimate upon request. As a minimum requirement, all control rooms should maintain an interior sound level lower than 80 dBA, which will minimize worker noise exposure. Should there be a need to communicate with workers inside a control room, however, then a better design criterion would be to limit sound levels to 60 dBA or less.
As mentioned above, for a personnel enclosure to work well, it is critical that worker(s) spend a significant portion of their workshift in the shelter. The amount of time needed inside the enclosure will depend on the magnitude of the existing noise exposure. Appendix A: Noise Exposure Computation of the OSHA Occupational Noise Exposure standard, 29 CFR 1910.95, can be used to help determine the amount of time needed inside an enclosure to reduce noise exposures below select target levels, such as a TWA of 90 dBA or 85 dBA.
Relocation
Finally, if it is not essential for the worker to spend significant time in the immediate vicinity of noisy equipment, then another option for reducing noise exposure would be to relocate the worker to a quieter area. Quite often, equipment operators will spend most of their time up close to the production or process equipment, when in fact, they could stand back 5 to 7 feet, where the sound level might be a few decibels less. For relocation to work, however, it is critical that the worker still be able to perform the same job function.
To help identify areas or zones where lower noise levels exist, a comprehensive sound survey of the production area is recommended. It is also valuable to plot the sound level data on an equipment layout or floor plan, then add or draw contour lines of equal sound levels. This results in a noise contour map, which is often useful because it provides a simple representation of the sound field over a large area. Besides identifying regions of lower noise levels, these maps may also be used to visually educate and train workers regarding where hearing protection is mandatory, and as a tool for identifying hot spots for potential noise controls.
-
-
Administrative and Work Practice Controls
Administrative controls, defined as “changes in the work schedule or operations that reduce worker noise exposures” (DHHS 98-126), may also effectively reduce noise exposure for workers. Examples include operating a noisy machine on the second or third shift when fewer people are exposed, or shifting a worker to a less noisy job once a hazardous daily noise dose has been reached.
Another administrative control involves redesigning workers' work schedules to reduce the amount of time that any one worker is located in the hazard area. To increase the effectiveness of this control, employers can also ensure that noise exposure is kept to a minimum in nonproduction areas frequented by workers. Select quiet areas to use as lunch rooms and work break rooms. If these areas must be near the production line, they should be acoustically treated (as describe elsewhere in this section) to minimize background noise levels. Employers can also increase the distance between workers and the noise source. This can be accomplished in many ways. For example, television monitors allow the worker to monitor a job or process at a safe distance from the noise-producing area; a boom-mounted drill increases the distance from the noise source to the worker. Additionally, noisy jobs on construction sites might be scheduled when other trades will not be affected.
Another administrative control involves creating policies that result in regularly scheduled equipment maintenance. Maintenance should be scheduled frequently enough to minimize the noise produced by equipment with parts that are loose or not lubricated. Regular maintenance should allow a piece of equipment to operate within 2 dBA of its lowest potential operating noise level. Maintenance workers can also be trained to observe and listen for noise sources in equipment. This might involve providing training on using sound level meters to perform surveys in work areas to identify areas with high noise levels.
-
Personal Protective Equipment
Hearing protection devices (HPDs) are a form of PPE and are the last line of defense for protecting workers from noise exposures. They may also be used in combination with engineering and administrative controls discussed above. HPDs are generally used during the time it takes to implement engineering or administrative controls or when such controls are not feasible or when engineering controls are implemented but still do not control the noise below acceptable levels. Unless great care is taken in establishing a hearing conservation program, workers will often receive very little benefit from HPDs. The best hearing protector, when fitted correctly, is one that is accepted by the worker and worn properly. If the worker exposure is above 85 dBA (8-hour TWA), hearing protection must be made available, along with the other requirements in the hearing protection program.
Earplugs come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and materials and can be reusable and/or disposable (Figure 10). Earplugs are designed to occlude the ear canal when worn. All hearing protectors are provided with an NRR. Although earplugs can offer protection against the harmful effects of impulse noise, and some earplugs are designed specifically to reduce this type of noise, the NRR is based on the attenuation of continuous noise and may not be an accurate indicator of the protection attainable against impulse noise. Earplugs are better suited for warm and/or humid environments, such as foundries, smelters, glass works, and outside construction in the summer.
Figure 10. Earplugs

Earmuffs are another type of hearing protector (Figure 11). They come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and materials and are relatively easy to dispense, as they are one-size devices designed to fit nearly all adult users. Earmuffs are designed to cover the external ear and thus reduce the amount of sound reaching the inner ear. Care must be taken to ensure that the seal of the earmuff is not broken by safety glasses, facial hair, respirators, hard hats, or other equipment, as even a very small leak in the seal can destroy the effectiveness of the earmuff. Earmuffs should be chosen based on the frequency that needs to be reduced. Refer to the EPA label on the manufacturer's product. Earmuffs are a good choice for intermittent exposure, given how easy they are to put on and take off. Additionally, in cold environments, their warming effect is appreciated (OTM/Driscoll).
Hearing bands are a third type of HPD (Figure 11) and are similar to earplugs, but with a stiff band that connects the portions that insert into a worker's ears. The band typically wraps around the back of the wearer's neck, though variations are available. Hearing bands come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and materials and are popular for their convenience. Hearing bands may not provide the same noise attenuation as properly fitting earplugs, as the portions that fit into the ears are stationary and cannot be twisted into place like earplugs.
Earplugs, earmuffs, or hearing bands alone might not provide sufficient protection from significantly high noise levels. In this case, workers should wear double hearing protection (e.g., earmuffs with earplugs). Avoid corded earplugs and hearing bands, as the cord/band would interfere with the muff seal.
Figure 11. Earmuffs (left) and Hearing Bands (right)

HPDs are rated to indicate the extent to which they reduce worker noise exposure. New technologies have been developed to test the effectiveness of earplugs and could eventually change the way hearing protection is rated. Although not required by the OSHA noise standard, several tools are available to employers that allow fit testing of HPDs, similar to respirator fit testing. HPD fit-testing enables employers to determine how well individual HPDs actually protect, and is also especially useful when workers have experienced an STS. See Appendix F for information on NRR methods, ratings, and requirements.
When utilizing HPDs, consideration must also be given for potential interference with communication requirements at the worksite, as they may make it difficult to hear warning alarms such as equipment alarms, emergency notifications, or backup alarms on mobile equipment. In these situations, communication headsets with integrated hearing protection may be a feasible solution, as they would provide hearing protection while allowing workers to hear and communicate with others. In addition, HPD fit-testing could be utilized to determine the appropriate attenuation for a given environment, by identifying an HPD that would provide necessary attenuation to protect the hearing, but not so much that it would interfere with the ability to hear warning alarms. Special consideration may be needed for workers with pre-existing hearing loss, as use of HPDs may further interfere with their ability to hear warning signals. However, it should be noted that such workers still must be protected from exposure according to requirements under the general industry and construction noise standards, as applicable, as there is no exception for employees who have diminished capacity to hear or who have been diagnosed as deaf (see letter of interpretation, August 3, 2004).
M. Training
Training that is required under the noise standard for general industry is outlined in 1910.95 Occupational Noise Exposure and includes:
(i)(4) Hearing Protectors: The employer shall provide training in the use and care of all hearing protectors provided to employees.
(k)(1) Training Program: The employer shall institute a training program for all employees who are exposed to noise at or above an 8-hour TWA of 85 dBA, and shall ensure employee participation in such program.
(k)(2) Training Program: The training program shall be repeated annually for each employee included in the HCP. Information provided in the training program shall be updated to be consistent with changes in protective equipment and work processes.
(k)(3) Training Program: The employer shall ensure that each employee is informed of the following:
-
The effects of noise on hearing;
-
The purpose of hearing protectors, the advantages, disadvantages, and attenuation of various types, and instructions on selection, fitting, use, and care; and
-
The purpose of audiometric testing, and an explanation of the test procedures.
(l) (1) Access to Information and Training Materials: The employer shall make available to affected employees or their representatives copies of this standard and shall also post a copy in the workplace.
Studies of HPD fit-testing results have indicated that roughly half of the workers achieve less than 5 to 15 dB of attenuation without training [Murphy et al. 2011]. HPD fit-testing cannot be substituted for the NRR when assessing the adequacy of a given protector to reduce noise exposure; however, HPD fit-testing can be used in addition to NRR. The OSHA/National Hearing Conservation Association (NHCA) Alliance has recommended HPD fit-testing as a best practice and valuable training tool that can help in training the worker to achieve an optimal fit.
Training is a key element in preventing hearing loss and other negative outcomes of noise such as tinnitus. Training needs to be tailored to specific work environments and to meet the needs of individual workers in educating them on the hazards they may be exposed to as well as measures (e.g., engineering, administrative, and safe work practice controls and PPE) to be used to prevent or mitigate exposures to those hazards. One example of tailoring noise training to specific workplace and worker needs is having qualified personnel perform sound surveys in work areas to identify areas with high noise levels and generate sound survey maps; those maps can then be used to visually educate and train workers regarding where hearing protection is mandatory, and as a tool for identifying hot spots for potential noise controls.
N. Hearing Conservation Programs (HCPs)
The basic elements of an HCP include monitoring, training, use of hearing protectors, and audiometric evaluations for noise-exposed workers (those above 85 dBA) required to be enrolled in the program (see 29 CFR 1910.95(c)). Training requirements for an HCP are provided in the previous Section M. For more information about determining whether the attenuation of a HPD is sufficient, see Appendix F; for evaluating benefits versus costs of HCPs, see Appendix H; and for more information on reviewing audiograms, see Appendix I.
One study characterized overall and specific costs associated with HCPs at US metal manufacturing sites, and examined the association between these costs and several noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) outcomes [Sayler et al., 2018]. Hearing impairment prevalence was about 15% overall. Higher expenditures for training and hearing protector fit-testing aspects of the HCPs were significantly associated with reduced STS prevalence. Higher training expenditures were also related to lower hearing impairment prevalence and high-frequency hearing loss rates. The study concluded that HCP costs were substantial and variable and that increased workplace spending on training and HPD fit-testing may help minimize NIHL.
III. Measurements
A. Equipment
Several sound-measuring instruments are available to CSHOs. These include sound level meters, noise dosimeters, and octave band analyzers. This section describes general equipment care, followed by the uses and limitations of each kind of instrument.
-
Noise Evaluation Instrument Care and Calibration
All instruments must be calibrated (according to the manufacturer's instructions) to ensure measurement accuracy. [29 CFR 1910.95(d)(2)(ii)]
Instruments that measure noise contain delicate electronics and require practical care. Store and transport the equipment in its custom case. Become familiar with the instrument manufacturer's recommendations for proper storage and rechargeable battery maintenance (i.e., some manufacturers recommend removing all batteries from stored equipment, while others require a primary battery to remain in the instrument). Make sure batteries will last the anticipated sampling period. A battery tester can be useful. CSHOs may need to install fresh batteries or recharge reusable batteries with a battery charger.
All noise-measuring instruments used by CSHOs require two types of calibration:
- Periodic factory-level calibration (e.g., annual)
-
Pre- and post-use calibration
It is important to understand the difference between these two types of calibrations. Both pre- and post-use calibrations are required for any noise instruments used by CSHOs. Acoustical calibrators used for pre- and post-use calibrations must also be calibrated on an annual basis.
Equipment manufacturers typically recommend periodic calibration on an annual basis. These rigorous testing protocols ensure that the electronic components are in good working order and detect shifts in performance that indicate gradual deterioration. Periodic calibration results in a calibration certificate documenting the standard of performance. Typically, the instrument will also receive a sticker indicating its last calibration date and when the next periodic calibration is due (Figure 12). An instrument owned by OSHA that is past its calibration due date must be returned to OSHA's Cincinnati Technical Center (CTC) to have its calibration renewed. Do not continue to use it past the calibration date.
Figure 12. Noise Dosimeter Calibration Sticker

OSHA's CTC is qualified to perform periodic (annual) calibration for the noise-monitoring instruments and acoustical calibrators commonly issued to CSHOs. CTC also coordinates periodic factory calibration of any OSHA-owned noise-monitoring instruments that it does not service directly.
Employers that lease or own Type I or Type II noise-measuring instruments can arrange annual calibration of the equipment through the equipment supplier or manufacturer.
During periodic calibration, the CTC also performs preventive maintenance to ensure that the equipment remains fully functional over its life expectancy. If the calibration team detects a problem, it services the instrument as necessary. When returning equipment to CTC for periodic calibration, be sure to include a note about any problems or concerns with equipment function so they can be evaluated as part of the maintenance process. If equipment is not functioning as expected, CTC requests that the instrument be returned for inspection, even if it is not yet due for calibration.
Octave band analyzers that are integrated into a sound level meter will be calibrated as part of the sound level meter. Detachable octave band analyzers must be returned to CTC for periodic calibration with the meter with which they are intended to be used.
Pre- and post-calibration procedures confirm that the instrument is functioning properly on the day that it is used and prove that it is still registering sound levels correctly at the end of the day. Pre- and post-calibrations also confirm that changes in temperature or humidity have not affected the instrument's accuracy. If practical, spot check the instrument with a calibrator after the stabilization period, per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
When unpacking a cold instrument in a warm environment, or moving from one temperature zone to another, allow the instrument at least 5 minutes to stabilize for each 18°F (10°C) of change.
Each instrument model is calibrated in a slightly different manner, but the general process follows basic standard steps. Typical daily pre-use calibration involves (1) setting up the instrument for use, (2) turning on both the electronic "calibrator" and the noise-measuring instruments to allow them to "warm up," (3) checking the calibrator and instrument battery charge, (4) testing the instruments with a standard tone of known pitch and intensity produced by the calibrator (e.g., 114 dB at 1,000 Hz), (5) checking the instrument reading during the test and making minor adjustments to the instrument if necessary, and (6) documenting the calibration results. For the post-use calibration check, the process is repeated, without step 5, after the instrument has been used. Both the pre- and post-use calibration must be documented. See Figures 13 and 14 for illustrations of this process for dosimeters and sound level meters, respectively.
Figure 13. Noise Dosimeter Calibration

Figure 14. Sound Level Meter Calibration

(Note: images on left indicate calibration of a sound level meter at 114 dB/1000 Hz, while images on the right display calibration of an octave-band analyzer at 94 dB/250 Hz)
Confirm that you understand the procedures for calibrating each of the instruments you use. If in doubt, review instructions in each instrument's user's manual and consult CTC if questions arise. In general, as long as the sound level readout is within 0.2 dB of the known source (the calibrator output), it is suggested that no calibration adjustments be made. If large fluctuations (greater than 1 dB) in the level occur, then either the calibrator or the instrument may have a problem.
Review your noise instrument calibration procedure and check whether your process:
- Confirms that both the calibrator and the instrument have not exceeded the periodic calibration due date.
- Uses the correct calibrator for the instrument.
- Uses the correct adaptor between the calibrator and the instrument microphone.
- Confirms the battery charge.
- Adjusts the instrument calibration when the tolerance is within the manufacturer's published limits (e.g., ±0.2 to 1dB) but rejects the equipment if the calibration reading is outside the limits (e.g., ±1 dB or more).
- Prevents use of equipment that is outside its periodic calibration due date or fails pre-use calibration.
- Creates a record of pre-use calibration.
Additionally, confirm that you know how to change or charge the battery in both the calibrator and the instruments. If in doubt, review instructions in each instrument's user's manual. A low battery is the number-one cause of equipment failing pre- and post-use calibration. Changing the battery will often bring the equipment back into an acceptable calibration range immediately, but a little practice is needed to change the battery quickly on some equipment. Most rechargeable batteries cannot be changed in the field so it is even more important their charge status is known and changed as necessary prior to instrument usage. Rechargeable batteries that can no longer be recharged must be replaced by CTC or the manufacturer. Be prepared, so that a low battery doesn't slow you down during an early morning calibration session (Figure 15).
Figure 15. Changing Equipment Batteries

Noise measurements collected by CSHOs cannot be used as a basis for citations unless they are obtained using equipment that has a current (within the past 12 months) periodic calibration certificate on file and that has received documented calibration before and after the measurements were made using accepted practices for documentation, as outlined in the OSHA Field Operations Manual.
-
Sound Level Meters (SLMs)
SLMs provide instantaneous noise measurements for screening purposes (Figure 16). During an initial walkaround, an SLM helps identify areas with elevated noise levels where full-shift noise dosimetry should be performed. In addition, SLMs are useful for:
- Spot-checking noise dosimeter performance.
- Determining a worker's noise dose whenever a noise dosimeter is unavailable or inappropriate.
- Identifying and evaluating individual noise sources for abatement purposes.
- Aiding in engineering control feasibility analysis for individual noise sources being considered for abatement.
- Evaluating the suitability of HPDs for the actual noise level in an area.
Figure 16. Sound Level Meter

-
Sound Level Meter Types and Performance
SLMs used by OSHA meet American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Standard S1.4-1971 (R1976) or S1.4-1983, "Specifications for Sound Level Meters." These ANSI standards set performance and accuracy tolerances according to three levels of precision: Types 0, 1, and 2 (also commonly referred to as Class 0, 1, and 2 in recent standards).
- Type 0 is used in laboratories.
- Type 1 is used for precision measurements in the field.
-
Type 2 is used for general purpose measurements.
The most widely used SLM for workplace evaluations, the Type 2 meter, performs with the minimum level of precision required by OSHA for noise measurements. These meters are usually sufficient for general purpose noise surveys. For compliance purposes, readings obtained with a Type 2 SLM are considered to have an accuracy of ±2 dBA.
One model of SLM typically used by CSHOs, the Quest SoundPro, is designed to operate in temperatures of 14° to 122°F (-10°C to 50°C).
Over this range, temperature has a modest effect on the accuracy of measurements (less than ±0.5 dB). Likewise, the sound level meter can be expected to operate effectively between 10% and 90% relative humidity.
In contrast, a Type 1 meter is considered to have an accuracy of ±1 dBA. The Type 1 meter accuracy, precision, and additional features make it the preferred model for obtaining readings that will be used to help design cost-effective noise controls.
For unusual measurement situations, refer to the manufacturer's instructions and appropriate ANSI standards for guidance in interpreting instrument accuracy.
Other types of SLMs also exist but do not meet ANSI requirements for the Type 2 or Type 1 designation. These meters, which are often modestly priced, can be useful pre-screening tools for employers seeking to identify noisy locations and track improvements during noise reduction efforts. They cannot, however, be used to document compliance with OSHA standards; only properly calibrated Type 2 or Type 1 meters can serve that purpose. For example, SLM applications are available for some smartphones. Such an application can give a rough estimate of the noise level in a particular location but may not be used to document compliance with OSHA standards.
All SLMs are affected by temperature and humidity; however, these instruments are intended to provide reliable readings within the normal range of workplace temperatures. During extreme weather, temperatures might be considerably outside that range in untempered storage (e.g., the trunk of a parked car). Avoid storing noise measurement equipment where the temperature could be lower than -13°F (-25°C) or higher than 158°F (70°C). Avoid carrying cold equipment into a very humid environment, which could permit moisture to condense on the instrument. To prevent this situation, do not keep noise equipment in the trunk of a cold car; instead, carry it in the passenger compartment and store it indoors at the destination. For equipment that must be carried for a brief time into a very cold area to collect a measurement, one strategy is to keep the equipment under a coat (or otherwise wrapped/insulated), if possible, to keep it from getting cold.
SLMs should be calibrated using the steps outlined in Section 1, above, and according to the manufacturer's instructions.
-
Using a Sound Level Meter
Different work environments and different SLM microphones might require variations in measurement procedures. For practical purposes, however, certain basic steps apply in most circumstances.
Figure 17. Sound Level Meter Positioning

Confirm that the SLM is properly calibrated and temperature-stabilized. Then, position the microphone in the monitored worker's hearing zone. OSHA defines the hearing zone as a 2-foot-wide sphere surrounding the head. Considerations of practicality and safety will dictate the actual microphone placement at each survey location. Note that when noise levels at a worker's two ears are different, the higher level must be sampled for compliance determinations.
Keep in mind that your body or surrounding equipment can influence the noise level, acting as a barrier between the noise source and the microphone. Hold the SLM away from your body to minimize this effect (Figure 17).
Consult the manufacturer for any specific instructions for positioning the model of SLM you plan to use. This may be particularly important when measuring in unusual settings. For example, the manufacturer may have specific instructions for sound level readings in a non-reverberant environment.
Question: I've heard that some SLMs should be pointed at the noise source, while others should be held at an angle (e.g., 70 degrees, 90 degrees).
Answer: In many cases, orientation makes no significant difference, but it is always best to follow any recommendation from the manufacturer. Such a recommendation would be based on microphone type. Typical recommendations include:
Free-field microphones -- point directly toward the noise source (a 0-degree angle).
Random incidence microphones -- hold at a 70-degree angle to the source.
Pressure microphones -- hold at a 90-degree angle to the source.CSHOs should consult with CTC regarding the microphone models provided with their SLMs.
Use a wind screen to reduce measurement errors caused by wind turbulence over the microphone. Typical wind screens are made of soft foam rubber and are designed to fit over the microphone (Figure 18). Although not necessarily needed indoors if air movement is minimal, a wind screen can be left in place for all measurements. Collected measurements can be affected by anything that comes across the face of the SLM microphone, such as hair, shirt collars, scarves, or other objects. The use of a wind screen reduces the effects of this incidental contact. Wind screens have the added advantage of protecting the microphone, at least somewhat, from damage resulting from impact, dust, paint overspray, moisture, etc.
Figure 18. Wind Screen

Most Type 1 and Type 2 sound level meters can be set to respond with either a "slow response" or a "fast response." The meter dynamics are such that the meter will reach 63% of the final steady-state reading within one time constant:
- Fast response corresponds to a 125-millisecond (ms) time constant.
-
Slow response corresponds to a 1-second time constant.
The meter screen shows the average sound pressure level measured by the meter during the period selected. In most industrial settings, the meter fluctuates less (and therefore is easier to read) when measurements are made with the slow response rather than the fast response. A rapidly fluctuating sound generally yields higher maximum sound pressure levels when measured with a fast response. The choice of meter response depends on the type of noise being measured, the intended use of the measurements, and the specifications of any applicable standards. For typical occupational noise measurements, including extremely elevated short-term noise (e.g., noise that will be compared to the 115 dBA maximum for a 15-minute period), the meter response on a sound level meter should be set at slow. For more information on OSHA's standard for extremely elevated short-term noise exposures see Section II.J.2 - OSHA Noise Standards.
Many SLMs also have "peak" and "impulse" response settings for measuring transient sounds (sounds that decay or pass with time). These settings are not interchangeable; the true peak value is the maximum value of the noise waveform, while the impulse measurement is an integrated measurement. It is appropriate to use the true peak reading only when determining compliance with OSHA's 140-dB peak (instantaneous) sound pressure level [29 CFR 1910.95(b)(1) or 29 CFR 1926.52(e)]. Avoid using the impulse response setting when measuring true peak sound pressure levels.
Note that noise dosimeters and SLMs that are set to integrate or average sound over a period of time do not use either the fast or slow time constant; they will sample many times per second.
-
Octave Band Analyzer
Most sounds are not a pure tone but rather a mix of several frequencies. The frequency of a sound influences the extent to which different materials attenuate that sound. Knowing the component frequencies of the sound can help determine the materials and designs that will provide the greatest noise reduction. Therefore, octave band analyzers can be used to help determine the feasibility of controls for individual noise sources for abatement purposes and to evaluate whether hearing protectors provide adequate protection.
-
Octave Band Analyzer Types and Performance
Octave band analyzers segment noise into its component parts. The standard octave band filter set provides filters with the following center frequencies: 16; 31.5; 63; 125; 250; 500; 1,000; 2,000; 4,000; 8,000; and 16,000 Hz. The special signature of a given noise can be obtained by taking SLM readings at each of these settings (assuming that the noise is fairly constant over time). The results may identify the octave bands that contain the majority of the total radiated sound power (Figure 19).
Figure 19. Octave Band Analyzer Settings and Center Frequencies

Press "Enter" (center arrow) key to switch screens.

(a) Sample bar chart with curves

(b) Tabulation screen
Sample bar chart screen: (A) selected frequency band (250 Hz ini example),
(B) selected frequency in curve, (C) amplitude (dB) in band.
Tabulation screen: lists amplitude in dB for each frequency band.For octave band analysis, the ideal SLM network (weighting) scale setting is one that provides no weighting at all, such as the Z-weighted scale, which has an unweighted flat response across the entire frequency spectrum from 10 Hz to 20,000 Hz. The C-weighted scale is also an acceptable option for octave band analysis because, in the range of most workplace noise level measurements, unweighted sound level measurements are less than 1 dB higher than the corresponding C-scale measurements. The A-weighted scale, however, is not an appropriate setting for octave band analysis because, by definition, it influences the meter response differently at various frequencies in the range of normal human hearing.
For a more detailed analysis, the spectrum is sometimes measured in one-third octave bands. Although one-third octave bands can be useful for noise engineers concerned with precise frequency measurements, the standard single octave bands are sufficient for most evaluations performed by OSHA.
Whether detachable or integrated into a sound level meter, an octave band analyzer receives its daily calibration in conjunction with the sound level meter with which it will be used. This might involve activating an additional setting during the daily meter calibration. Consult the user's manual for the equipment you will be using.
-
Using the Octave Band Analyzer
The Type 1 SLMs used by OSHA (such as the Quest SoundPro) have built-in octave band analysis capability. Some other models of sound level meter are designed to work with a separate octave band analyzer that is physically attached to the meter (Figure 20). In either case, the sound level meter microphone operates normally, but the noise signal detected by the microphone is separated into its component frequencies. When the octave band analyzer is activated and a particular frequency band selected, the meter readout provides the decibel level associated with that frequency. By sequentially switching the meter to each frequency band and taking a reading, the CSHO can determine which octave bands contribute most to the noise.
For example, an octave band analysis providing the following results indicated that the frequencies around 500 Hz and 1,000 Hz were most prominent (Table III-1):
Table III-1. Octave Band Analysis (Noise A) Hz
31.5
63
125
250
500
1,000
2,000
4,000
8,000
16,000
dB
68
69
72
76
89
92
74
77
71
71
In contrast, the following octave band analysis (Table III - 2) obtained during concrete demolition (multiple noise sources) indicated that many frequencies contributed to the noise level at that position -- a distance of 60 feet from the demolition point. At that point, the overall sound level was 91 dB, demonstrating a standard principle of sound: the sum of all octave bands is greater than any single octave band reading, but the logarithmic values cannot be summed by simple arithmetic addition. See Appendix B.3 for more information on determining the sum of two or more sound levels.
Table III-2. Octave Band Analysis (Noise B) Hz
31.5
63
125
250
500
1,000
2,000
4,000
8,000
16,000
dB
81
87
83
83
83
86
86
87
82
68
Figure 20. Octave Band Analyzer Graph

Some octave band analyzers can be set to automatic function (i.e., the instrument automatically checks the sound level of each frequency band and stores the results). Other instruments require the user to manually switch between the different frequency bands, recording each reading in sequence.
Variable frequency sounds and sounds that constantly vary in intensity present a challenge to frequency analysis. Unless the sound is relatively constant throughout the process of evaluating all frequency bands, it might not be possible to obtain an accurate reading. The CSHO should attempt to determine whether cyclic sounds have a stable period during which readings would be more accurate.
-
-
Noise Dosimeter
Like an SLM, a noise dosimeter can measure sound levels. However, the dosimeter is actually worn by the worker to determine the personal noise dose during the workshift or sampling period (Figure 21). Noise dosimetry is a form of personal sampling, averaging noise exposure over time and reporting results such as a TWA exposure or a percentage of the PEL.
Dosimeters can be used to:
- Make compliance measurements according to OSHA's noise standard.
-
Measure the worker's exposure to noise over a period of time (e.g., a task or an entire workshift) and automatically compute the necessary noise dose calculations.
Increasingly, some SLMs can function as noise dosimeters (although they are larger than typical dosimeters), while many noise dosimeters provide instantaneous sound level readings in decibels and therefore can be used as Type 2 SLMs. Some models including the Casella dBadge2 and Svantek SV1041S can now be configured to have built-in octave band analyzers as well.
Figure 21. Noise Dosimeter

-
Noise Dosimeter Types and Performance
Most noise dosimeters operate with the precision and accuracy of a Type 2 SLM. Therefore, the variations in dosimeter types are primarily a function of either the physical form or the analytical features of each model. Historically, the typical noise dosimeter has included a small positionable microphone connected to the dosimeter by a thin cable. The microphone sits in the worker's hearing zone (e.g., shoulder or lapel near the ear), while the dosimeter clips to the worker's belt. Advances in miniature electronics and wireless technology, however, have permitted manufacturers to offer similar capabilities in a wider range of physical forms (e.g., wireless microphones that clip to the worker's shoulder and transmit information back to a base station, miniature microphones that measure sound levels in the worker's ear). On most new models of dosimeters, the microphone is mounted to the body of the instrument, and the instrument is clipped onto the worker near the workers’ hearing zone (Figure 22).
Figure 22. Clip-on Noise Dosimeter

Many of the newer model dosimeters feature Bluetooth connectivity with smartphone applications. These applications let the user control certain dosimeter functions (e.g., start and stop) and allow for remote viewing of the real-time measurement data.
It is important to understand the differences between the noise dosimeters available to CSHOs as their functions may vary. Simple dosimeters record a single channel and report basic dosimetry results. More complex models can record as if they were three or four separate dosimeters (sometimes called “virtual” dosimeters), each integrating the sound level over time using different measurement parameters (e.g., 3 dB and 5 dB exchange rates, and different threshold settings). Some dosimeters like the Svantek SV104IS allow the user to change the measurement parameters and recompile the data after a study has been completed. This feature may prevent loss of data if the measurement parameters were set incorrectly during the study.
Noise dosimeters are subject to the same sensitivity to temperature and humidity as SLMs. Although some have water-resistant housings, they should still be treated as sensitive electronic instruments and be protected from moisture and physical impact. The dosimeter calibration process is nearly identical to that for sound level meters. Frequently, for a given brand of instruments, the same calibrator can be used for a manufacturer's SLMs and noise dosimeters by using different microphone adapters (Figure 23). Many dosimeters now use an optional auto-calibration feature that recognizes the acoustical calibrator’s output signal and enters calibration mode automatically. The product manuals should be consulted to determine if this feature is available.
Figure 23. Calibrator Adapter

Noise dosimeters routinely must run for 8 to 10 hours per day. This means battery function is particularly important. Some models might require new batteries each time they are used. Just as for SLMs, each dosimeter must receive periodic calibration every 12 months and a daily calibration and battery check before each use. They also require a post-use calibration check. The documentation procedures are the same as those for SLMs.
-
Using Noise Dosimeters
According to OSHA's noise standard (29 CFR 1910.95), the noise dosimeter is the primary instrument for making compliance measurements. Before use, the dosimeter must be set up to record noise exposure using the following criteria:
- Exchange rate: 5 dB
- Frequency weighting: A
- Response: slow
- Criterion level: 90 dBA (Action Level) or 90 dBA (PEL).
-
Threshold: 80 dBA (Action Level) or 90 dBA (PEL).
As noted above, most dosimeters can simultaneously record exposure using two or more sets of criteria. With these instruments, the CSHO can obtain separate noise exposure levels based on both the 80 dBA and the 90 dBA threshold. Other noise dosimeters that lack this feature must be set to record using one of these thresholds or the other.
Instrument accuracy must be taken into account when making compliance determinations with the OSHA PEL and Action Level. Type-2 dosimeters have an accuracy of ±2 dBA, therefore:
-
When determining compliance with the 90 dBA-TWA PEL, an overexposure has occurred when exposures exceed a TWA of 92 dBA (90 + 2 dBA). Using the dose conversion formula from Appendix B.8, this corresponds to a dose of 132%. This determination would be performed using exposure data from the 90-dBA threshold setting on the dosimeter.
-
When determining compliance with the 85 dBA-TWA Action Level, a hearing conservation program would be required when exposures equal or exceed a TWA of 87 dBA (85 + 2 dBA). Using the dose conversion formula from Appendix B.8., this corresponds to a dose of 66%. This determination would be performed using exposure data from the 80-dBA threshold setting on the dosimeter.
In addition to the 8-hour TWAs, OSHA's noise standards list a short-term level of 115 dBA for a 15-minute period, which is not to be exceeded; this is for steady state sounds measured on the slow response setting. Although sound this loud is unusual, some dosimeter models indicate when the maximum allowable sound level of 115 dBA has been exceeded. This signal should not be used for compliance determination, however, because it might not take the duration of the exposure to this noise level into consideration. But noise that exceeds 115 dBA should be incorporated into the overall TWA noise exposure determination (see Section II.J.2- OSHA Noise Standards for more information). The standard for short-term noise levels is distinct from OSHA's instantaneous ceiling limit of 140 dBA for impact noises (occurring less frequently than one per second and typically measured using a sound level meter set to the fast response setting.)
You will need to make other decisions regarding dosimeter setup. For example, the typical noise dosimeter offers several options for the frequency with which noise is sampled and data logged. The more frequently the data are logged, the more data points are stored (and the larger the file size).
The calibrated noise dosimeter fastens to the worker's belt or shoulder area if using a clip-on type dosimeter, with the microphone positioned on the shoulder (see Figures 24-25). In either case, orient the microphone so it points straight up--you might need to adjust the clip to find a functional position. Avoid positioning the microphone where it could become enfolded in clothing or rub against cloth or other materials, both of which could influence the results.
If appropriate, run the microphone cable under the worker's outer layer of clothing to keep it out of the way and prevent it from snagging on objects in the work area. The dosimeter can hang inside the outer layer of clothes as well (an advantage in wet weather), but the microphone must remain in the open air without contacting other surfaces (except the base on which it clips).
Some dosimeter models are capable of taking separate measurements (studies) for different job tasks or processes within the same workshift. The dosimeter can isolate the loudest job task the worker performs. This data can be reviewed later by the CSHO to determine which job tasks contributed most to a worker's overall 8-hour TWA. This feature is useful for assessing engineering controls.
The dosimeter microphone must be protected from wind and harsh materials. Wind screens are optional indoors if air currents are minimal. Always use a windscreen in areas with air motion, outdoors, and in dusty locations or during jobs when the microphone might get dirty (Figure 24). The foam rubber wind screen will help protect the microphone. Additional precautions are required to protect the microphone under the particularly harsh conditions that occur during abrasive blasting, when the microphone should normally be clipped inside the abrasive blasting helmet.
Special consideration will need to be taken to determine microphone placement when monitoring workers who are wearing protective head gear such as abrasive blasting helmets or supplied air respirators. In many of these cases, the helmet/hood of this type of equipment would not be considered as a hearing protective device, and the microphone should be placed under the helmet/hood when measuring employee exposures. Care should be taken to ensure that the microphone does not contact surfaces inside the helmet/hood which may incur inaccurate noise measurements. Similarly, the microphone should also be positioned so that it is not located within any direct air streams such as from a supplied air respirator, which may also cause erroneous readings. Additional care may be necessary in running the dosimeter cable under any respirator or hood seals so that it does not interfere with such seals and as approved by the respirator manufacturer, as applicable. In some special cases, protective headwear such as abrasive blasting helmets may be considered as a secondary hearing protective device (earplugs worn under the helmet would be considered the primary hearing protective device). When considering the possibility for inclusion of the helmet as providing hearing protection, consultation with the manufacturer is necessary to determine the design, intent, and attenuation performance data associated with this scenario. If the helmet is determined to act as a hearing protector, the microphone should be placed outside the helmet when determining noise exposures and evaluating hearing protection worn by the employee. However, as previously mentioned, particular care is likely needed in order to protect the microphone in harsh environments; a wind screen would be necessary but for extremely harsh conditions it may not be feasible to position the microphone outside the hood/helmet. For questions related to assessing exposures and microphone placement associated with protective headwear and respirators, CSHOs should contact their regional OSHA office enforcement personnel or the OSHA Health Response Team for guidance, as necessary.
Workers are understandably curious about the noise dosimeter, and particularly the microphone. Take time to explain that it only collects information on how loud the sounds are--it does not record speech. Activate the dosimeter and replace its screen cover, or lock out the controls before the worker begins working. Take sound level measurements frequently during the course of the noise dosimetry. The sound level measurements document the noise in the area at specific points in time and from specific sources. These values both validate the dosimeter reading and provide insight into how and when exposure is occurring. Some noise dosimeters log data that can be downloaded to a computer and later graphed against time to show how the worker's noise exposure varies over the course of a shift. This is a useful feature, but is not a substitute for good notes on the workplace and the sources of noise in specific times and places.
Figure 24. Microphone Positioning and Wind Screen Use

Figure 25. Clip-on Dosimeter Positioning

The OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center, Health Response Team (HRT), maintains the following specialized noise analysis equipment, which can be used for noise exposure and engineering control evaluations:
Sound Level Meter and Octave Band Analyzer
The HRT maintains multipurpose Type I sound level meters and octave band analyzers, which can also be operated as sound intensity analyzers for identifying noise sources and determining engineering controls. In addition, this equipment includes a building acoustics system for measuring noise decay and determining the reverberation characteristics for a given room. Based on the noise decay data, calculations can be performed to estimate potential noise reduction if absorptive materials are applied to room surfaces, such as the walls and ceiling.
Specialized Noise Dosimeters
The HRT maintains specialized dosimeters which can be used to support inspections. The HRT can also provide guidance on using dosimeters utilized by the agency, including downloading and analyzing data obtained during inspections.
In addition, the HRT maintains an in-ear dosimetry system that can be used to assess exposures under sound-generating headsets. See Appendix G for more information.
IV. Investigation Guidelines
A workplace noise investigation typically involves:
- Advance planning, including determining whether sound levels at the site might be hazardous.
- Reviewing employer records.
- Reviewing the Hearing Conservation Program and audiograms.
- Reviewing the OSHA 300 Log for hearing loss cases.
- Determining if workers have hearing loss.
- Conducting the walkaround evaluation.
- Identifying the sources of noise.
- Documenting noise levels.
- Conducting follow-up monitoring.
- Determining the noise's potential effect on workers.
-
Evaluating the employer's efforts to protect workers' hearing (hazard abatement and control).
In some workplaces your visit will be the first time a thorough investigation has been performed; frequently, however, at least some aspects of noise investigations will have been completed previously through the employer's workplace health and safety measures or sometimes as part of seemingly unrelated activities, such as expanding operations or upgrading equipment. To conduct an investigation, you will need to determine what information is already available through employer or industry records, and then confirm it and fill in the gaps. To ensure that the investigation is efficient, however, you must be prepared to accomplish both these steps simultaneously, which requires some advance planning.
A. Planning the Investigation
An effective noise investigation begins before you arrive on site. First, conduct research based on type of industry to determine whether noise hazards are likely. If so, plan to conduct noise measurements and monitoring. Confirm that the instruments' annual calibrations are current (i.e., have not expired), ensure that the batteries are fresh, and calibrate the SLM and noise dosimeters before the opening conference. This will permit you to begin obtaining sound level measurements during your initial walkaround at the site. After these preparations, you will also be ready to start obtaining personal noise dosimetry samples early in the visit, providing an opportunity to collect samples of significant duration. The resulting noise dosimetry might not be full shift, but it will provide valuable information regarding worker noise exposure that first day on site.
Sources of information about whether you are likely to encounter noise hazards at an establishment include:
- Previous inspection records for the establishment, employer, or other facilities in the same or similar industries.
- BLS information summarizing state or national data from the "hearing loss" column of employers' OSHA 300 Logs.
- OSHA records on noise-related citations from inspections conducted across the nation.
- NIOSH reports on the industry, including Health Hazard Evaluations (HHEs).
-
Your own knowledge of or experience with the industry and its processes.
-
Searching Online for Industry Noise Statistics
- BLS Report on Hearing Loss in an Industry
Reports of hearing loss by industry are summarized in BLS's "Table SNR08: Incidence Rates of Nonfatal Occupational Illness, by Industry and Category of Illness." This extensive table lists, by industry, the incidence of reported illnesses per 10,000 full-time workers, as shown on OSHA 300 Logs that employers are required to submit. The table includes a column for hearing loss. Comparing the hearing loss reporting rates in various industries will give you an estimate of the impact that noise has on the industry you are inspecting compared with other industries. Note that variations in hearing loss reporting rates can influence the apparent incidence rate.
BLS publishes this information annually each fall, covering the previous year's data. Check for the latest edition of Table SNR08, or for previous years' tables, at the Bureau of Labor Statistics web site.
Table IV - 1 shows an example from BLS Table SNR08 for NAICS 3211 (Sawmills and wood preservation); an incidence rate of 32.4 cases per 10,000 workers was due to hearing loss.
Table IV-1. Example Incidence Rates of Nonfatal Occupational Illness Industry
NAICS Code
Incidence rates per 10,000 full-time workers
Total Cases
Skin Diseases or Disorders
Respiratory Conditions
Poisonings
Hearing Loss
All Other Illnesses
Sawmills and wood preservation
3211
45.5
--
3.3
--
32.4
7.7
Extracted from BLS Table SNR08, published in 2019.
-
Noise Citations by Industry
If the establishment has not been inspected previously, OSHA's online records can show whether the noise and hearing conservation standards are among those frequently cited in this industry, or whether the industry is listed as one that receives numerous noise citations.
The CSHO can easily search the inspection information database to determine whether previous inspections of that industry, or a similar industry, resulted in citations under OSHA's noise standards. To access inspection records, start at OSHA's “Data & Statistics” page. Note that this web page gathers information from the OSHA Information System (OIS) database. Select "Frequently Cited OSHA Standards" from the options presented and enter the NAICS for the industry (or leave blank for a list of all NAICS).
The search provides a table of results consisting of a ranked list of the standards cited in that industry for the previous fiscal year.
Using NAICS 3211 (Sawmills and Wood Preservation) as an example again, the search showed that 1910.95 was the 4th most frequently cited standard in this industry that year. The search returns the information as a data table, shown below as Table IV-2.
Table IV-2. Inspection Statistics for NAICS 3211 – Sawmills and Wood Preservation in FY 2020
(Organized by Most Frequently Cited Standard, Top 5 listed)Standard
Citations
Inspections
Penalty
Description
243
58
$1,058,230
All Standards cited for Sawmills and Wood Preservation
55
27
$527,130
The control of hazardous energy (lockout/tagout).
37
16
$170,304
Sawmills.
18
10
$54,841
Mechanical power-transmission apparatus.
15
6
$7,978
Occupational noise exposure.
15
7
$8,345
Hazard communication.
Notes: Standards are presented as eight-character part/section levels consisting of the part number followed by the standard number. Standard numbers less than 1000 require leading zeros: 1910.95 becomes 19100095.
For the top row labeled "Total," the value in the “Inspections” column represents the number of inspections in which one or more citations were issued. Note that the total is not the sum of the number of inspections associated with each standard cited; multiple standards may be cited in one inspection.
Interpreting the table: Citations were issued during 58 inspections conducted in NAICS 3211 between October 2019 and September 2020 (FY 2020). OSHA's noise standard, 1910.95, was cited during six (10%) of those 58 inspections. Overall, the noise standard was cited 15 times, putting it among the top 5 most frequently cited standards for that year. The dollar penalties for noise standard violations accounted for 0.75% of the total $1,058,230 in penalties associated with citations issued in NAICS 3211 in FY 2020. Note that OSHA might also have conducted other inspections in that NAICS that did not result in citations; inspections that did not include citations are not counted in this table.
Few inspections likely occurred in a small industry during a single year. For smaller industries, the CSHO might obtain additional useful information by searching a wider range of dates (e.g., several years). From the “Data & Statistics” page, select "Search Inspections By NAICS" and enter the SIC or NAICS and the date range desired. The resulting data table shows all the inspections conducted in that industry within the requested time period. The table indicates the number of violations for each inspection but does not list them individually. Clicking on the inspection number, however, will open the inspection's information screen, showing which standards were violated.
Additional data searches can also be performed directly through OIS. An extensive range of search options and reports is available. CSHOs can refer to Area or Regional office personnel for assistance with OIS report functions, as necessary.
-
NIOSH HHEs by Industry
To access NIOSH HHEs that mention noise exposure levels or dosimetry data, go to Health Hazard Evaluations and select "Find an HHE Report." In the search screen that appears, search by keyword "noise," choose an industry category, and if desired limit the dates. For example, between 2000 and the end of 2020, NIOSH reported on 91 HHEs that included an evaluation of occupational noise exposure.
B. Reviewing Employer Records
Review employer records to determine whether hazardous noise levels have been found in the past and to evaluate the employer's hearing conservation and recordkeeping programs. The records can also indicate what steps the employer has taken to reduce any excessive noise exposure and whether there is evidence that workers are experiencing noise-induced hearing loss. Audiometric testing records should be requested and reviewed as well as the OSHA 300 Log required under 1904.10 to determine if work-related hearing loss cases have been recorded. Also, ask the employer for noise questionnaires that may be in use. Refer to CPL 02-02-072, Rules of Agency Practice and Procedure Concerning OSHA Access to Employee Medical Records (8/22/07), for guidance on appropriately requesting, reviewing, documenting, and retaining worker audiogram records.
If you can conduct the walkaround inspection before the records review, review the employer's records while noise dosimeters are operating. (Periodically return to the work area to confirm that the equipment is still operating properly and to collect sound level measurements to compare with the dosimeter data.)
Request copies of previous noise surveys or evaluations that included sound level measurements. Note noise levels that exceed the AL, along with the associated location, equipment, and activities. Inquire about the duration of exposure and determine which workers might be exposed to the noise by using the equation for calculating the TWA for the percent dose (see Appendix B). Look at noise dosimetry data to determine whether workers were exposed over the AL or the PEL. If the measurements are being used to show compliance, check that the equipment used to make the measurements was at least a Type 2 SLM (or dosimeter) with periodic and daily calibration fully documented.
1. Audiometric Program and Audiograms
OSHA requires workers who have daily TWA noise exposures of 85 dBA or more to be enrolled in an HCP that includes annual audiometry. Audiometric testing itself does not conserve hearing, but can be a useful tool to assess the effectiveness of the HCP. As previously noted, a threshold shift of 10 dB or more for the pure tone average of 2000, 3000 and 4000 Hz (PTA234) in either ear is considered a “standard threshold shift” (STS). An STS that persists on retesting requires several actions: the worker must be counselled regarding the change in hearing; hearing protection devices must be fitted or refitted; and the STS may need to be recorded as a work-related injury. OSHA standard 1904.10 “Recording criteria for cases involving occupational hearing loss” contains recordkeeping requirements for STSs in the OSHA 300 Log, and additional guidance is contained in Appendix I.
Regarding audiometric evaluations, the 2019 federal register notice for Standards Improvement Project IV (https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2019/05/14/2019-07902/standards-improvement-project-phase-iv) is now effectively part of the recordkeeping elements pertaining to the noise standard (see 1904.10(b)(6)). The notice states: “Physician or other licensed health care professional (PLHCP) must follow the rules set out in 1904.5 to determine if the hearing loss is work-related. If an event or exposure in the work environment either caused or contributed to the hearing loss, or significantly aggravated a pre-existing hearing loss, the PLHCP must consider the case to be work-related. It is not necessary for work to be the sole cause, or the predominant cause, or even a substantial cause of the hearing loss; any contribution from work makes the case work-related. The employer is responsible for ensuring that the PLHCP applies the analysis in Section 1904.5 when evaluating work-related hearing loss, if the employer chooses to rely on the PLHCP’s opinion in determining recordability.”
Look at the results of any audiometric evaluations. Determine whether the audiometry was performed by a qualified individual using calibrated equipment and whether results of audiometric testing are compared to the worker's previous audiometric test results. Employers may contract audiometric services or conduct monitoring at the worksite. Qualified individuals include licensed or certified audiologists, otolaryngologist (Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) specialist), or other physician. Audiograms can be performed by a technician who is certified by the Council of Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation (CAOHC). The standard also allows testing to be performed by a technician who has “satisfactorily demonstrated competence in administering audiometric examinations, obtaining valid audiograms, and properly using, maintaining and checking calibration and proper functioning of the audiometers being used.” All technicians performing audiometry must be responsible to an audiologist, otolaryngologist, or physician. For information on definition of a “physician” under 1910.95 and what credentials would qualify a person to perform the duties ascribed under the standard, refer to the 2016 letter of interpretation.
Check if calibration records are available and current for audiometers. Also determine if booths/rooms used for audiometric testing have been tested for background noise levels according to 1910.95 Appendix D. An octave-band analyzer can be used to verify background levels, as needed.
The standard allows the use of microprocessor audiometers. These devices are often called an “automatic audiometer” and have many advantages over manual testing. The test is pre-programmed, and depending on the model, the microprocessor can provide testing instructions to the patient, and can be linked to a computer installed with software that performs STS calculations. There are portable tablet-based systems, also considered “microprocessor audiometers”, that operate in a similar manner and may be used on-site for audiometric testing. It should be noted that microprocessor audiometers must meet all requirements for audiometric testing as outlined by 1910.95. Also note that a technician using a microprocessor audiometer does not need to be certified but still needs to be responsible to an audiologist, ENT, or other physician. CSHOs can contact the OSHA Directorate of Technical Support and Emergency Management (DTSEM) or Directorate of Enforcement Programs (DEP) for assistance when evaluating audiometric systems, as needed.
Compare the most recent audiogram with the baseline audiogram. If an STS is observed, review data for intervening years to determine when the STS occurred. The baseline audiogram is usually, but not always, the first audiogram. If a later audiogram shows lower hearing thresholds, the medical professional reviewing the audiogram can determine if the improvement is significant enough to revise the baseline. If a persistent STS is determined, the audiologist, ENT, or physician will adopt the annual audiogram as the revised baseline for future comparisons.
Evaluate data for each ear separately. A threshold shift can occur in one ear and not the other. Use threshold data only for the three required frequencies: 2,000, 3,000, and 4,000 Hz. Compare each audiogram to the baseline and take the average of the difference in the threshold at the three required frequencies. If the average is less than 10 dB, no STS has occurred. If the average is 10 dB or more, an STS has occurred.
If a worker has an STS on an annual audiogram, the employer may perform a 14-hour noise-free repeat audiogram within 30 days. If the second audiogram does not show the STS, then the second audiogram is considered the annual audiogram. This is called a temporary threshold shift (TTS) and would not need to be recorded. Check the OSHA 300 Logs to determine whether the employer has recorded cases of hearing loss. The employer should be asked how the determination was made to re-establish baselines and about any apparent hearing loss cases recorded (or those cases not recorded) on the OSHA 300 Logs. For cases that are removed from the OSHA 300 Log, there should also be documentation from the medical professional that such removal is appropriate.
The OSHA noise standard provides the option in a non-mandatory appendix (1910.95 Appendix F) for employers to apply age corrections to employee audiograms to consider the contribution of aging when determining whether an STS has occurred. In occupational hearing conservation programs, age adjustments may voluntarily be used to subtract expected age effects but are not required. 1910.95(g)(10)(ii) states: “In determining whether a standard threshold shift has occurred, allowance may be made for the contribution of aging (presbycusis) to the change in hearing level by correcting the annual audiogram according to the procedure described in Appendix F: ‘Calculation and Application of Age Correction to Audiograms.’"
Current OSHA age-correction tables provided in 1910.95 Appendix F, however, are based on 40-year-old data, with small samples, an upper age limit of 60 years, and use median thresholds of non-noise-exposed workers. An important caveat about median-based age correction that should be considered when deciding whether to do age correction: there is an assumption that age-related hearing loss is the same for every person. In fact, the table numbers are simply the median, or 50th percentile, values from a particular survey. Within the survey group, half of participants had better thresholds, and half had worse thresholds, than those reported as the medians. This means that age correction will sometimes over-correct, and sometimes under-correct, for the effects of age. After age correction, some threshold shifts that have actually been caused by noise will no longer be counted as STS (false negatives) and some threshold shifts that were actually caused entirely by aging will still be counted as STS (false positives). For these reasons and others, in 1998 NIOSH recommended that age correction not be applied to an individual’s audiogram for significant threshold shift calculations (Criteria for a Recommended Standard, Occupational Noise Exposure, NIOSH Publication 98-126).
A set of population-based age adjustment tables have recently been developed using data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) which was then validated using a database of exposed workers (male firefighters and emergency medical service workers). Results from this validation study (https://doi.org/10.1080/14992027.2019.1698068) included: cross-sectional trends implied less change with age than assumed in current U.S. regulations; different trends were observed among people identifying with non-Hispanic Black race/ethnicity; four age adjustment tables (age range: 18-85) were developed (women or men; non-Hispanic Black or other race/ethnicity); and, validation outcomes showed that the population-based tables matched median longitudinal changes in hearing sensitivity well. This study concludes that these population-based tables provide a suitable replacement for those implemented in the current noise standard and that the tables based on the NHANES data address a broader range of worker ages, account for differences in hearing sensitivity across race/ethnicity categories, and have been validated for men using longitudinal data. These age adjustment tables can be found in the supplemental material from the study. If an employer chooses to use age correction other than the tables in Appendix F, that decision to age adjust, and therefore which table to use, must be made by a certified audiologist, otolaryngologist, or other physician and must take into account the employee’s noise exposure levels, years of exposure, inclusion in a hearing conservation program, use of hearing protection, and other medical history. The employer should provide a copy of the published reference and tables to the CSHO. For additional guidance in utilizing age adjustment data, CSHOs can contact the OSHA Office of Occupational Medicine and Nursing (OOMN).
To apply age correction values, subtract the age correction value for the worker's age at the time of the baseline audiogram from their age at the time of the suspected threshold shift. Subtract the difference in the age correction values from the difference between the current and baseline audiograms. Take the average of the age-corrected threshold shifts at the three required frequencies; if the average is 10 dB or higher, an STS has occurred. See Appendix I for more information about interpreting audiograms and adjusting audiograms for age.
2. Employer Hearing Conservation Program
If the walkaround has not yet been completed, follow through by investigating noisy locations in person. If the walkaround has already been conducted, review your noise measurements taken at high-noise-level operations.
Where workers are exposed to noise at the AL or higher, examine the employer's HCP. Check that the program includes the basic elements (e.g., monitoring, training, noise exposure reduction measures, audiometric evaluation) and that noise-exposed workers are enrolled in the program. Look for evidence that noise-exposed workers are receiving hearing conservation training and have been fitted with and taught to use their HPDs correctly. Confirm that the employer provided a choice of HPDs and that this PPE provided an appropriate level of protection for the workplace noise level. For more information about determining whether the attenuation of a HPD is sufficient, see Appendix F.
- BLS Report on Hearing Loss in an Industry
C. Conducting the Walkaround Evaluation
Prepare your equipment for the walkaround evaluation. You will need an SLM (Type 2 or Type 1) and, depending on the extent of the evaluation, an octave band analyzer that is compatible with your SLM and noise dosimeters, and a noise instrument calibrator.
Check that you have the correct batteries and spare batteries for all instruments. Calibrators often require a different size battery than SLMs or noise dosimeters.
Pack so that you have the following readily accessible: tape measure (preferably a 100-foot length), pens and paper for sketching the worksite layout, and standard noise measurement forms.
While conducting noise evaluations, you should wear protective equipment appropriate for the site, including hearing protection. Keep earplugs or muffs with you at all times and wear them whenever you are: in an area that the employer has designated as a noise-hazardous zone (e.g., by posting signs or if your escort tells you hearing protection is required); when you find that measured noise levels approach 85 dBA; or any other time that you suspect that noise levels are elevated. Note: use hearing protection anywhere it is noisy enough that you would have to raise your voice to carry on a conversation with someone 3 feet away. In some situations, double hearing protection might be necessary (see ADM 04-00-003, OSHA Safety and Health Management System).
The walkaround inspection is a chance for you to see the workers' working conditions first hand and to measure noise levels using the SLM or noise dosimeter (set to operate as a SLM). Use your senses to identify areas that might have hazardous noise, and then use the SLM to document the noise levels.
For each noise level measurement, include a description of the noise source (including a photograph), record the distance from the source at which the measurement was made, and note how many and which workers are potentially exposed. Record both the A- and C-weighted noise levels, and obtain frequency spectrum readings if an OBA is utilized. Also record the approximate duration of the noise, which is especially important for intermittent noises.
Interview workers and supervisors to inquire about which areas they think are most noisy at the site. Also, ask which are the noisiest areas in which they work. As you visit these areas, identify the sources of noise, and use the SLM to determine whether sound levels could be hazardous.
Select workers for noise dosimetry and carefully explain the process, including the fact that the microphone only measures how loud or quiet the noise is; it does not record speech. Follow the dosimeter manufacturer's instructions to use the instrument, being careful to record the time the instrument is turned on and off. Throughout the day, use the sound level meter to corroborate the noise dosimeter readings. Readings taken at times when significant noise events occur can be particularly useful, as are series of sound level readings obtained at regular intervals (e.g., once or twice per hour, or 10 times per shift).
Create a Noise Diagram (Noise Mapping)
The noise diagram or schematic is a useful strategy for recording noise levels in context. The diagram can help determine which workers have noise exposure, and it is useful for demonstrating the location of hazardous areas to workers and the employer. Use a plant schematic or sketch the general floor plan. Mark and identify noisy processes. Use the SLM to determine the noise level adjacent to the noisy equipment or process and at various distances from the noise source. Specifically, measure noise at the hearing zone position for workers in the vicinity.
Next move away from the noise source, making sequential measurements to determine the "hazard radius"-- the distances from the noise source at which the noise level drops to the PEL and the AL (Figure 24). Mark the distances in the sketch. Also, the dimensions of the work area and the materials that were used to construct the room should be identified.
Figure 24. Taking Measurements for a Noise Diagram

Your completed sketch will show a series of contours around the noise source(s) (Figure 25). Expect the contours for adjacent noise sources to overlap. Workers operating entirely outside the contour are not exposed to noise in excess of the AL. Workers whose tasks take them closer to the equipment might experience exposures between the AL and the PEL, or even in excess of the PEL. Take photographs to document the type of equipment or process.
Figure 25. Drawing a Noise Diagram
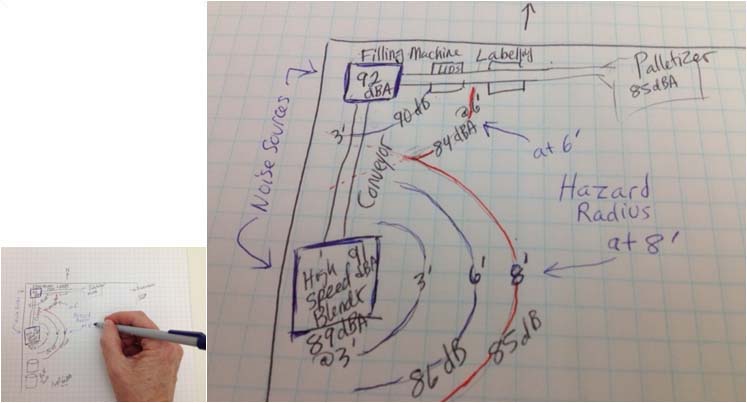
Where noise levels exceed the PEL, an octave band analyzer can help you determine the frequency profile of the sound. This information can aid in pinpointing the cause of the sound (e.g., slipping belt, vibrating supports) and will be useful for planning control measures.
The SLM is also useful for confirming the extent to which the employer's-noise reduction measures have reduced workers' noise exposure. In this case, octave band analysis can help confirm that the materials used are appropriate for controlling the particular noise.
When monitoring is complete at the end of the day, follow standard procedures for recording results from the instruments. If necessary, consult the instrument user's manual or contact CTC for assistance. Dosimeter output usually includes the TWA (normalized to 8 hours), the LAVG or LEQ representing the average dose for the period monitored, the percent dose, and the maximum or peak reading. Do not neglect to perform the post-use calibration check on each instrument.
D. Follow-Up Monitoring
If noise levels documented by SLM readings or dosimetry on the first day indicate that additional sampling is required, you will need to return to conduct follow-up monitoring. The additional monitoring could be necessary to confirm that workers are adequately protected or that an overexposure exists, or you might need to monitor another operation not being performed on the first day. Since the follow-up monitoring will focus on noise dosimetry, prepare to arrive in time to start monitoring with calibrated equipment just as the shift begins. The goal is to sample for a full sample time of 8 hours for comparison to the PEL, and for longer shifts sample as much of the shift as possible for comparison to the action level (see Section E “Extended Workshifts” below). The dosimeter can be removed and paused if the worker leaves the work site for breaks or lunch, but can be left on if such breaks are taken in the work area.
E. Extended Workshifts
For employees working longer than an 8-hour shift, an evaluation must be performed to determine compliance with the Action Level (AL) for hearing conservation. Dosimeters used by OSHA collect data using both the 80 dBA threshold for the AL, and 90 dBA threshold for the PEL. Therefore, it is necessary to utilize the 80 dBA threshold data for the AL when performing the evaluation described in this section.
[Note that this type of evaluation is not performed when determining compliance with the PEL. For any period(s) of exposure summing 8 hours within the workshift, exposures are required to be below the TWA of 90 dBA, and the data from the 90 dBA threshold dosimeter would be utilized accordingly. For more information, see OSHA Memorandum Nov. 10, 1999.]
The AL is 50% Dose, or 85 dBA-TWA. When correcting for 2 dB instrument error, the corrected AL is 66% Dose, or 87 dBA-TWA (see Section III.A.4 for more information). An HCP is required whenever exposures equal or exceed the AL (see 29 CFR 1910.95).
Compliance with the AL is determined by performing dosimetry for as much of the shift as possible; full-shift dosimetry will provide the best results.
When determining compliance with the AL, there are 3 options available, all of which will obtain an equivalent result, summarized below. Note that when doing these comparisons, if any of the parameters equal or exceed the associated AL value (Dose, TWA, or adjusted AL), then an HCP would be required. Also see Appendix B.9 for more information.
Option 1: Compare using Dose.
Compare the Dose measured from the instrument with the Dose Action Level of 66% (corrected for 2 dB instrument error).
This is the simplest option, and can be done for any shift length. As soon as the dose equals or exceeds 66% Dose at any time of the shift, the AL is exceeded. However, it is important to monitor as much of the shift as possible to obtain the maximum dose possible.
Option 2: Compare using TWA.
Compare the TWA measured from the instrument to the 87 dBA-TWA Action Level (corrected for 2 dB instrument error).
This is similar to Option 1, but puts the comparison in terms of dBA instead of Dose %. Also note that TWA can be calculated from Dose and vice-versa, using the equations in Appendix B.8.
Option 3: Compare using adjusted AL.
Calculate an adjusted Action Level for the extended shift using the equation from Appendix B.9, and add 2 dB for instrument error. Then, compare this result to the average sound level measured for the extended shift (LAVG).
Example – Extended Workshifts
Consider the following data obtained during full-shift monitoring with a dosimeter:
-
Shift Length = 570 minutes = 9.5 hours
-
Dose = 71%
-
LAVG = 86.3 dBA
Option 1: Compare using Dose.
The measured Dose of 71% exceeds the 66% Dose Action Level; hearing conservation program is required.
Option 2: Compare using TWA.
Using the conversion formula from Appendix B.8 and the measured Dose of 71%, the following TWA is calculated:
TWA = 16.61 log10 [71/100] + 90 = 87.5 dBA
The calculated TWA of 87.5 dBA exceeds the Action Level of 87 dBA-TWA; hearing conservation program is required.
(Note: The TWA may also be obtained directly from the dosimetry results, if available.)
Option 3: Compare using adjusted AL.
Using the shift length of 9.5 hours, the adjusted Action Level can be calculated according to the equation from Appendix B.9:
AL = 16.61 log10 [50/(12.5x9.5)] + 90 = 83.8 dBA
Add 2 dBA for instrument error: 83.8 + 2 = 85.8 dBA
The LAVG of 86.3 dBA measured for the 9.5 hour shift exceeds the corrected/adjusted AL of 85.8 dBA; hearing conservation program is required.
V. Hazard Abatement and Control
A. Engineering Controls
Engineering controls meant to reduce noise levels can take many forms. They can reduce noise at the source by replacing or modifying equipment, or they can reflect or absorb noise along the transmission path before it reaches the receiver. HPDs worn by a worker also block noise before it reaches the receiver's (i.e., the worker's) ears, but because they are worn by the worker, HPDs are considered PPE rather than engineering controls.
For hearing loss prevention purposes, engineering controls are defined as any modification or replacement of equipment, or related physical change at the noise source or along the transmission path (with the exception of HPDs), that reduces the noise level at the worker's ear. Engineering controls should be effective, efficient, and economical. According to CPL 2-2.35A Appendix A, effective controls reduce noise levels by at least 3 dB. Efficient controls should not cause extra hazards, production problems, or maintenance or sanitation issues. Economical controls are cost-effective for the employer (discussed in Section B of this section).
This section describes several types of engineering noise controls, focusing on the different ways various materials can be used to reduce a receiver's noise exposure. Noise is typically generated either by the surface motion of a vibrating solid material or by turbulence in a fluid, including air. All engineering control options either reduce the amount of noise generated by these events or interfere with the path between the noise source and the receiver.
A number of references on engineering controls are listed in Section VII-Resources. Some have been in use many years; however, many of the principles of noise control are as relevant now as they were decades ago. Additionally, considerable information is available in:
In this chapter
Appendix J – Three Ways to Jump Start a Noise-Control Program
Section VII – Resources (Subsections A and E)
On the Internet
Washington State Department of Labor and Industries' Noise Reduction Ideas Bank
NIOSH's Industrial Noise Control Manual (document number 79-117a)
Hansen, C.H. and B. Goelzer. Engineering Noise Control. World Health Organization.
- Source Treatment
- Mechanical Impacts
The driving force in a piece of equipment with a rotating part typically produces additional noise when the rotating part is out of balance or when the bearings are worn. The sound typically increases as the speed of the rotation increases. One simple, cost-effective way to reduce this noise is through preventive maintenance, which includes properly lubricating and aligning moving parts. For more information on controlling noise through preventive maintenance, see Appendix J.
Another way to reduce the noise generated by the driving force of a piece of equipment is to decrease the speed of the equipment. The tradeoff with this approach is that in some processes there may be an associated loss in productive capacity.
In processes that involve impacts, increasing the duration of impact while reducing the force can reduce the driving force as well. This concept is illustrated in Figure 26. A worker can bend a piece of metal by hitting it with a hammer and applying a large amount of force over a short period of time or by applying the same force with the pliers over a longer time period, thereby reducing the noise.
Figure 26. Reducing Driving Force
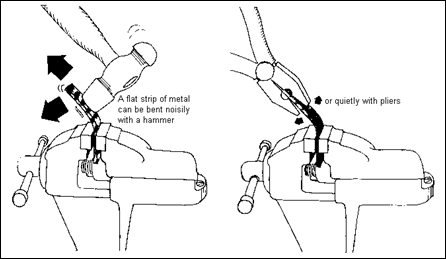
-
Reduce High Velocity of Fluid Flow
Fluid (whether air or liquid) that moves through vents, valves, and piping at high velocities can generate noise due to turbulence.
Figure 27 shows that installing softer bends in the pipe and increasing the distance between the valves will reduce the turbulence in the line and, consequently, reduce the noise generated. This solution takes up more space and is often not possible in a process. However, it is sometimes possible in air ejection processes to reduce the required velocity of the air flowing from the nozzle by increasing the accuracy of the aim of the nozzle. Often, large pressure drops across valves, which cause noise, can be prevented with in-line diffuser silencers, which reduce the pressure upstream of the valve. Installing a muffler on the end of the nozzle is another option. All these methods can help reduce noise from compressed air sources. For additional information see Appendix J.
Figure 27. Reducing Turbulence in a Steam Pipeline

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
-
Mufflers and Silencers
Mufflers (also called silencers) can be used on noisy, pressurized air equipment to reduce noise at the source. A muffler is a device that reduces the noise level from a moving air or gas stream, such as one found in a pneumatic tool (Figure 28). Like the muffler on an automobile, it absorbs some noise before it can reach the receiver (in this case, the ears of the worker who is exposed to the noise). Mufflers come in several configurations, some more sensitive to dust and moisture than others. In general, mufflers must be cleaned on a regular basis to be effective at reducing noise; if they are not cleaned, they actually can increase noise levels. Consult the muffler manufacturer for recommended cleaning procedures and frequency.
Figure 28. Schematic of Muffler Interior

-
Reduce Pneumatic and Compressed Air Systems
A special case of high-velocity fluid flow is compressed air, which is used widely for many purposes, such as:
- Blowing debris off parts and surfaces
- Moving products on assembly lines
- Spraying paint and other substances
-
Driving pneumatic tools
Compressed air causes noise exposure in most major industry sectors. Because compressed air is so common (and loud), it accounts for a large percentage of all workplace noise exposure.
Fortunately, noise from compressed air sources is easy and relatively inexpensive to abate. Examples of options for reducing noise from compressed air include:
- Adjusting the pressure regulator to reduce the air pressure in the air line coming from the compressor to the minimum pressure needed to accomplish the task. Lower pressure is not only quieter, but it saves energy and is safer. (To reduce serious injuries, OSHA requires that air pressure be held to 30 pounds per square inch or less when it could potentially contact skin).
- Replacing noisy air nozzles, guns, and wands with quieter models that have built-in noise-control features. Some models produce strong air thrust while reducing noise, using less compressed air, and saving energy (Figure 29).
- Installing additional air pressure control valves so air lines can be controlled individually to their effective minimum.
- Retrofitting pneumatic tools, compressors, and machinery by adding pneumatic mufflers or inline diffuser silencers and expansion chamber silencers. These function by providing the escaping exhaust air stream a larger area through which to expand and exit--so the air is released at a lower speed and pressure. This control option can cut noise by 20 dB or more.
- Purchasing equipment that comes with these features and replacing the noise control (nozzle or silencer) if function deteriorates.
-
Updating workplace policies to reduce reliance on compressed air where it is unnecessary. For example, vacuuming instead of using compressed air for cleaning. This method also reduces air contaminants (such as spilled or settled dust containing a hazardous substance) that would become airborne when blown with compressed air.
For more information on controlling noise from pneumatic and compressed air systems, see Appendix J.
Figure 29. Noise-Reducing Compressed Air Nozzles

-
Retrofit Applications
Reduce Response of Vibrating Surfaces by Vibration Damping
Damping is another means of noise reduction. It dissipates energy associated with vibration, often using a coating applied to the surfaces of the noise source. For example, in parts manufacturing, metal parts are transferred via metal chutes, causing excessive noise from the impact of metal on metal. When the chute is coated with a damping material (e.g., mastic, asphalted felt), the noise level is reduced. Figure 30 shows a steel plate covering a moving part on a piece of equipment. A sheet of plastic foil is placed between the two steel plates, providing a damping effect.
Figure 30. Damping Effect

Damping is typically used to dissipate energy associated with large, thin, vibrating panels on pieces of equipment. For low-frequency noise, significant reductions in noise levels can occur when as little as 50% of the surface area of the vibrating panels is treated with damping material. It is necessary to treat the entire panel with damping material in order to achieve similar reductions in high-frequency noise.
Damping materials fall into three major categories: free-layer, constrained-layer, and constrained-layer laminates.
Simple free-layer damping materials consist of rubbery "viscoelastic" materials that can be painted, sprayed, troweled, or adhered (i.e., with adhesive or magnetism) onto the noisy surface. Typically, on sheet metal, a layer of damping material half the thickness of the metal (or 10% by weight) will eliminate the "ringing" from impact. A much thicker layer of damping material, two to three times the thickness of the metal, will increase the sound-absorption coefficient of the metal to approximately 0.3 to 0.6 (see section 2.i. below for more information on the sound absorption coefficient).
Constrained-layer damping materials add a rigid second layer adhered firmly over the viscoelastic layer. This effectively increases the damping effect, even with a very thin layer of the viscoelastic material. The rigid second layer must be inelastic (i.e., it must not stretch in any direction), but it can be quite thin-even a thin metal sheet or foil will work. This combination of materials is popular because it reduces noise efficiently but takes up little space. This concept is demonstrated in the previous figure, in which two steel plates are separated by a layer of plastic foil. Commercial vendors have developed numerous versions of these materials, including metal tapes; the tape provides the inelastic properties, while the adhesive provides the viscoelastic layer.
Constrained-layer laminates follow the same principle but laminate additional layers and thicknesses of rigid material (metal or wood). These laminates offer both good noise reduction properties and strength, to the extent that some typically noisy mechanical parts (e.g., covers for moving/mechanical parts, conveyer chutes) can be made of the laminate. The transmission loss of plywood and other composite materials is improved when a viscoelastic layer is sandwiched between layers. One drawback is that special techniques are required to bend, cut, or weld these laminated materials.
When determining which damping materials to use, one should consider the typical temperature and frequencies present in the equipment and consult the damping material manufacturers to identify optimal materials.
Keep in mind that the machine, the product being manufactured, and the process itself can all create and radiate noise. Consider the illustration in Figure 31 (conveying rocks into a hopper). In the example on the left side, the rocks impacting the metal-paneled walls of the hopper cause it to ring like a bell. As shown on the right side, reducing the free-fall height (by backing up the conveyor) such that there is only a short drop significantly reduces the potential energy, which reduces the resultant noise. Additionally, a durable rubber-like material is added to damp the hopper and minimize the ability of the metal panel to flex and vibrate, which eliminates this noise at the source. Damping material can be added to either side of the metal surface (Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control).
Figure 31. Reducing Free Fall Height

Damping materials are often used to reduce the response of a vibrating surface. They work by dissipating the mechanical energy of a vibrating panel in a way that does not allow the energy to re-radiate into the air as noise. The mechanical energy from a vibrating surface is typically converted into heat in the damping material, though the change in temperature is usually too small to be noticeable by touch. Large, flat surfaces that vibrate are likely to radiate more noise than smaller, stiffer surfaces. It is often not cost-effective, especially for large machines, to treat the entire machine with damping materials. Damping material attached to the center of a vibrating plate is more effective than the same amount of material attached on the sides of the same plate. This concept is displayed in Figure 32, in which a circular blade is outfitted with a sheet metal disc with a rubber buffer layer between the sheet metal and the blade.
Figure 32. Adding Damping Material to a Saw Blade

Reducing Structure-Borne Noise by Vibration Isolation
When a machine rotates, cycles, and indexes, it often transfers some vibratory energy in the casing, pipes, and metal structure. Even though these parts of the machine may not be an efficient radiator of airborne sound, the vibrations can be carried (via solid connections) to a surface area that can convert this energy into airborne noise. When structure-borne vibration is identified as a primary source, isolation of the exiting force from the structure is the most desirable and effective control. Figure 33 represents a vibrating piece of equipment that has been isolated using spring isolators to prevent noise transfer into the concrete floor (Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control).
Figure 33. Isolated Structure-Borne Noise
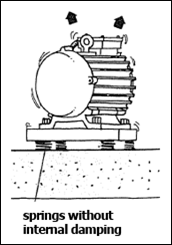
(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
Noise control by reducing structure-borne vibration involves installing vibration mounts and providing proper lubrication and maintenance for equipment. Regular maintenance ensures proper operation of equipment and is less expensive than other engineering controls; this maintenance can include tightening belts and lubricating moving parts. Structure-borne vibration can also be reduced by isolating a vibrating piece of equipment--if identified as the primary source of noise--using vibration mountings or shock absorbers (Figure 34). The picture on the left shows neoprene isolators, while the picture on the right shows spring isolators. Vibration isolation mounts are effective for reducing low-frequency noise.
Figure 34. Neoprene and Spring Vibration Isolators

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
-
Substitute for the Source
One way to reduce noise at the source is to replace noisy equipment with a quieter alternative. Manufacturers are aware of noise issues on equipment and often offer quieter models. When it comes time to replace equipment, employers are increasingly considering noise level as one of the selection criteria. Some employers develop "buy-quiet" programs as part of purchasing policies to ensure that noise levels are taken into consideration.
- Mechanical Impacts
-
Path Treatment
-
Sound Absorption
Reflected sound (sound reverberating from the walls, ceiling, and floor) will add to the sound wave propagating directly from the source to the receiver, thus increasing the overall noise level within a room. Acoustical absorptive materials are used to reduce this reflected sound; installed on the walls or ceiling (Figure 35), they absorb and dissipate the sound before it can be reflected. Materials used for sound absorption are usually porous or fibrous (e.g., fiberglass, mineral wool, felt, polyurethane foams).
Figure 35. Sound-Absorption Paneling

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
The room shown in Figure 35 has been treated with absorption panels in the ceiling space. Note that adding this material to reduce the reverberant sound does not reduce the direct sound coming from the equipment: that sound will always exist, even if the equipment is placed outside, where little to no reflection exists. When treating a ceiling with absorptive material, a useful guideline is that the noise level will not be significantly reduced for workers at ground level when acoustical panels are installed at ceiling heights greater than 15 feet. In this situation, workers are most likely affected primarily by the direct sound wave. Vertically hung panels can create new problems, such as interference with ventilation, lighting, and sprinkler patterns. Also, for this form of treatment to provide a measurable noise reduction, the original room must be acoustically "hard." In other words, the room surfaces must be made of highly reflective materials, such as concrete or painted cinder block.
As well as the sound material used to absorb sound in a room or enclosure, it is common to use sound-isolating material (also known as sound transmission loss material) to block sound from propagating from one room to another, or from inside an enclosure to outside. Often, as with enclosures and pipe insulation, one desires a combination of absorptive and sound isolation qualities. Unlike damping materials, however, it is critical for the sound-absorption material to be directly exposed to the source or noise. Attaching acoustical foam on the outside of a metal enclosure does not reduce noise; the material needs to be on the inside surface areas. This may sound simple, but it is not uncommon to find materials improperly used in this manner. Keep the function of each material in mind.
For the purpose of designing noise controls, it is useful to be able to compare the characteristics of different materials. The tendency of a material to absorb or reflect a sound is numerically represented by its absorption coefficient: the ratio of sound energy absorbed by the material to the sound energy incident to (striking) the material's surface. This coefficient is a decimal value between 0 (all sound reflected and none absorbed) and 1 (all sound absorbed). In simple terms, a material that reflects 66% of the sound energy that reaches it will absorb the remaining 34% and have an absorption coefficient of 0.34. Materials that absorb sound particularly well, such as fiberglass acoustical panels, have absorption coefficients approaching 1. An absorption coefficient reported as greater than 1 is an artifact of the test conditions.
Table V-1 displays the sound-absorption coefficients for three common sound-absorbent materials. The amount of noise absorbed by these materials depends on the density and thickness of the material and the frequency of the sound (Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control).
Table V-1. Effect of Thickness on Sound-Absorption Coefficients Material
Range of Volume Density (lb/ft3)
Range of Thickness (Inches)
Random-Incident Sound-Absorption Coefficient with Solid Backing (#4 Mounting)
Thickness (Inches)
Density (lb/ft3)
Octave-Band Center Frequency (Hz)
125
250
500
1,000
2,000
4,000
Resilient fiberglass with resinous binder
1 to 3
1/2 to 6
1.0
1.5
0.12
0.28
0.73
0.89
0.92
0.93
-
-
2.0
1.5
0.24
0.77
0.99
0.99
0.99
0.99
-
-
2.0
3.0
0.22
0.82
0.99
0.99
0.99
0.99
Rigid fiberglass board
3 to 6
1/2 to 2
1.0
6.0
0.08
0.25
0.74
0.95
0.97
0.99
Open-cell acoustical foam
1.8 to 2.5
1/4 to 2
1.0
1.8
0.22
0.35
0.61
0.98
0.94
0.99
(Driscoll, Room Acoustics V2)
As described above, frequency influences sound absorption by materials. Table V-2 shows the absorption coefficient for common building materials at different frequencies. Note that dense materials, such as rough concrete, absorb lower frequencies better than other materials, while high frequencies are better absorbed by less dense materials, such as carpet and fiberglass. Painting concrete creates a smooth surface that greatly increases the percentage of sound that is reflected at all frequencies.
Table V-2. Absorption Coefficients of Common Surface Materials and Finishes Material
125 Hz
250 Hz
500 Hz
1,000 Hz
2,000 Hz
4,000 Hz
Brick, unglazed
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.07
Brick, unglazed, painted
0.01
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.03
Carpet, heavy, on concrete
0.02
0.06
0.14
0.37
0.60
0.65
Carpet, heavy, on 40 oz hairfelt or foam rubber pad
0.08
0.24
0.57
0.69
0.71
0.73
Carpet, 40 oz per square yard, with latex backing, over felt or foam rubber pad of same density (on concrete)
0.08
0.27
0.36
0.34
0.48
0.63
Concrete block, coarse
0.36
0.44
0.31
0.29
0.36
0.25
Concrete block, painted
0.1
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.09
0.08
Fabric, light velour, 10 oz/square yard, hung straight in contact with wall
0.03
0.04
0.11
0.17
0.24
0.35
Fabric, medium velour, 14 oz/square yard, draped in half
0.07
0.31
0.49
0.75
0.72
0.60
Fabric, heavy velour, 18 oz per square yard, draped in half
0.14
0.35
0.55
0.72
0.72
0.65
Plywood paneling, 3/8 inch thick (1 cm)
0.28
0.22
0.17
0.09
0.10
0.11
Floors, concrete or terrazzo
0.01
0.01
0.015
0.02
0.02
0.02
Floors, linoleum, asphalt (vinyl), rubber, or cork tile on concrete
0.02
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.02
Floors, wood
0.15
0.11
0.10
0.07
0.06
0.07
Floors, wood parquet in asphalt on concrete
0.04
0.04
0.07
0.06
0.06
0.07
Glass, large panes of heavy plate glass
0.18
0.06
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.02
Glass, ordinary window glass
0.35
0.25
0.18
0.12
0.07
0.04
Gypsum board, ½ inch, nailed to 2x4 wood frame 16 inches on center
0.29
0.10
0.05
0.04
0.07
0.09
Marble or glazed tile
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.02
Opening, covered by grill (e.g., ventilating)
0.25-0.75
Plaster, gypsum or lime, smooth finish on tile or brick
0.013
0.015
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
Plaster, gypsum or lime, rough finish on lath
0.14
0.10
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
Plywood paneling, 3/8 inch thick
0.28
0.22
0.17
0.09
0.10
0.11
Water surface (pond or swimming pool)
0.008
0.008
0.013
0.015
0.020
0.025
Fiberglass boards and blankets, 2 inches thick, 1.5 to 3 pounds per square foot
0.17
0.55
0.80
0.90
0.85
0.8
Sources: NIOSH, 1979; Cox and D'Antonio, 2004.
Dense, heavy materials typically have low absorption coefficients (i.e., they reflect a high percentage of the sound energy). Because they do not absorb much sound energy, they do not transmit much sound as little sound penetrates through them.
-
Reducing Noise Transfer Across Barriers--Using Sound Transmission Loss Materials
Table V-3 and V-4 show various transmission loss values for common building materials at specific frequencies and material thicknesses. Note that the values in these tables are measured under ideal laboratory conditions as a resource for comparing different materials. In the workplace, the noise exposure experienced by the receiver would not actually be reduced by the reported transmission loss value, because imperfections in enclosures, barriers, or other noise controls made of these materials permit sound to go around the material, leak through cracks or utility paths, or pass through other materials with lower transmission loss values (e.g., a door jamb, window glass) that were also used in construction.
Table V-3 demonstrates how the thickness of two materials (plywood and steel) influences the transmission loss values for the materials, and Table V-4 compares the relative transmission loss values for common building materials.
Table V-3. Effect of Thickness on Transmission Loss Values for Plywood and Steel (dB) Material
125 Hz
250 Hz
500 Hz
1,000 Hz
2,000 Hz
4,000 Hz
Plywood, 1/4 in., 0.7 lb/ft2
17
15
20
24
28
27
Plywood, 3/4 in., 2 lb/ft2
24
22
27
28
25
27
Steel, 18 gauge, 2 lb/ft2
15
19
31
32
35
48
Steel, 16 gauge, 2.5 lb/ft2
21
30
34
37
40
47
Table V-4. Relative Transmission Loss for Example Materials (dB) Material
125 Hz
250 Hz
500 Hz
1,000 Hz
2,000 Hz
4,000 Hz
Brick, 4 in.
30
36
37
37
37
43
Cinder block, 7⅝ in., hollow
33
33
33
39
45
51
Concrete block, 6 in., lightweight, painted
38
36
40
45
50
56
Curtains, lead vinyl, 1½ lb/ft2
22
23
25
31
35
42
Door, hardwood, 2⅝ in.
26
33
40
43
48
51
Fiber tile, filled mineral, 5/8 in.
30
32
39
43
53
60
Glass, plate, 1/4 in.
25
29
33
36
26
35
Glass, laminated, 1/2 in.
23
31
38
40
47
52
Panels, perforated metal with mineral fiber insulator, 4 in. thick
28
34
40
48
56
62
Plywood, 1/4 in., 0.7 lb/ft2
17
15
20
24
28
27
Plywood, 3/4 in., 2 lb/ft2
24
22
27
28
25
27
Steel, 18 gauge, 2 lb/ft2
15
19
31
32
35
48
Steel, 16 gauge, 2.5 lb/ft2
21
30
34
37
40
47
Sheet metal laminate, 2 lb/ft2, viscoelastic core
15
25
28
32
39
42
Source: Lord et al., 1980.
Sound-absorbing materials are a valuable addition to acoustic enclosures and barriers, which can interrupt a noise path. Acoustic enclosures can be either full or partial and can surround either the noise source or the worker. A personnel enclosure works best if it is lined with sound-absorbing material. An alternative is an enclosure that surrounds a piece of equipment (a noise source), as pictured in Figure 36. Employers and workers should consider the risk of equipment overheating when surrounded by an acoustic enclosure.
Partitions or barriers can be constructed when a total enclosure is not possible. Barriers block mid and high frequencies better than low frequencies due to the greater diffraction of low-frequency sounds. Low frequencies can travel around corners and through holes, whereas high frequency sounds are more likely to be blocked (OTM/Driscoll).
Figure 36. Noise Barriers and Enclosures
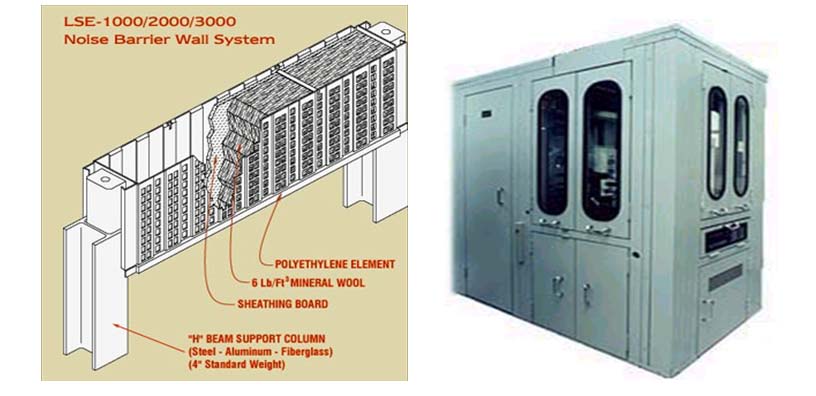
(OTM/Driscoll)
Sound-absorption and reflection properties of different materials means that certain materials are better at interrupting noise than others. Additionally, the way they interrupt noise varies with the frequency of the sound and the physical characteristics of the material. The ability of a material to interrupt sound can be described by its ability to absorb sound and, separately, by the extent to which it does (or does not) transmit the portion of the sound it absorbs.
Generally, soft, thick, fuzzy, and porous materials absorb sound well, permitting only a modest amount of the sound to reflect off the surface back into the space. In contrast, hard, smooth surfaces tend to reflect a high percentage of the sound.
Heavy, dense materials absorb low-frequency sounds better than high-frequency sounds. Protective barriers made of these materials are better at reflecting high-frequency sounds but absorb the low-frequency sounds.
A barrier's ability to attenuate sound that it absorbs is described by its transmission loss. Transmission loss, measured in decibels in laboratory tests, represents a sample of a barrier material's ability to prevent sound energy from propagating through the material to produce sound on the other side. A sample of material with an excellent transmission loss may reduce the sound level through a test panel of that material by up to 60 dB. Both the material and the thickness of the sample influence its transmittal loss.
When constructing a partial barrier, it is important to consider factors other than the barrier material. For example, for a barrier to be effective, a receiver (worker) should be located in the direct field as opposed to the reverberant field. A barrier's effectiveness in attenuating noise is maximized in a non-reverberant environment. Therefore, if a receiver's noise exposure is predominantly from reverberation, the effectiveness of the barrier will be limited. The barrier should be placed as close as possible to the receiver or the noise source to minimize the angles from which sound is reflected to the receiver.
The dimensions of the barrier are also important. In general, the width of a barrier on either side of the noise source should be twice the height of the barrier. Additionally, any cracks or gaps in the barrier can significantly diminish the transmission loss value. Any gap through which air can pass will allow a significant amount of noise to pass as well.
-
Reducing Reverberation
A common way to reduce reverberation in a room is to install sound-absorbing materials, such as acoustic tiles, in strategic places on the walls and ceiling surrounding the noise source. Reverberation can be greater when the room surfaces are hard (e.g., concrete, cinder block, corrugated metal); in these environments, sound-absorbing materials can be beneficial. This is a common treatment in theaters, broadcast studios, and sound-recording booths. Figure 37 shows a large, open room in which sound-absorbing baffles and acoustic tiles are hanging from the ceiling. This engineering control will do nothing to reduce the noise level from the noise source but will reduce the reflection of noise back into the room. As was mentioned previously, this type of control works best in a small room (less than 10,000 square feet) with low ceilings (less than 15 feet). In a room with high ceilings, the main source of noise to which workers are exposed is most likely direct noise from the source. Sound-absorbing materials should never be painted, as this would cover the pores in the material, thereby preventing noise from being absorbed.
Figure 37. Sound-Absorbing Baffles
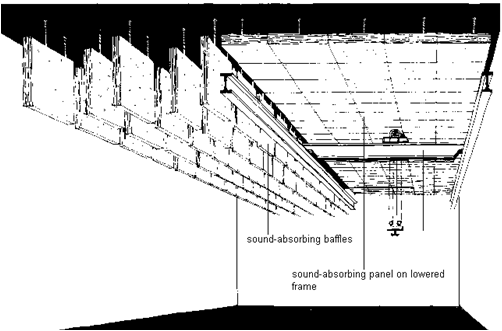
Reflective and absorptive materials are able to reduce noise levels in different ways. Engineered noise-control laminates combine two or more layers of diverse materials with different properties, often with an air space between them. These layered materials absorb a high percentage of sound and then attenuate the sound to maximize the transmission loss. The sound is effectively captured with minimal reflection and transmission.
An alternate method of interrupting the noise path is to relocate the noise source. For example, air expansion at valves can cause significant noise; these valves can be routed to an area away from the worker by extending the piping, which would remove the noise source from the worker, thereby reducing the worker's noise exposure.
-
Acoustical Enclosures
Acoustical enclosures are the most popular path treatment used in industry. Such an enclosure is composed of a dense outer casing, often with a sound-absorptive material on the interior surfaces to help dissipate the acoustical energy.
Enclosures can present difficulties for the production process. Using them can involve many challenges, such as interior heat buildup, limited physical and visual access to the equipment, difficulty getting the product in and out of the enclosure without sacrificing some noise reduction, and maintenance personnel needing to disassemble the enclosure when repairing equipment. It is not unusual for a reassembled enclosure to lose much of its effectiveness due to poor fittings and small gaps or openings in the enclosure.
Despite the challenges associated with enclosures, they are often the most effective way to control noise hazards. A well-designed and relatively airtight enclosure can provide as much as 30 dB to 40 dB of noise reduction. For example, Figure 38 shows an enclosure with large retractable doors, large observation windows, internal lighting, and ventilation, among other features (Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control).
Figure 38. Large Equipment Enclosure with Retracting Doors

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
Complete enclosures around noise sources are not always possible due to requirements to access maintenance panels and equipment controls, provide ventilation, or keep the process flowing. In these cases, a partial enclosure may still substantially reduce noise. Like full enclosures, partial enclosures should have effective barrier materials on the outside and should be lined with absorptive materials on the inside. Because noise will escape through the opening, the noise path should be treated with sound-absorbing materials if possible. Also, the number of openings should be limited and should be directed away from workers, if possible. Figure 39 shows a partial enclosure that allows access while affording the operator some protection from the noise source.
Where possible, it is beneficial to combine noise control with machine guarding requirements to protect workers from other physical hazards (e.g., pinch points, crushing hazards). For more information on integrating noise control with machine guarding, see Appendix J.
Figure 39. Partial Enclosure

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
Enclosing a noise source is often impractical if there is not enough space or if workers need to access the noise source for maintenance or operational reasons. In these cases, lagging could be a more practical solution. Lagging, essentially a localized form of enclosure, can be wrapped around pipes or ducts that generate noise. The lagging should be designed following the same principles outlined for enclosures: with effective barrier materials on the outside and sound-absorptive materials on the inside.
Lagging is generally installed from the inside out, by first encircling the pipe or duct with the absorptive inner material, then applying an airtight limp barrier material as a protective covering. The airtight outside barrier of the lagging can be composed of asphalt paper, linoleum, neoprene sheeting, lead, loaded vinyl, or other materials with similar qualities. Placed against the pipe or duct, the lagging's inner absorptive material provides isolation between the outer layer and the noise source and also helps absorb noise from the source.
-
Shields or Barriers
A barrier is a partial wall, or partition, between the noise source and the receiver. It is made of a solid, dense material with high sound transmission loss. Sound barriers create a sound shadow at the location of the receiver, thus attenuating noise exposure.
Figure 40. Large Partition Wall

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
Note the large partition wall on the right side of the photograph in Figure 40. A barrier should be as tall as possible and be as close to the worker or the noise source (in between the two) as feasible in order to maximize the reduction in noise exposure. Of course, if a receiver is inside a room, reverberations from the ceilings and walls can diminish the effectiveness of a barrier. For this reason, indoor barriers are most effective when workers are in the direct field of sound from the noise source, as opposed to the reverberant field. Even outdoors, it is possible for noise to reflect from nearby buildings and contribute to the noise exposure of the receiver.
Insertion Loss vs. Transmission Loss
Insertion loss is the difference in sound pressure level (dB) measured at a fixed point before and after the noise control is installed. This common measure of acoustic performance represents the change in sound pressure level (dB) for the surroundings due to the "insertion" of noise reduction materials.
Transmission loss is the difference in sound power level across the noise reduction material. It is the difference between measurements made on either side of the material.
A noise barrier is effective when its transmission loss is at least 10 dB greater than the insertion loss expected (see text box for definitions of transmission loss and insertion loss). If it is not, sound transmitted through the barrier may contribute significantly to the noise exposure of the receiver. One effective strategy for further reducing noise levels with barriers is to create barriers with multiple layers, sandwiching a material of different density (such as air) between the layers. Two 5-inch masonry walls spaced a few inches apart will have a greater transmission loss from one side to the other than a solid masonry wall that is 10 inches thick.
-
-
Receiver Treatment
-
Enclosures (Cabs, Control Rooms, Isolation Booths)
The receiver (the worker) can be protected from noise by an isolation booth. In the construction industry, a common example of a personnel enclosure is the cab on heavy equipment, such as a dozer. Figure 41 shows another type of personnel enclosure (in this case, a multi-person control room). The design concepts for personnel enclosures are similar to those for equipment enclosures, but because they are used to enclose people, safe access and egress, fresh air supply, and thermal comfort are critical considerations. For any personnel enclosure, the room or booth's ability to exclude noise is impaired while the door is open. Workers are more likely to keep the door closed if they perceive that the atmosphere inside the booth is at least as comfortable as it is outside the booth. Workers generally use a personnel enclosure most effectively--keeping the door closed to exclude noise--when the enclosure provides tempered air (seasonally heated or air conditioned) and a sense of air movement inside.
Figure 41. Personnel Enclosure

(Driscoll, Principles of Noise Control)
-
B. Engineering Controls and Economic Feasibility
-
Overview
The cost of achieving acceptable noise levels varies greatly, depending on the industry. Even within specific industries, noise levels can vary widely with different processes, practices, and equipment. When a facility does make changes that include engineering control measures in a noisy area, it rarely follows up with a detailed noise evaluation that documents the changes, costs, and extent to which noise decreased. As a result, published literature contains relatively few specific examples comparing the costs and benefits of engineering controls.
The economic feasibility of lowering noise levels with engineering controls is an important factor in deciding whether to implement specific controls. In addition to the direct costs of design, materials, construction or installation, and maintenance of engineering controls, these controls can have indirect costs and benefits, such as decreasing worker absenteeism, increasing or decreasing worker productivity, and increasing or decreasing the life of process equipment. Furthermore, if an engineering control reduces worker TWAs below 85 dBA, the need for a hearing conservation program is eliminated, along with the associated costs. These costs include expenses for audiometry, training, HPDs, recordkeeping, and program administration.
As a general rule, engineering controls increase in cost as their implementation moves further from the design stage. It is typically cheaper to control noise by "designing it out" (i.e., modifying equipment or facility design plans to reduce the sound level associated with the finished product) than to purchase new production equipment. Purchasing new production equipment is also typically cheaper than retrofitting existing equipment with noise controls. Each facility must be responsible for evaluating which noise reduction options are most appropriate for it. Facilities will have different options for significantly reducing noise levels at the lowest possible cost.
The following case studies provide a sample of engineering control options that have proven effective and economically feasible for other facilities. The studies are categorized by the engineering control technique involved. Cost information is included when available.
-
Engineering Control Case Studies
-
Acoustic Absorption
Case study: A fixed-base router initially produced a noise level of 84.8 dBA in testing. Workers placed 3M Thinsulate foam over the motor intake and exhaust vents. After the foam was installed, the router produced a noise level of 77.4 dBA, approximately 8 dBA less than the original noise level. The authors of this study estimated that it cost less than $1 per router to implement (Koning et al., 2003).
Case study: A company manufactures cement blocks in 8",10", and 12" sizes according to orders. Cement, fly ash, and other raw materials are brought in on railcars and stored in silos. The ingredients are then mixed and sent to the block machine, which initially generated noise levels of 95 dBA. The employer installed acoustical panels around the block machine, lowering the noise generated by the machine to 88 dBA. The employer stated that the eight acoustical panels cost $45 each, for a total cost of $400.
Case study: A company manufactures mattresses and foundation products. The mattresses are assembled on a steel table. The nail gun operator (who assembles the mattresses) was previously exposed to noise levels of 93 dBA. The employer implemented the following changes: replaced the steel tables with wooden tables; reduced the nail gun from 110 psi to 85 psi; placed acoustical insulation on the top, bottom, and around the wooden tables; and wrapped foam around the table legs to absorb the vibration to the concrete floor. These measures lowered the noise generated to 87 dBA. The total cost was $500.
-
Damping
Case study: A high-speed, strip-fed punch press was used in a manufacturing process to stamp electrical components. The equipment generated noise levels of 101 dBA when operating at an average of 271 strokes per minute. To reduce the noise level, the manufacturer installed anti-vibration mounts and applied a self-adhesive damping sheet to the sheet metal surfaces of the equipment. These measures lowered the noise generated by the equipment by 9 dBA to 92 dBA.
Case study: A feeder bowl was used to sort aluminum disks and produced 101 dBA. The best way to reduce this noise level was to apply a damping compound to the feeder bowl. The damping compound reduced the noise level 12 dBA to 89 dBA. Five gallons of the compound cost $180 to $250, plus the approximate labor cost of $27 per hour and 1 hour per bowl.
-
Design
Case study: A company used a tungsten-carbide-tipped blade to cut aluminum. The blade produced an average noise level of 97 dBA; the company reduced this noise level to 91 dBA by replacing it. The original blade was 350 mm in diameter, with 84 teeth and a thickness of 3.5 mm; the new blade was also 350 mm in diameter but had 108 teeth and a thickness of 3.2 mm. The former blade cost between $10 and $40, whereas the blade with more teeth cost between $60 and $400 (Government of Western Australia, 2009).
Case study: A company designed a bulldozer whose engine ran at a rated speed 5% lower than a typical bulldozer. The bulldozer also included other noise reduction measures, such as a cab damper mount. At 15 meters from the newly designed bulldozer, the noise level is 10 dB lower than a typical bulldozer (60 dB vs. 70 dB). The bulldozer operator's exposure was 7 dB lower than with the previous design. The costs of the old and new designs are difficult to compare but range from $70,000 for a 1990 version of the old design to $235,000 for the new design.
Case study: A U.S. government agency recognized that it had been spending money on retrofit noise controls while still buying new loud equipment. The agency determined that a two-prong approach was needed: buying new quiet equipment while continuing to retrofit old noisy equipment. By implementing a "Buy Quiet and Quiet by Design" requirement, the agency compelled noise emissions to be considered equally with other factors when buying equipment near an 80-dBA threshold. Among other tools in a "Buy Quiet Process Roadmap" created to help procurement officers identify and purchase quieter equipment, the agency developed a process for quantifying the long-term costs of noise exposure for the candidate products being considered for purchase. Both these costs and the equipment noise level are considered in the final purchase decision.
Case study: A standard pneumatic production rock drill was compared to a prototype pneumatic rock drill incorporating engineering noise-control measures (varying thrust pressure and water flow rate at the bit). By using the manufacturer's recommended operating pressure of 496 kPa (72 psi), the prototype's sound power was 10 dBA less than that of the standard drill. The drills' penetration rates were within 6 percent of each other, indicating that the noise control was effective without sacrificing performance (NIOSH, 2009).
-
Isolation
Case study: A bench grinder and finish grinder in an electrical contractor's workshop were resting on a metal cabinet against the wall. The equipment generated noise levels of 95 dBA. The equipment was removed from the cabinet and placed on pedestals, which were mounted to the floor with rubber mounts. As a result, the noise level dropped to 91 dBA. This control cost approximately $150. (HSE, 2005a)
-
Insulation (Enclosure/Barrier)
Case study: A company manufactured folding cartons. The cartons were produced in stacks, which were held together by uncut portions of the carton material. The cartons were separated using an air chisel powered by compressed air. This chisel generated noise levels of up to 95 dBA. A simple barrier wall of ¼-inch plywood was constructed, consisting of a frame with plywood attached to either side. The sound level of the receiver was reduced to 85 dBA.
-
Maintenance
Case study: A 20-ton press was used in a manufacturing process to pierce aluminum plates. By replacing the bearings and providing proper lubrication when needed, the noise levels were reduced between 7 dBA and 16 dBA. These maintenance measures also increased the tonnage of the equipment to its original rating.
Case study: NIOSH evaluated the noise exposure of heavy equipment operators using new and older models of bulldozers. The newest bulldozer studied had noise controls consisting of acoustic foam on the ceiling of the rollover and falling object protection system, an exhaust muffler, and an enclosed engine compartment, all missing on the older bulldozers. Even with no cab, the newest bulldozer had the lowest recorded operator's noise dose of all the bulldozers (139% OSHA PEL). The operator of the new bulldozer with intact noise controls (except cab) had noise exposures 1/4 to 1/10 that of workers operating dozers lacking noise controls but otherwise in good condition (up to 1,397% OSHA PEL). (NIOSH, 1979)
-
Silencing (Pneumatic)
Case study: A manufacturing process involved the use of a hoist motor for materials handling. The motor's air exhaust exposed the operator to 115 dBA. The manufacturer installed a muffler on the exhaust, reducing the noise level to 81 dBA. Off-the-shelf mufflers cost anywhere up to $150 each, plus the cost of maintenance labor, which can be assumed to be $27 per hour (in 2009 dollars) for 1 hour per month.
Case study: A powder mill dropped ground product by gravity into a large orbital sifter. This process generated a noise hazard for the equipment operators, but the powder would destroy a traditional silencer. The facility manufactured a flexible connector between the pipe and the sifter that allowed the sifter to move and stay connected to the pipe above, while not allowing the sifter to direct noise energy through the inlet. An oversized silencer was then fitted over the flexible connector to catch the noise that leaked from the connector, reducing the noise level by 8 dB to 82 dB. The cost was £750 (equivalent to $1,309.34 at the time [2005]).
Case study: A pneumatic nail gun generated a noise level of 94.5 dBA at its muffler. A team of student researchers developed a way to construct an additional muffler to reduce the noise level to 75.5 dBA using common materials that cost less than $5 in total. These materials included a Viton O-ring, PVC housing, an 8-mm bolt, and a hose plug.
-
-
Economic Feasibility Analysis
There are various methods that CSHOs can use to evaluate the economic feasibility of noise engineering controls relative to current enforcement policy (see CPL 2-2.35A Appendix A and OSHA's Field Operations Manual) and for pre-citation documentation purposes. These methods are useful whenever the daily noise exposure exceeds the levels listed in 29 CFR 1910.95 and 20 CFR 1926.52. A summary of some of these methods is contained in Appendix G. CSHOs should also refer to regional or national office enforcement personnel for guidance when performing economic feasibility analyses on engineering controls, according to current regional/national policies and procedures, as applicable.
VI. References
Acoustical Solutions. 2012. Glossary of Terms. Acoustical Solutions, Inc. Accessed April 2012.
ACGIH®. 2020. TLVs® and BEIs®: Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents & Biological Exposure Indices.
Allied Witan. 2010. Personal communication between John Gibble of Allied Witan and Eastern Research Group, Inc. June 7.
AIHA. 2003. The Noise Manual. 5th edition. Edited by E.H. Berger et al. Fairfax, VA: American Industrial Hygiene Association.
Barron, R.F. 2003. Industrial Noise Control and Acoustics. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Bell, L.H. and D.H. Bell. 1994. Industrial Noise Control: Fundamentals and Application. 2nd edition. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Bruce, R.D., A.S. Bommer, and C.T. Moritz. 2003. Noise, Vibration, and Ultrasound. In The Occupational Environment: Its Evaluation, Control, and Management, Second Edition. Fairfax, Virginia: American Industrial Hygiene Association. Pages 435-475.
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2009. Occupational employment and wages: 49-9043 maintenance workers, machinery. May.
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2009b. Employer costs for employee compensation. June.
Centers for Disease Control. 1996. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Preventing Occupational Hearing Loss-A Practical Guide. Eds. John R. Franks, Mark R. Stephenson, and Carol J. Merry. NIOSH.
Cox, T.J. and P. D'Antonio. 2004. Acoustic absorbers and diffusers: theory design and application. New York, NY: Spon Press, Appendix A.
Driscoll, D.P., and L.H. Royster. 2003. Chapter 9: Noise Control Engineering. In American Industrial Hygiene Association. The Noise Manual. 5th edition. Edited by E.H. Berger et al. Fairfax, VA: American Industrial Hygiene Association.
Driscoll, Dennis P. 2011. "The Economics of Noise Control Engineering Versus the Hearing Conservation Program." Associates in Acoustics, Inc. October 11. Lecture.
Driscoll, Dennis P. No date. "The Principles of Noise Control." Associates in Acoustics, Inc. Lecture.
Driscoll, Dennis P. No date. "Room Acoustics V2." Associates in Acoustics, Inc. Lecture.
Flamme, G.A., K.K. Deiters, M.R. Stephensen, C.L. Themann, W.J. Murphy, and D.C. Byrne. 2019.
Population-based age adjustment tables for use in occupational hearing conservation programs.
International Journal of Audiology. 59, 20-30.
Government of Western Australia. 2009. Department of Commerce, WorkSafe Division. Noise control fact sheet--buying quiet.
Federal Register. 1996. Health Standards for Occupational Noise Exposure in Coal, Metal, and Nonmetal Mines; Proposed Rule, 61 FR 66348, Dec. 17, 1996.
HSE (Health and Safety Executive). 1995. Anti-vibration treatment of high-speed presses.
HSE (Health and Safety Executive). 1998. Control of noise at power presses. Engineering Sheet No. 29.
HSE (Health and Safety Executive). 2005a. Guidance: bench grinder and linisher.
HSE (Health and Safety Executive). 2005b. Powder Mill.
Koning, M., J. LaLonde, S. Larner, D. Prime, and A. Tufnell. 2003. Study of noise transmission from an electric router.
Lord, H.W., W.S. Gatley, and H.A. Evensen. 1980. Noise Control for Engineers, Krieger Publications.
Machinery Trader. 2010. Product search for Komatsu D85EX-15. Last accessed August 2010.
Mascus. 2010. Product search for Komatsu D85A-21. Last accessed August 2010.
Masterson, E.A., J.A. Deddens, C.L. Themann, S. Bertke, and G.M. Calvert. 2015. Trends in hearing loss by industry sector, 1981-2010. American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 58, 392-401.
Memtech. No date. Vibratory feeder bowl: a case study in industrial sound dampening.
Murphy, W.J., M.R. Stephenson, D.C. Byrne, B. Witt, and J. Duran. 2011. Effects of training on hearing protector attenuation. Noise and Health. 13: 132-141.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. No date. Buy-Quiet Process Roadmap.
NIOSH. 2002. Pneumatic nail gun. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
NIOSH. 2009. A technique for estimating the sound power level radiated by pneumatic rock drills and the evaluation of a CSIR prototype rock drill with engineering noise controls. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
NIOSH. 1979. Industrial Noise Control Manual (document number 79-117a). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
NIOSH. No date. Heavy construction equipment noise study using dosimetry and time-motion studies. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
North Carolina Department of Labor. 2000. Occupational Safety and Health Division. Field Operations Manual: Chapter XV-- Industrial Hygiene Compliance. North Carolina OSHA, February.
OSHA IMIS. 2007. Integrated Management and Information System, Noise Exposure records 1997-2006.
OSHA. 2001. Regional Instruction; Region III; Directive Number STD 1-4.1A Effective Date July 19, 2001. Subject: Enforcement of the Occupational Noise Exposure Standards, 29 CFR 1910.95, 1926.52, and 1926.101, Inspection Procedures and Interpretive Guidance; Appendix C: Economic Feasibility of Noise Control Engineering, and Table C-2: Noise Control Engineering Cost Assumptions.
OSHA. 2000. Technical Manual. Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
OSHA. 2011. Meeting Summary: Stakeholder Meeting on Preventing Occupational Hearing Loss.
OSHA. No date. Occupational Noise Exposure, Safety and Health Topics. Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
OSHA/Driscoll. 2002. Noise and Hearing Conservation, Noise and Hearing Conservation eTool. Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Produced under contract by Dennis Driscoll.
OSHA. 1980. Noise Control-A Guide for Workers and Employers (Publication Number 3048) (engineering control sections only). Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
OSHA. 1982. Standard Interpretation. Letter to Mr. Jonathan A. Jacoby from OSHA, 26 March: Question of whether the noise standard is adjusted for workshifts greater than 8 hours [1910.95].
OSHA. 1987. Standard Interpretation. Use of Walkman Radio, Tape, or CD Players and Their Effect When Hearing Protection is in Use [1910.95(i)(2)(i); 1910.95(i)(2)(II)].
OSHA Region III. 2001. Enforcement of the Occupational Noise Exposure Standards, 29 CFR 1910.95, 1926.52, and 1926.101, Inspection Procedures and Interpretive Guidance [including Appendix C: "Economic Feasibility of Noise Control Engineering," and Table 5-6. Noise Control Engineering Cost Assumptions] -- Directive Number STD 1-4.1A. July 19.
OSHA. 1997. Standard Interpretation. Placement of the noise dosimeter microphone for measuring the noise exposure of an employee using an airline respirator equipped with a shroud [1910.95].
OSHA. 2007. Rules of agency practice and procedure concerning OSHA access to employer medical records -- Directive Number CPL 02-02-072. Effective Date: 8/22/07.
OSHA/NHCA Alliance. 2008. Best Practice Bulletin: Hearing Protection-Emerging Trends: Individual Fit Testing.
OSHA/NIOSH. 2018. Preventing Hearing Loss Caused by Chemical (Ototoxicity) and Noise Exposure. Safety and Health Information Bulletin, SHIB 03-08-2018. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2018-124.
OTI/Driscoll. No date. Industrial Noise, Online Course, #2200. OSHA Training Institute. Produced under contract by Dennis Driscoll.
Quest Technologies. 2010. NoisePro Personal Noise Dosimeter User Manual.
Quest Technologies. 2009. QC-10 and QC-20 Sound Calibrators Operator's Manual.
Quest Technologies. 2007. SoundPro Models SE and DL Hand Held Sound Level Meter and Real-Time Frequency Analyzer Owner's Manual.
Sayler, K.S., P.M. Rabinowitz, L.F. Cantley, D. Galusha, and R.L. Neitzel. 2018. Costs and effectiveness of hearing conservation programs at 14 US metal manufacturing industries. International Journal of Audiology. 57, 3-11.
Seixas, N.S. and Neitzel, R. 2002. Response to ANPR on Hearing Conservation Program for Construction Workers, Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Docket H-011G. Department of Environmental Health, University of Washington. October 22.
Seixas, N. and Neitzel, R. 2004. Noise Exposure and Hearing Protection Use Among Construction Workers in Washington State. Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences, School of Public Health and Community Medicine, University of Washington. Seattle. September.
Sekhon, N.K. and Masterson ,E.A. 2020. Prevalence of hearing loss among noise-exposed workers within the services sector, 2006-2015. International Journal of Audiology. 59, 948-961.
Staudt, A., K.W. Whitworth, L.C. Chien, L.W. Whitehead, and D.G. Ruize de Porras 2019. Association of organic solvents and occupational noise on hearing loss and tinnitus among adults in the U.S., 1999-2004. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 92, 403-413.
Themann, C.L. and Masterson, E.A. 2019. Occupational noise exposure: A review of its effects, epidemiology, and impact with recommendations for reducing its burden. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 146, 3879.
U.S. Department of Labor. 2011. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Survey of Occupational Injuries and Illnesses--Summary Estimates Charts Package. October 11.
U.S. Department of Labor. 1983. OSHA, Office of Regulatory Affairs. Regulatory Impact and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis of the Hearing Conservation Amendment. Table 7. February.
Hansen, C.H. and B. Goelzer. Engineering Noise Control. World Health Organization.
VII. Resources
A. Reference Books and Articles
- Comprehensive Review--Noise, Hearing Loss, Noise Control
American Industrial Hygiene Association. 2003. The Noise Manual. 5th edition. Edited by E.H. Berger et al. Fairfax, VA: American Industrial Hygiene Association.
A comprehensive manual on noise hazard and control for industrial hygienists and safety professionals. A revised edition is anticipated in the near future.
Dobie, Robert A. 1993. Medical-Legal Evaluation of Hearing Loss. Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Extensive information on occupational hearing loss.
Sataloff, R.T. and Sataloff, J. 1993. Occupational Hearing Loss, Second Edition. Marcel Decker, Inc.
Detailed information regarding occupational hearing loss.
Suter, A.H. 2002. Construction Noise: Exposure, Effects, and the Potential for Remediation; a Review and Analysis. AIHA Journal 63:768-789. November/December.
- Noise Control and Engineering
Investigators develop new products and applications for noise control; however, the principles and basic materials of noise control remain unchanged. Some earlier titles remain useful. Books can be obtained through new or used book sellers and through interlibrary loan programs.
Barron, R.F. 2003. Industrial Noise Control and Acoustics. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Bell, L.H. and D.H. Bell. 1994. Industrial Noise Control: Fundamentals and Application. 2nd edition. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Bruce, R.D., A.S. Bommer, and C.T. Moritz. 2003. Noise, Vibration, and Ultrasound. In The Occupational Environment: Its Evaluation, Control, and Management. 2nd edition. Fairfax, VA: American Industrial Hygiene Association, pp. 435-475.
Cheremisinoff, N. 1996. Noise Control in Industry: A Practical Guide. Westwood, NJ: Noyes Publications.
Cox, T.J. and P. D'Antonio. 2004. Appendix A. In Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application. New York, NY: Spon Press.
Diehl, George M. 1973. Machinery Acoustics. Wiley-Interscience. New York, NY.
NIOSH. 1980. Compendium of Materials for Noise Control. DHEW (NIOSH) Publication No. 80-116.
calculatorNIOSH. 1978. Industrial Noise Control Manual. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 79-117.
This manual includes 61 case histories on noise-control modifications for industrial processes and equipment. It displays decibel and octave band analysis of noise levels before and after control methods were applied. It also presents relative costs of many control methods (in 1978 dollars).
Peterson, A.P.G. 1980. Noise and Vibration Control. In Handbook of Noise Measurement. 9th edition. Concord, MA: GenRad, Inc., pp. 239-259.
Hansen, C.H. and B. Goelzer. Engineering Noise Control. World Health Organization.
B. Noise Physics
MC Squared System Design Group, Inc. No date. Wavelength of sound -- calculator.
This tool calculates the wavelength of any airborne noise frequency in inches, feet, and meters.
C. Hearing Loss
- Hearing Loss--Reporting
Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation. 2005. Determining When Hearing Loss Is Work Related.
National Hearing Conservation Association. 2011. NHCA Guidelines for Recording Hearing Loss on the OSHA 300 Log.
- Hearing Loss--Incident Rates
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2011. TABLE SNR08: Incidence Rates of Nonfatal Occupational Illness, by Industry and Category of Illness, 2010.
This extensive table lists, by industry, the incidence of reported illnesses per 10,000 full-time workers. The table includes a column for hearing loss. BLS publishes this information annually each fall, covering the previous year's data. Check for the latest edition and previous years here.
- Hearing Loss Prevention
American National Standards Institute/American Society of Safety Engineers. 2007. Hearing Loss Prevention for Construction and Demolition Workers. ANSI/ASSE A10.46-2007.
This ANSI document recommends standards for hearing conservation programs for construction and demolition workers. Recommendations cover hazard identification, hazard control, hearing protection devices, audiometry, training, recordkeeping, and program evaluations. An appendix lists noise levels (in decibels) that are likely to be exceeded by several dozen different construction activities and cites a source for each listed level.
D. Sound Levels of Equipment, Occupations, and Activities
See also ANSI/ASSE A10.46-2007 under the "Hearing Loss Prevention" heading.
Noise Navigator® Sound Level Database. 2008.
An extensive database of over 1,700 sound level measurements reported by various references for a wide range of equipment and activities (occupational, recreational, and military noise sources). A reference for each source is provided. The "Intro" tab of this Excel spreadsheet introduces the spreadsheets in which the sound level measurements are organized. This database is compiled by E-A-R/Aero Company and the University of Washington; as of spring 2012, the current version (1.4) is dated 2008.
Noise Database for Prediction of Noise on Construction and Open Sites. 2005.
Eight tables reporting average measurements for noise from equipment used on construction and open sites in the United Kingdom (UK). Organized by construction phase and type; noise level information includes both unweighted octave band Leq levels and overall A-weighted Leq values (in decibels). This document was commissioned by the UK government and published in 2005.
Noise Emissions for Outdoor Equipment.
This European Commission database lists operating noise levels for several dozen categories of outdoor equipment. The European Commission requires equipment manufacturers to accompany their equipment with a declaration of conformity, stating that the equipment conforms to the provisions of noise-limiting directives issued by the European Community governing organizations (e.g., Directive 2000/14/EC of the European Parliament and Council, May 8, 2000). Equipment manufacturers continue to add new information to this database in a standard format.
E. Noise Control
- Engineering Controls and Noise-Control Programs
Colgate-Palmolive. 2012. Excellence Award Corporate-Wide: Colgate-Palmolive Company.
Colgate-Palmolive won the 2012 Safe-in-Sound award through an extensive international effort to reduce noise exposure in its facilities around the world. This online presentation outlines the company's efforts and successes and presents a summary of numerous adopted engineering modifications (with photos, notes on the changes made, and examples of noise reductions achieved).
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Approximate Sound Power-Pressure Conversion Worksheet.
A simplified conversion method for sound pressure/power conversion; part of the NASA Buy-Quiet Roadmap.
- Buy-Quiet and Quiet by Design Programs
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. 2012. Buy-Quiet Process Roadmap.
This is an online tool for navigating the procurement of low-noise equipment. Part of the NASA EARLAB Auditory Demonstration Laboratory website, the Roadmap can be accessed from the "Buy-Quiet Purchasing" tab in the top navigation menu. Other NASA hearing conservation resources, such as the "Auditory Demonstrations" series and "TWA Calculator," are also part of this website. All are available as free, publicly accessible digital downloadable files. This site is hosted and maintained by Nelson Acoustics as a service to the noise-control and hearing conservation technical community and was updated in 2012.
The website describes itself as follows: "The Roadmap guides users through a stepwise process that includes project planning, researching the marketplace, selecting an achievable noise emission criterion, and developing a specification document. The Roadmap also includes guidelines for identifying the appropriate government procurement strategy for each purchase, based on an assessment of the purchase-specific long-term financial and noise exposure risk. The Roadmap is applicable to both public and private sector organizations, and the downloadable forms and worksheets can be customized to each organization. There is a very brief tutorial PowerPoint presentation here."
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Buy Quiet.
Information on the NIOSH Buy Quiet initiative.
F. Cost of Hearing Loss/Cost of Hearing Conservation Programs
Nelson, D.A. 2012. White Paper: The Long-Term Cost of Noise Exposure.
NASA's Roadmap (see entry in the previous section) includes this paper, which provides one alternative methodology for calculating the cost of long-term exposure to the noise emission of various products being considered for a particular purchase. This allows the comparison of the true cost of candidate products that may differ in noise emission and price. Users may input their own experience; for example, as discussed in Appendix G of this chapter, hearing conservation costs vary widely due to factors such as economies of scale, geography, and what elements are included in the calculation). NASA seeks feedback on this methodology in order to continue to improve and update the Roadmap.
Driscoll, D.P. and L.H. Royster. 2003. Chapter 9: Noise Control Engineering. In American Industrial Hygiene Association. The Noise Manual. 5th edition. Edited by E.H. Berger et al. Fairfax, VA: American Industrial Hygiene Association.
See "Benefits and Costs of Noise Control" on pages 281-289.
G. Acoustical Consultants
National Council of Acoustical Consultants. 2012. What Sets an Expert Apart?
This site also includes an online directory of consultants.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. No date. When to Hire an Acoustical Consultant: Get Help Before You Get in Over Your Head.
This Web page (part of NASA's Roadmap) lists examples of situations where an acoustical engineer can provide valuable expertise and when a product representative can be useful. The site also describes credentials that acoustical professionals might have.
American Industrial Hygiene Association. Search for a Consultant.
Industrial hygiene professionals develop hearing conservation programs, conduct noise evaluations, measure sound levels, and perform noise dosimetry. In the box for "Specialty," select "Hearing Conservation/Noise Reduction."
H. Associations, Education, and Conferences
Acoustical Solutions, Inc. ASI University.
This noise-control materials manufacturer's website offers general background information on understanding noise-control principles and terminology. Offers continuing education related to noise through the American Institute of Architects.
Acoustical Society of America.
International scientific society in acoustics dedicated to increasing and diffusing the knowledge of acoustics and its practical applications. Offers continuing education.
Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation.
Offers continuing education.
National Council of Acoustical Consultants.
"The acoustician seeks to understand and quantify the production, control, transmission and effects of sound." Offers continuing education.
National Hearing Conservation Association.
Sponsor of annual conference; offers continuing education.
Institute of Noise Control Engineering.
Sponsor of the annual conference "Inter-Noise, International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering." Offers continuing education.
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A--GLOSSARY
Action Level (AL): An 8-hour time-weighted average of 85 decibels, measured on the A-scale, with slow response (equivalently, a dose of 50%). Only sounds 80 dBA and higher are integrated into the AL (the threshold level is 80 dBA).
A-weighting: A measurement scale that approximates the "loudness" of tones relative to a 40-dB sound pressure level, 1,000-Hz reference tone. A weighting is said to best fit the frequency response of the human ear: when a sound dosimeter is set to A-weighting, it responds to the frequency components of sound much like your ear responds. A-weighting has the added advantage of being correlated with annoyance measures and is most responsive to the mid-frequencies, 500 Hz to 4,000 Hz.
B-weighting: B-weighting is similar to A-weighting but with less attenuation. B-weighting was an attempt to approximate human perception of loudness for moderately high sound pressure levels. It is now outdated and no longer used.
C-weighting: A measurement scale that approximates the "loudness" of tones relative to a 90-dB sound pressure level, 1,000-Hz reference tone. C-weighting has the added advantage of providing a relatively "flat" measurement scale that includes very low frequencies.
Criterion level: The continuous equivalent 8-hour A-weighted sound level (as dBA) that constitutes 100% of an allowable noise exposure (dose)--in other words, the permissible exposure limit. For OSHA purposes, this is 90 dB, averaged over 8 hours on the A scale of a standard dosimeter set on slow response.
Dose (%): Related to the criterion level, a dose reading of 100% is the maximum allowable exposure to accumulated noise. For OSHA, 100% dose occurs for an average sound level of 90 dBA over an 8-hour period (or an equivalent exposure). If a TWA reading is used rather than the average sound level, the time period is no longer explicitly needed. A TWA of 90 dBA is the equivalent of 100% dose. The dose doubles every time the TWA increases by the exchange rate. Table A-1 shows the relationship between dose and the corresponding 8-hour TWA exposure.
Example: OSHA uses an exchange rate of 5 dBA. Suppose the TWA is 100 dB for an 8-hour exposure. The dose doubles for each 5-dB increase over the criterion level of 90 dBA. The resulting dose is therefore 400%. With an 8-hour TWA of 80 dBA, the dose would halve for each 5 dBA below the criterion level. The resulting dose would be 25%. When taking noise samples of duration shorter than the full workday, dose is an easy number to work with because it is linear with respect to time.
Example: If a 0.5-hour screening sample results in 9% dose and the workday is 7.5 hours long, the estimated dose for the full workday would be 135% (7.5 ÷ 0.5 × 9%). This is computed making the assumption that the sampled noise will continue at the same levels for the full 7.5-hour workday. While short-term dose measurements cannot be used to support a citation, they can be effectively used as a screening tool to determine whether full-shift sampling is warranted.
Example: A worker is employed in a high noise area for half an hour each day, and the remainder of the 8-hour workday is spent in a quiet office area. If the worker is exposed to 93 dBA for half an hour, the dosimeter will read 10%. Because no additional dose will be accumulated while working in the quiet office area, the equivalent 8-hour TWA will be 73.4 dBA, as shown in Table A-1.
|
Dose (% Noise Exposure) |
8-Hour TWA (dBA) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 73.4 |
| 25 | 80 |
| 50 | 85 |
| 75 | 87.9 |
| 100 | 90 |
| 150 | 92.9 |
| 200 | 95 |
| 300 | 97.9 |
| 400 | 100 |
| 500 | 101.6 |
| 600 | 102.9 |
| 800 | 105 |
| 1000 | 106.6 |
| 1600 | 110 |
| 3200 | 115 |
| 6400 | 120 |
| * When measured with a 5-dB exchange rate and a 90-dBA PEL. | |
| ** Additional data points are provided in Table A-1 in Appendix A, Section II of the noise standard (29 CFR 1910.95), particularly in the 80-999% dose range. | |
Exceedance level: The level exceeded by the measured noise level for an identified fraction of time. Exceedance levels may be calculated for many time fractions over the course of a shift and are typically expressed with percentages (L%). For example, an L40 equal to 73 dBA would mean that for 40% of the run time, the decibel level was higher than 73 dBA.
Exchange rate (or doubling rate): The increase or decrease in decibels corresponding to twice (or half) the noise dose. For example, if the exchange rate is 5 dBA, 90 dBA produces twice the noise dose that 85 dBA produces (assuming that duration is constant). The OSHA exchange rate is 5 dBA (see Table D-2 of the construction noise standard, 29 CFR 1926.52, and Tables G-16 and G-16a of the general industry noise standard, 29 CFR 1910.95).
Only instruments using a 5-dBA exchange rate may be used for OSHA compliance measurements. CSHOs should be aware that the following organizations use noise dosimeters with a 3-dBA exchange rate: NIOSH, EPA, ACGIH, and most foreign governments. The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) previously used a 4-dBA exchange rate; however, all branches (except the U.S. Navy) now have adopted the 3-dBA exchange rate.
Hertz (Hz): Unit of vibration frequency, numerically equal to cycles per second.
Impulsive or Impact noise: Impulsive or impact noise is characterized by a sharp rise and rapid decay in sound levels and is less than 1 second in duration.
Intensity of sound: Intensity of sound is measured in watts per square meter. To calculate the intensity level in decibels, find the ratio of the intensity (I) of sound to the threshold intensity (I0).
dB = 10 log10 (I / I0)
Lavg (or LAVG): The average sound level measured over the run time of measurement. This becomes a bit confusing when thresholds are used, because the average does not include any sound below the threshold. Sound is measured in the logarithmic scale of decibels, so the average cannot be computed by simply adding the levels and dividing by the number of samples. When averaging decibels, short durations of high levels can significantly contribute to the average level.
Example: Assume the threshold is set to 80 dBA and the exchange rate is 5 dBA (the settings of OSHA's Action Level). Consider taking a 1-hour noise measurement in an office where the A-weighted sound level was typically between 50 dBA and 70 dBA. If the sound level never exceeded the 80-dBA threshold during the 1-hour period, then the LAVG would not indicate any reading at all. If 80 dBA was exceeded for only a few seconds due to a telephone ringing near the instrument, then only those seconds will contribute to the LAVG, resulting in a level perhaps around 40 dBA (notably lower than the actual levels in the environment).
Ldn (or LDN): Representing the day/night sound level, this measurement is a 24-hour average sound level, where 10 dB is added to all of the readings taken between 10 p.m. and 7 a.m. This is primarily used in community noise regulations where there is a 10-dB "penalty" for nighttime noise but is not used to evaluate compliance with OSHA standards, as it is not an occupational issue.
Leq: The true equivalent sound level measured over the run time. LEQ is functionally the same as LAVG, except that it is only used when the exchange rate is set to 3 dB and the threshold is zero.
Linear weighting: A weighting most commonly found on upper model sound level meters, typically used when performing octave band filtering analysis.
Max level: The highest weighted sound level that occurred, also allowing for the response time to which the meter is set. If the meter is set for A-weighting with slow response, the max level is the highest A-weighted sound that occurred when applying the slow response time.
Noise dosimeter: A type of sound level meter that measures and integrates noise over time providing a value of the average dose. This instrument can calculate the daily noise dose based on a full workshift of measurements, or a dose from a shorter sample. The operator can select different noise dose criteria, exchange rates, and thresholds.
Octave bands: Sounds that contain energy over a wide range of frequencies are divided into sections called bands, each one octave. A common standard division is in 10 octave bands identified by their center frequencies, 16; 31.5; 63; 250; 500; 1,000; 2,000; 4,000; 8,000, and 16,000 Hz. For each octave band, the frequency of the lower band limit is one-half the frequency of the upper band limit. This is the most common type of frequency analysis performed for workplace exposure evaluation and control. An alternative frequency band, the one-third octave band, is defined as a frequency band such that the upper band-edge frequency, f2, is the cube root of two times the lower band frequency, f1: f2 = (2)1/3 f1. The level of detail provided by one-third octave bands, however, is rarely required for occupational noise evaluation and control.
Peak noise: The highest instantaneous sound level that a microphone detects. Unlike the max level, the peak is detected independently of the slow or fast response for which the unit is set.
Example: The peak circuitry is very sensitive. Test this by simply blowing across the microphone. You will notice that the peak reading may be 120 dB or greater. When you take a long-term noise sample (such as a typical 8-hour workday sample for OSHA compliance), the peak level is often very high. Because brushing the microphone over a shirt collar or accidentally bumping it can cause such a high reading, the user must be careful not to place too much emphasis on the reading.
Permissible exposure limit (PEL): An 8-hour time-weighted average of 90 decibels, measured on the A-scale, with slow response (equivalently, a dose of 100%). Only sounds 90 dBA and higher are integrated into the PEL (the threshold level is 90 dBA).
Receiver: A person exposed to noise that originates at a noise source. If the receiver is exposed to a hazardous noise level, the exposure can be reduced through various noise-control methods.
Response: Instruments that measure time-varying signals are limited in how fast they can respond to changes in the input signal. Sound dosimeters can operate with a wide variety of response times, but the industry has chosen two particular response times to standardize measurements. These are known as the slow and fast response times. OSHA, the Mine Safety and Health Administration, and ACGIH all require the slow response for sound dosimetry. The standardized time constant for the slow response is 1 second.
Sound level meter: An instrument that converts sound pressure in air into corresponding electronic signals. The signals may be filtered to correspond to certain sound weightings (e.g., A-weighted scale, C-weighted scale).
Threshold level: The A-weighted sound level at which a personal noise dosimeter begins to integrate noise into a measured exposure. For example, if the threshold level on a sound level meter is set at 80 dBA, it will capture and integrate into the computation of dose all noise in the worker's hearing zone that equals or exceeds 80 dBA. Sound levels below this threshold would not be included in the computation of noise dose. Use an 80-dBA threshold for measurements related to hearing conservation programs and a 90-dBA threshold for exposure results related to the need for engineering or administrative controls.
The hypothetical exposure situations shown in Table A-2 illustrate the relationship between criterion level, threshold, and exchange rate and show the difference of using a dosimeter with an 80-dBA threshold versus a 90-dBA threshold to characterize a worker's noise exposure. For example, an instrument with a 90-dBA threshold will not capture any noise below that level and will thus give a readout of 0%, even if the worker being measured is actually being exposed to 89 dBA for 8 hours (i.e., to 87% of the allowable noise dose over any 8-hour period).
| Exposure Conditions | Dosimeter With Threshold Set at 80 dBA (% of measured dose) | Dosimeter With Threshold Set at 90 dBA (% of measured dose) |
|---|---|---|
|
90 dBA for 8 hours |
100.0% |
100.0% |
|
89 dBA for 8 hours |
87.0% |
0.0% |
|
85 dBA for 8 hours |
50.0% |
0.0% |
|
80 dBA for 8 hours |
25.0% |
0.0% |
|
79 dBA for 8 hours |
0.0% |
0.0% |
|
90 dBA for 4 hours plus 80 dBA for 4 hours |
62.5% |
50.0% |
|
90 dBA for 7 hours plus 89 dBA for 1 hour |
98.4% |
87.5% |
|
100 dBA for 2 hours plus 89 dBA for 6 hours |
165.3% |
100.0% |
Assumes 5 dB exchange rate, 90 dBA PEL, ideal threshold activation, and continuous sound levels.
Time-weighted average (TWA): A constant sound level lasting 8 hours that would result in the equivalent sound energy as the noise that was sampled. TWA always averages the sampled sound over an 8-hour period. This average starts at zero and grows. It is less than the Lavg for a duration of less than 8 hours, is exactly equal to the Lavg at 8 hours, and grows higher than the Lavg after 8 hours.
Example: Think of a TWA as having a large 8-hour container that stores sound energy. If you run a dosimeter for 2 hours, your Lavg is the average level for those 2 hours-consider this a smaller 2-hour container filled with sound energy. For TWA, take the 2-hour container and pour that energy into the 8-hour container. The TWA level will be lower. Again, TWA is always based on the 8-hour container. When measuring using OSHA's guidelines, TWA is the proper number to report if the full workshift was measured.
Type 1/Type 2 (or Class 1 and Class 2): Two different accuracy specifications for noise measurements. Type 1 measurements are accurate to approximately ±1dB and Type 2 measurements are accurate to approximately ±2dB. The accuracy of the measurements varies, however, depending on the frequency of the sound being measured.
Z-weighting: An unweighted measurement scale that does not apply any attenuation or weighting to any frequency. Instead, this scale provides a flat response across the entire spectrum from 10 Hz to 20,000 Hz, making it useful for octave band analysis and evaluating engineering controls.
APPENDIX B--SAMPLE EQUATIONS AND CALCULATIONS
B.1 Sound Pressure Level
The human ear can hear a broad range of sound pressures. Because of this, the sound pressure level (Lp) is measured in decibels (dB) on a logarithmic scale that compresses the values into a manageable range. In contrast, direct pressure is measured in pascals (Pa). Lp is calculated as 10 times the logarithm of the square of the ratio of the instantaneous pressure fluctuations (above and below atmospheric pressure) to the reference pressure:
Lp = 10 × log10(P/Pref)2
Where P is the instantaneous sound pressure, in units Pa, and Pref is the reference pressure level, defined as the quietest noise a healthy young person can hear (20 µPa).
Example: If a piece of equipment produces a sound pressure of 2 Pa, the sound pressure level is calculated:
Lp = 20 log10 (2/0.00002) = 20 log10(100,000) = 20 × 5.0 = 100 dB
B.2 Sound Power Level
Sound power level (Lw) is similar in concept to the wattage of a light bulb. In fact, Lw is measured in watts (W). Unlike Lp, Lw does not depend on the distance from the noise source. The sound power level is calculated using the following equation:
Lw = 10 × log10(W/Wref)
Where W is the acoustic power in watts and Wref is the reference acoustic power, 10-12.
Example: The sound power level associated with a typical face-to-face conversation, which may have a sound power of 0.00001 W, is calculated:
Lw = 10 × log10(0.00001/10-12) = 70 dB
B.3 Combining and Averaging Sound Levels
Decibels are measured using a logarithmic scale, which means decibels cannot be added arithmetically. For example, if two noise sources are each producing 90 dB right next to each other, the combined noise sound pressure level will be 93 dB, as opposed to 180 dB. The following equation should be used to calculate the sum of sound pressure levels, sound intensity levels, or sound power levels:
Total L = 10 x log10(Σ1n 10Ln/10)
Often, using this equation to quickly sum sound levels when there is no calculator or computer available is difficult. The following table can be used to estimate a sum of various sound levels:
| Difference Between Two Levels to Be Added | Amount to Add to Higher Level to Find the Sum |
|---|---|
| 0-1 dB | 3 dB |
| 2-4 dB | 2 dB |
| 5-9 dB | 1 dB |
| 10 dB | 0 dB |
Example: There are three noise sources immediately adjacent to one another, each producing a sound pressure level of 95 dB. The combined sound level can be found using the table above. The difference between the first two noise sources is 0 dB, which means the sum will be 95 + 3 = 98 dB. The difference between 98 dB and the remaining noise source (95 dB) is 3, which means the sum will be 98 + 2 = 100 dB.
B.4 Adding Noise Exposure Durations to Determine Compliance with OSHA Standards
Under the OSHA PEL, workers are not permitted to be exposed to an 8-hour TWA equal to or greater than 90 dBA. OSHA uses a 5-dBA exchange rate, meaning the noise level doubles with each additional 5 dBA. The threshold to measure noise is 90 dBA when determining compliance to the PEL. The following chart shows how long workers are permitted to be exposed to specific noise levels:
| Permissible Duration (Hours per Day) |
Sound Level (dBA, Slow Response) |
|---|---|
| 8 | 90 |
| 4 | 95 |
| 2 | 100 |
| 1½ | 102 |
| 1 | 105 |
| ½ | 110 |
| ¼ or less | 115 |
The values in the chart above are from Table G-16 in the general industry standard, 29 CFR 1910.95. To calculate a permissible duration that is not addressed in this chart, use the following equation:
T= 8 / (2(L-90)/5)
Where T is the permissible duration (in hours) and L is the measured sound level (in dBA).
A worker's daily noise exposure typically comes from multiple sources, which have different noise levels for different durations. When adding different noise levels from various noise sources, only noise levels exceeding 90 dBA should be considered. The combined effect of these noise sources can be estimated using the following equation:
Sum = C1/T1 + C2/T2 + C3/T3 + Cn/Tn
Where Cn is the total duration of exposure at a specific noise level, and Tn is the total duration of noise permitted at that decibel level. If the sum equals or exceeds "1," the combined noise level is greater than the allowable level. If the sum is less than "1," the combined noise level is less than the allowable level.
Example: A worker in a machine shop is exposed to 95 dBA for 2 hours, 69 to 78 dBA for 4 hours (including a 15-minute break and 45-minute lunch), and 90 dBA for 3 additional hours.
| Example: Worker's Activity | Time | Measured Sound Level |
|---|---|---|
| Milling machine | 6:00 a.m. - 8:00 a.m. | 95 dBA |
| Break room | 8:00 a.m. - 8:15 a.m. | 69 dBA |
| Parts department | 8:15 a.m. - 11:15 a.m. | 78 dBA |
| Lunch (in break room, 45 min.) |
11:15 a.m. - 12:00 noon | 69 dBA |
| Milling assist | 12:00 noon - 3:00 p.m. | 90 dBA |
To determine if the worker's noise exposure exceeds a 90 dBA TWA, use the previous equation. Because the noise levels in the break room (69 dBA) and parts department (78 dBA) are below the 90 dBA threshold, these periods of the day are not included in the calculation. According to the chart above, workers are permitted to be exposed to 95 dBA for 4 hours per day and 90 dBA for 8 hours per day. Calculate the ratio of actual exposure duration to permissible exposure duration for each time segment and add them: 2/4 + 3/8 = 7/8. The resulting value (7/8) is less than 1; therefore, this worker's exposure does not exceed the 90 dBA PEL. However, a separate calculation would be required to determine if a hearing conservation program is required, and this evaluation would utilize an 80 dBA threshold.
B.5 Calculating the Equivalent A-Weighted Sound Level (LA)
Occasionally, it is necessary to convert a set of octave band sound pressure levels into an equivalent A-weighted sound level. This is easily done by applying the A-scale correction factors for the nine standard octave center frequencies and combining the corrected values by decibel addition (see B.3 above). The A-scale correction factors are the values of the A-weighting network at the center of each particular octave band. The value derived by combining the corrected values for each octave band is designated the A-weighted sound level (dBA).

Example:
| Octave Band Center Frequency (Hz) | Example Lp (dB) | A-Scale Correction Factor (dB) * | Corrected Values (dB)** |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31.5 | 94 | -39 | 55 |
| 63 | 95 | -26 | 69 |
| 125 | 92 | -16 | 76 |
| 250 | 95 | -9 | 86 |
| 500 | 97 | -3 | 94 |
| 1,000 | 97 | 0 | 97 |
| 2,000 | 102 | +1 | 103 |
| 4,000 | 97 | +1 | 98 |
| 8,000 | 92 | -1 | 91 |
|
*Look up on A-weighted network chart for each value Lp. **Lp corrected to the A-scale = Li. |
|||
The A-weighted sound level is calculated by combining the corrected band levels:
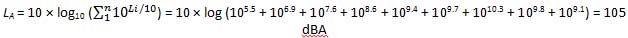
Where LA is the A-weighted sound level and Li is the corrected decibel level value for each individual octave band.
B.6 Calculating Sound Pressure Level at a Distance
If a sound is generated at a point source in a free field, meaning there are no walls or other obstructions, the sound pressure level, Lp, will be reduced by 6 dB each time the distance from the noise source is doubled. Alternatively, Lp will increase by 6 dB in a free field each time the distance to the noise source is halved. Consider the following example:
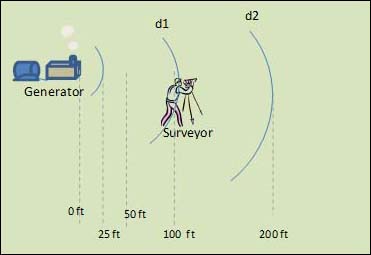
Example: A worker is surveying an open field, which has a diesel generator running in the middle of it. The worker is 100 ft from the generator and is exposed to a noise level of 85 dBA. When the worker is 25 ft from the generator, the noise level will be 97 dBA. At 200 ft from the generator the worker will be exposed to a noise level of 79 dBA.
Calculating the sound pressure level at a specific distance from a noise source is often useful. The following equation allows one to calculate the sound pressure level at any distance from a noise source in a free field:
Lpd2 = Lpd1 + 20 × log(d1/d2)
Where Lpd2 is the sound pressure level at the new distance from the noise source, Lpd1 is the sound pressure level at the original distance, d1 is the original distance, and d2 is the new distance.
Example: The sound pressure level of an aircraft engine in the middle of an open runway is 120 dBA at a distance of 50 ft from the receiver. The sound pressure level at a distance of 80 ft is calculated using the equation above. Lpd1 is 120 dBA, d1 is 50 ft, and d2 is 80 ft. Therefore, Lpd2 is 120 + 20 × log(50/80), which is 116 dBA.
B.7 Average Sound Level, Dose, and Sample Period
Note: formulas in B.7-B.9 are based on a 5 dB exchange rate.
The relationship between the average sound level (LAVG), Dose (D), and sample period (T) is given by the following:
LAVG = 16.61 x log10[D/(12.5xT)] + 90
Where:
LAVG = continuous average sound level (dBA) measured for the time period sampled
D = Dose (%) for the time period sampled
T = time period sampled (hours)
If solving for Dose (LAVG is known), then the above equation can be re-arranged to the following:
D = 12.5 x T x 10[(LAVG-90)/16.61]
B.8 Conversion between Dose and TWA
Using the LAVG equation from B.7, note the case for an eight-hour shift (T = 8 hr), which by definition LAVG = TWA, resulting in the following equation. Note that this is the TWA to Dose conversion formula, as contained in 1910.95 App A:
TWA = 16.61 x log10(D/100) + 90
Where:
TWA = 8-hour time-weighted average sound level (dBA)
D = Dose (%)
If solving for Dose (TWA is known), then the above equation can be re-arranged to the following:
D = 100 x 10[(TWA-90)/16.61]
Example: A factory hires a health and safety consultant to measure the noise exposure of the workers. The consultant writes a report that states that workers are exposed to 183% Dose, according to the general industry standard, 29 CFR 1910.95. Convert this Dose into an 8-hour TWA.
TWA = 16.61 x log10(183/100) + 90 = 94.4 dBA
B.9 Extended Workshifts
The Occupational Noise Exposure standard requires employers implement a hearing conservation program whenever worker noise exposures equal or exceed an 85 dBA TWA, or a 50% dose, also known as the “Action Level” (AL). The LAVG equation in B.7 can be used to calculate the AL in dBA for any work shift length (T), and using a Dose = 50%, as follows (also see OSHA Standard Interpretation, 1982):
AL = 16.61 x log10[50/(12.5xT)] + 90
Where:
AL = Action Level (dBA)
T = time period sampled (hours)
Using the above equation for various shift lengths T, the Action Level values in Table B-9.1 are obtained. Note that each value in the “Uncorrected” column in Table B-9.1 represents a 50% Dose, as shown.
| T (hours) |
Uncorrected for Instrument Error |
Corrected for Instrument Error (+2 dBA) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL (dBA) |
Dose (%) |
AL (dBA) |
Dose (%) |
|
| 8 | 85.0 | 50 | 87.0 | 66 |
| 9 | 84.2 | 50 | 86.2 | 66 |
| 10 | 83.4 | 50 | 85.4 | 66 |
| 12 | 82.1 | 50 | 84.1 | 66 |
| 16 | 80.0 | 50 | 82.0 | 66 |
Instrument accuracy must be taken into account when making compliance determinations. Type-2 dosimeters are considered to have an error of ±2 dBA, and the Action Level must be corrected, accordingly. For example, for an 8-hour shift, the corrected Action Level would be 87 dBA (85 + 2 dBA). Using the Dose equation from B.8, the Dose representing a TWA of 87 dBA can be calculated, resulting in a Dose of 66%, as follows:
D = (100)*10[(87-90)/16.61] = 66%
Therefore, a TWA exposure equal to or exceeding 87 dBA or a Dose of 66%, as measured by the instrument, would require compliance with the hearing conservation requirements of the noise standard.
Table B-9.1 also shows each Action Level corrected for instrument error, by adding 2 dBA to each value. Also, each corrected AL (dBA) can be converted to Dose using the Dose equation from B.7, where LAVG = AL, and inputting the appropriate time period, T. This results in a Dose of 66% for each time period. These values are shown in the “Corrected” column in Table B-9.1.
Note that compliance with the AL for extended workshifts can be determined using any of the following parameters: Dose, TWA, or adjusted AL. See Section IV.E. for more information and examples.
APPENDIX C--ULTRASOUND
Ultrasound is any sound whose frequency is too high for the human ear to hear. (The upper frequency that the human ear can detect is approximately 15 to 20 kilohertz, or kHz, although some people can detect higher frequencies, and the highest frequency a person can detect normally declines with age.) Most of the audible noise associated with ultrasonic sources, such as ultrasonic welders or ultrasonic cleaners, consists of subharmonics. Even though the ultrasound itself is inaudible, the subharmonics it generates can affect hearing and produce other health effects.
C.1 Health Effects and Threshold Limit Values (TLVs®)
Research indicates that ultrasonic noise has little effect on general health unless there is direct body contact with a radiating ultrasonic source. Reported cases of headache and nausea associated with airborne ultrasonic exposures appear to have been caused by high levels of audible noise from source subharmonics.
Subharmonics are sound waves with frequencies that are a fraction (e.g., one-half, one-quarter) of the original ultrasound frequency. Because they are lower than the ultrasound, the human ear can detect them.
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH®) has established permissible ultrasound exposure levels.
The information regarding application of the ACGIH® Ultrasound TLVs® is copyrighted by ACGIH® and is not publicly available. It may be accessed on the ACGIH® website subject to their permissions of use. OSHA personnel are directed to access OSHA’s intranet for more information.
For additional information on ultrasound exposure levels, ceiling values, and 8-hour TWAs that apply to other frequencies, as well as ceiling values measured underwater, refer to the complete ACGIH TLV for ultrasound (see ACGIH, 2020, Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents & Biological Exposure Indices).
C.2 Controls
High-frequency noise is highly directional and is associated with short wavelengths. This means that it is easily reflected or blocked by any type of barrier. The wavelength of a 16-kHz tone, for example, is about 3/4 inch. A modest barrier, extending just 1 to 2 inches beyond the source, is generally sufficient to reflect noise of approximately the same frequency away from a nearby worker. High-frequency audible noise is also easily absorbed by many acoustical materials, such as glass fiber or foam.
C.3 International Ultrasound Exposure Limit Recommendations
Over the past decades, several countries have set exposure limits or recommended levels for ultrasound at various frequencies. The differences in limits are great and reflect differences in the interpretation and analysis of studies on ultrasound and human health. Table C-2 lists ceiling values measured in air in dB, as opposed to 8-hour TWAs or ceiling values measured in water in dB. Though ultrasonic frequencies are not audible to the human ear, it is clear that the international community is concerned about the effects that subharmonic frequencies have on human health.
|
Frequency (kHz) |
Decibel Limits Proposed By: |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Japan |
USSR |
Sweden |
ACGIH |
Canada |
European Union |
|
|
8 |
90 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
10 |
90 |
- |
- |
105 |
- |
- |
|
12.5 |
90 |
75 |
- |
105 |
- |
- |
|
16 |
90 |
85 |
- |
105 |
75 |
- |
|
20 |
110 |
110 |
105 |
105 |
75 |
105 |
|
25 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
105 |
|
31.5 |
110 |
110 |
115 |
115 |
110 |
115 |
|
40 |
110 |
110 |
115 |
115 |
110 |
115 |
|
50 |
110 |
110 |
115 |
115 |
110 |
115 |
Adapted from: Health Canada. 2008. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Ultrasound: Part II -- Industrial & Commercial Applications -- Safety Code 24.
For a detailed review of ultrasound effects on human hearing, published literature, international ultrasound standards, and recommendations for future directions, see:
Lawton, B.W. 2001. Damage to Human Hearing by Airborne Sound of Very High Frequency or Ultrasonic Frequency. Health and Safety Executive.
The report concludes: There is not sufficient data in the literature to support, or even contemplate, a dose response relation between occupational exposure to VHF noise and resultant hearing risk.
APPENDIX D--COMBINED EXPOSURE TO NOISE AND OTOTOXIC SUBSTANCES
Ototoxic substances came gradually to the attention of occupational health and safety professionals in the 1970s, when the ototoxicity of several industrial chemicals, including solvents, was recognized. The possibility of noise/solvent interaction was raised more recently, when Bergström and Nyström (1986) published the results of a 20-year epidemiological follow-up study in Sweden, started in 1958 and involving regular hearing tests in workers. Interestingly, a large proportion of workers employed in the chemicals divisions of companies suffered from hearing impairment, although noise levels were significantly lower than those in sawmills and paper pulp production. The authors suspected that industrial solvents were an additional causative factor in hearing loss.
Workers are commonly exposed to multiple agents. Physiological interactions with some mixed exposures can lead to an increase in the severity of harmful effects. This applies not only to the combination of interfering chemical substances, but also in certain cases to the co-action of chemical and physical factors. In this case, effects of ototoxic substances on ear function can be aggravated by noise, which remains a well-established cause of hearing impairment.
According to the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (2009), experiments with rats have shown that combined exposure to noise and solvents induced synergistic adverse effects on hearing. "Good evidence" has been accumulated on the adverse effects on hearing of the following solvents:
- Toluene, ethylbenzene, n-propylbenzene
- Styrene and methylstyrenes
- Trichloroethylene
- p-Xylene
- n-Hexane
- Carbon disulfide
The rat cochlea is sensitive to aromatic solvents, unlike that of the guinea pig or chinchilla (Campo et al., 1993; Cappaert et al., 2003; Davis et al., 2002; Fechter, 1993). These findings have been attributed to metabolic and other toxicokinetic differences (Campo and Maguin, 2006; Davis et al., 2002; Gagnaire et al., 2007). Because of their metabolism, rats are considered comparatively good animal models for the investigation of the ototoxic properties of aromatic solvents in humans (Campo and Maguin, 2006; Kishi et al., 1988).
Examples of relevant literature on interactions between noise and specific substances include:
- Toluene (Brandt-Lassen et al. , 2000; Johnson et al., 1988; Lataye and Campo, 1997; Lund and Kristiansen, 2008)
- Styrene (Lataye et al., 2000; Lataye et al., 2005; Mäkitie et al., 2003)
- Ethylbenzene (Cappaert et al., 2001)
- Trichloroethylene (Muijser et al., 2000)
- Carbon monoxide (Lacerda et al., 2005)
- Lead (CDC-HHE, 2011)
Lataye et al. (2005) found interactive effects of noise at 85 dB with a styrene exposure concentration of 400 parts per million (ppm)4. In general, though, high levels of noise and high concentrations of solvents were used in most of these investigations. Because of these special conditions, extrapolation to occupational exposure conditions can be challenging (Cary et al., 1997).
Investigators suggest that exposure to these solvents can provoke irreversible hearing impairment, with the cochlear hair cells (organ of Corti) being considered a target tissue for these solvents (Figure 5; Campo et al., 2007).
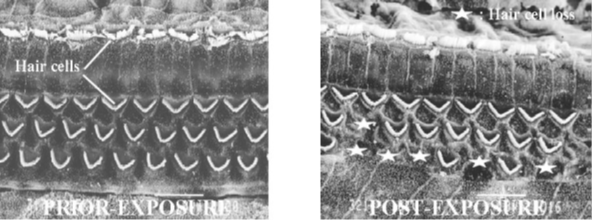
Scanning electron micrograph of a rat organ of Corti prior to (left panel) and after (right panel) toluene exposure (from European Agency for Safety and Health, 2009, as published in Lataye et al., in 1999).
Although the cochlea suffers damage, particularly during co-exposure, recent studies have reported that solvents reduce the protective role played by the middle-ear acoustic reflex, an involuntary muscle contraction that normally occurs in response to high-intensity sound stimuli. A disturbance of this reflex would allow more acoustic energy into the inner ear (Campo et al., 2007; Lataye et al., 2007; Maguin et al., 2009).
A number of epidemiological studies have investigated the relationship between hearing impairments and co-exposure to both noise and industrial solvents (Chang et al., 2003; De Barba et al., 2005; Johnson et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2005; Morata, 1989; Morata et al., 1993, 2002; Morioka et al., 2000; Prasher et al., 2005; Sliwinska-Kowalska et al., 2003, 2005). Due to confounding factors, straightforward conclusions could not easily be drawn from these studies. However, the evidence of additive or synergistic ototoxic effects due to combined exposure to noise and solvents is very strong (Lawton et al., 2006; Hoet and Lison, 2008).
A longitudinal study (Schäper et al., 2003; Schäper et al., 2008) on the relationship between hearing impairment measured by pure tone audiometry and occupational exposure to toluene and noise has not found ototoxic effects in workers exposed to a concentration of toluene lower than 50 ppm. The observed hearing loss was associated only with noise intensity. However, the use of hearing protection was not taken into account in the conclusions relative to the potential interaction between noise and toluene on hearing.
A clear relationship between solvent and hearing impairment is difficult to assess through the available epidemiological studies. The workplace environments where noise and solvents can be simultaneously present are typically complex (for example, see critical review of Lawton et al., 2006; Hoet and Lison, 2008). Quite often, the workers were exposed to multiple substances. Furthermore, most of these studies had a cross-sectional design that featured a number of weaknesses in the interpretation of the findings. For instance, chronic effects were related to currently measured exposures. In some cases, the exposure concentrations measured at the time of the study were markedly lower than those ascertained in past years (Morata et al., 1993).
All in all, there are limited data on dose-response relationships or clear effects on auditory thresholds in humans (for reviews, see Lawton et al., 2006; Hoet and Lison, 2008). However, animal data clearly show an effect. Further human studies are needed for clarification of these issues. However, in the interim, one cannot rule out a likely relationship between solvent exposure and hearing impairments.
Overall, in combined exposure to noise and organic solvents, interactive effects may be observed depending on the parameters of noise (intensity, impulsiveness, frequency, duration, etc.) and the solvent exposure concentrations. In cases of concomitant exposures, animal studies suggest that solvents might exacerbate noise-induced impairments even though the noise intensity is below the permissible limit value.
The text in this Appendix is adapted from a comprehensive review of solvent/noise interaction, published as:
European Agency for Safety and Health. 2009. Combined Exposure to Noise and Ototoxic Substances. [Reproduction of this report is authorized, provided the source is acknowledged.]
Other useful review articles on solvent noise interactions:
Campo, P. 2000. Noise and Solvent, Alcohol and Solvent: Two Dangerous Interactions on Auditory Function.
Kim, J. 2005. Combined Effects of Noise and Mixed Solvents Exposure on the Hearing Function Among Workers in the Aviation Industry. (Introduction includes a good overview of other studies on the same topic.)
Volpin, A. 2006. Interactions Between Solvents and Noise: State of the Art. (Link is to abstract.)
4To put this exposure level in perspective, 29 CFR 1910.1000, Table Z-2, lists OSHA’s 8-hour TWA PEL for styrene as 100 ppm, with a 200 ppm peak, and up to 600 ppm permitted for no more than 5 minutes in a 3-hour period.
References Cited in This Appendix
Bergström, B. and B. Nyström. 1986. Development of Hearing Loss During Long-Term Exposure to Occupational Noise--A 20-Year Follow-up Study. Scand. Audiol. 15: 227-34.
Brandt-Lassen, R., S.P. Lund, and G.B. Jepsen. 2000. Rats Exposed to Toluene and Noise May Develop Loss of Auditory Sensitivity Due to Synergistic Interaction. Noise Health 3(9): 33-44.
Campo, P. and K. Maguin. 2006. Solvent-Induced Hearing Loss: Mechanisms and Prevention Strategy. International Workshop on Health Effects of Exposure to Noise and Chemicals--Ototoxicity of Organic Solvents. Nofer Inst. of Occup. Med., Lodz, Poland, November 15-16 (conference report).
Campo, P., R. Lataye, and P. Bonnet. 1993. No Interaction Between Noise and Toluene on Cochlea in the Guinea Pig. Acta Acoust. 1: 35-42.
Campo, P., K. Maguin, and R. Lataye. 2007. Effects of Aromatic Solvents on Acoustic Reflexes Mediated by Central Auditory Pathways. Toxicol. Sci. 99(2): 582-90.
Campo, P., T.C. Morata, and O. Hong. 2013. Chemical Exposure and Hearing Loss. Disease-a-Month. 59(4): 119-138.
Cappaert, N.L., S.F. Klis, H. Muijser, B.M. Kulig, and G.F. Smoorenburg. 2001. Simultaneous Exposure to Ethylbenzene and Noise: Synergistic Effects on Outer Hair Cells. Hear. Res. 162(1-2): 67-79.
Cappaert, N.L., S.F. Klis, H. Muijser, B.M. Kulig, L.C. Ravensberg, and G.F. Smoorenburg. 2003. Differential Susceptibility of Rats and Guinea Pigs to the Ototoxic Effects of Ethyl Benzene. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 24: 503-10.
Cary, R., S. Clarke, and J. Delic. 1997. Effects of Combined Exposure to Noise and Toxic Substances--Critical Review of the Literature. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 41(4): 455-65.
CDC-HHE. 2011. Centers for Disease Control--Health Hazard Evaluation Report, Noise and Lead Exposures at an Outdoor Firing Range--California, HETA 2011-0069-3140, September.
CDC-NIOSH. 2018. Centers for Disease Control—National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Safety and Health Information Bulletin. Preventing Hearing Loss Caused by Chemical (Ototoxicity) and Noise Exposure. SHIB 03-08-2018, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2018-124.
Chang, S.J., T.S. Shih, T.C. Chou, C.J. Chen, H.Y. Chang, and F.C. Sung. 2003. Hearing Loss in Workers Exposed to Carbon Disulfide and Noise. Environ. Health Perspect. 111: 1620-24.
Davis, R.R., W.J. Murphy, J.E. Snawder, C.A. Striley, D. Henderson, A. Khan, and E.F. Krieg. 2002. Susceptibility to the Ototoxic Properties of Toluene Is Species Specific. Hear. Res. 166(1-2): 24-32.
De Barba, M.C., A.L. Jurkiewicz, B.S. Zeigelboim, L.A. De Oliveira, and A.P. Bellé. 2005. Audiometric Findings in Petrochemical Workers Exposed to Noise and Chemical Agents. Noise Health 7(29): 7-11.
European Agency for Safety and Health. 2009. Combined Exposure to Noise and Ototoxic Substances.
Fechter, L.D. 1993. Effects of Acute Styrene and Simultaneous Noise Exposure on Auditory Function in the Guinea Pig. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 15: 151-5.
Hoet, P. and D. Lison. 2008. Ototoxicity of Toluene and Styrene: State of Current Knowledge. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 38: 127-70.
Johnson, A.C., L. Juntunen, P. Nylén, E. Borg, and G. Höglund. 1988. Effect of Interaction Between Noise and Toluene on Auditory Function in the Rat. Acta Otolaryngol. 105: 56-63.
Johnson, A.C., T.C. Morata, A.C. Lindblad, P.R. Nylén, E.B. Svensson, E. Krieg, A. Aksentijevic, and D. Prasher. 2006. Audiological Findings in Workers Exposed to Styrene Alone or in Concert With Noise. Noise Health 8: 45-57.
Kishi, R., I. Harabuchi, T. Ikeda, H. Yokota, and H. Miyake. 1988. Neurobehavioural Effects and Pharmacokinetics of Toluene in Rats and Their Relevance to Man. Br. J. Ind. Med. 45: 396-408.
Lacerda A., Lerous T, Morata T. 2005. Ototoxic effects of carbon monoxide exposure: a review; Pro-Fono Revista de Atualizacao Cientifica, Barueri (SP), v. 17, n.3, p. 403-412, set.-dez.
Lataye, R. and P. Campo. 1997. Combined Effects of a Simultaneous Exposure to Noise and Toluene on Hearing Function. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 19: 373-82.
Lataye, R., P. Campo, and G. Loquet. 2000. Combined Effects of Noise and Styrene Exposure on Hearing Function in the Rat. Hear. Res. 139: 86-96.
Lataye, R., P. Campo, G. Loquet, and G. Morel. 2005. Combined Effects of Noise and Styrene on Hearing: Comparison Between Active and Sedentary Rats. Noise Health 7(27): 49-64.
Lataye, R., K. Maguin, and P. Campo. 2007. Increase in Cochlear Microphonic Potential After Toluene Administration. Hear. Res. 230(1-2): 34-42.
Lawton, B.W., J. Hoffmann, and G. Triebig. 2006. The Ototoxicity of Styrene: a Review of Occupational Investigations. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 79: 93-102.
Loquet, G., P. Campo, and R. Lataye. 1999. Comparison of Toluene-Induced and Styrene-Induced Hearing Losses. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 21(6): 689-97.
Lund, S.P. and G.B. Kristiansen. 2008. Hazards to Hearing from Combined Exposure to Toluene and Noise in Rats. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 21(1): 47-57.
Maguin, K., P. Campo, and C. Parietti-Winkler. 2009. Toluene Can Perturb the Neuronal Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channels Involved in the Middle-Ear Reflex. Toxicol. Sci. 107(2): 473-81.
Mäkitie, A.A., U. Pirvola, I. Pyykkö, H. Sakakibara, V. Riihimäki, and J. Ylikoski. 2003. The Ototoxic Interaction of Styrene and Noise. Hear. Res. 179(1-2): 9-20.
Morata, T.C. 1989. Study of the Effects of Simultaneous Exposure to Noise and Carbon Disulfide on Workers' Hearing. Scand. Audiol. 18: 53-8.
Morata, T.C., D.E. Dunn, L.W. Kretschmer, G.K. Lemasters, and R.W. Keith. 1993. Effects of Occupational Exposure to Organic Solvents and Noise on Hearing. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 19: 245-54.
Morata, T.C., A.C. Johnson, P. Nylen, E.B. Svensson, J. Cheng, E.F. Krieg, A.C. Lindblad, L. Ernstgard, and J. Franks. 2002. Audiometric Findings in Workers Exposed to Low Levels of Styrene and Noise. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 44: 806-14.
Morioka, I., N. Miyai, H. Yamamoto, and K. Miyashita. 2000. Evaluation of Combined Effect of Organic Solvents and Noise by the Upper Limit of Hearing. Ind. Health. 38(2): 252-7.
Muijser, H., J.H. Lammers, and B.M. Kullig. 2000. Effects of Exposure to Trichloroethylene and Noise on Hearing in Rats. Noise Health 2(6): 57-66.
Prasher, D., H. Al-Hajjaj, S. Aylott, and A. Aksentijevic. 2005. Effect of Exposure to a Mixture of Solvents and Noise on Hearing and Balance in Aircraft Maintenance Workers. Noise Health 7(29): 31-9.
Schäper, M., P. Demes, M. Zupanic, M. Blaszkewicz, and A. Seeber. 2003. Occupational Toluene Exposure and Auditory Function: Results From a Follow-up Study. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 47: 493-502S.
Schäper, M., A. Seeber, and C. van Thriel. 2008. The Effects of Toluene Plus Noise on Hearing Thresholds: an Evaluation Based on Repeated Measurements in the German Printing Industry. Int .J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 21: 191-200.
Sliwinska-Kowalska, M., E. Zamyslowska-Szmytke, W. Szymczak, P. Kotylo, M. Fiszer, W. Wesolowski, and M. Pawlaczyk-Luszczynska. 2003. Ototoxic Effects of Occupational Exposure to Styrene and Co-exposure to Styrene and Noise. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 45: 15-24.
Sliwinska-Kowalska, M., E. Zamyslowska-Szmytke, W. Szymczak, P. Kotylo, M. Fiszer, W. Wesolowski, and M. Pawlaczyk-Luszczynska. 2005. Exacerbation of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss by Co-exposure to Workplace Chemicals. Environ. Tox. Pharmacol. 19: 547-53.
APPENDIX E--HISTORICAL ANALYSIS OF AFFECTED INDUSTRIES AND JOBS
1. Affected Industries
About IMIS Data
In reviewing IMIS data, note that the exposure levels are not necessarily typical of all worksites and occupations within an industry. Rather, IMIS provides insight regarding the noise exposure levels for workers in the jobs that OSHA monitored while visiting workplaces. Typically, OSHA identified those jobs as having some potential for noise exposure.
Workplace noise exposure is widespread. Historical analysis of OSHA's Integrated Management Information System (IMIS) data for 1979 through 2006 showed that workers were exposed to hazardous noise levels in every major industry sector.
Tables E-1 through E-4 summarize the noise measurements obtained by OSHA in each major industry sector1. These tables also present the median noise levels and the percentage of noise measurements over either the action level (AL), 85 dBA, or the permissible exposure limit (PEL), 90 dBA2. The data appear in separate tables because OSHA uses different criteria for the AL and PEL (see Section III.A.4). Each noise measurement entered into IMIS is related to either the AL or the PEL, depending on the threshold level designated during dosimeter setup.
OSHA obtained the vast majority of IMIS noise exposure samples in manufacturing facilities. Manufacturing is among the loudest industries, with 43% of the IMIS noise samples exceeding the PEL of 90 dBA TWA. In addition, 47% of the samples taken in the construction industry exceeded the PEL. The IMIS exposure records for the manufacturing industry are presented by three-digit North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) codes in two tables (Tables E-3 and E-4) (relative to the AL and PEL, respectively).
In addition to median dBA and percent over the PEL, Table E-4 shows the distribution of manufacturing industry dosimetry measurements at the PEL and higher (by dBA level).
|
Industry |
Total Records |
Median dBA |
% Over the AL |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Agriculture |
206 |
86.8 |
64% |
|
Utilities |
396 |
82.8 |
36% |
|
Mining |
40 |
88.0 |
78% |
|
Construction |
1,382 |
86.9 |
62% |
|
Manufacturing |
80,120 |
87.3 |
67% |
|
Wholesale/retail |
2,908 |
85.6 |
54% |
|
Transportation |
1,190 |
82.6 |
36% |
|
Finance |
71 |
78.2 |
27% |
|
Services |
5,107 |
83.9 |
44% |
|
All other private sector |
34 |
90.6 |
88% |
|
Government |
935 |
83.7 |
44% |
|
Industry |
Total Records |
Median dBA |
% Over the PEL |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Agriculture |
354 |
86.8 |
33% |
|
Utilities |
513 |
81.2 |
19% |
|
Mining |
56 |
85.6 |
27% |
|
Construction |
3,133 |
89.2 |
47% |
|
Manufacturing |
116,983 |
88.7 |
43% |
|
Wholesale/retail |
3,342 |
86.7 |
33% |
|
Transportation |
1,261 |
80.9 |
16% |
|
Finance |
88 |
75.2 |
15% |
|
Services |
5,167 |
83.2 |
23% |
|
All other private sector |
231 |
89.8 |
47% |
|
Government |
822 |
82.3 |
23% |
|
NAICS |
NAICS Title |
Total Records |
Median dBA |
% Over the AL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
311 |
Food Manufacturing |
6,100 |
88.6 |
79% |
|
312 |
Beverage and Tobacco Product Manufacturing |
34 |
87.4 |
85% |
|
314 |
Textile Product Mills |
1,749 |
87.3 |
69% |
|
315 |
Apparel Manufacturing |
817 |
82.7 |
36% |
|
316 |
Leather and Allied Product Manufacturing |
406 |
86.6 |
61% |
|
321 |
Wood Product Manufacturing |
9,836 |
89.3 |
79% |
|
322 |
Paper Manufacturing |
2,879 |
86.9 |
65% |
|
323 |
Printing and Related Support Activities |
2,256 |
84.1 |
43% |
|
324 |
Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing |
217 |
86.3 |
57% |
|
325 |
Chemical Manufacturing |
1,762 |
85.6 |
54% |
|
326 |
Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing |
6,381 |
86.4 |
61% |
|
327 |
Nonmetallic Mineral Product Manufacturing |
4,034 |
87.0 |
63% |
|
331 |
Primary Metal Manufacturing |
6,306 |
89.3 |
80% |
|
332 |
Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing |
15,248 |
87.6 |
69% |
|
333 |
Machinery Manufacturing |
7,514 |
85.5 |
53% |
|
334 |
Computer and Electronic Product Manufacturing |
219 |
85.0 |
50% |
|
335 |
Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing |
2,679 |
85.8 |
57% |
|
336 |
Transportation Equipment Manufacturing |
5,660 |
87.4 |
67% |
|
337 |
Furniture and Related Product Manufacturing |
3,867 |
86.8 |
64% |
|
339 |
Miscellaneous Manufacturing |
2,156 |
85.6 |
55% |
|
NAICS |
NAICS Title |
Total Records |
Median dBA |
% Over the PEL |
% Noise Measurements in dB Range |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
90 to 94 dB |
95 to 100 dBA |
100 to 104 dBA |
105 dBA+ |
|||||
|
311 |
Food Manufacturing |
9,070 |
89.5 |
47% |
34% |
11% |
2% |
0% |
|
312 |
Beverage and Tobacco Product Manufacturing |
40 |
85.6 |
25% |
25% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
|
314 |
Textile Product Mills |
2,790 |
89.4 |
47% |
31% |
11% |
4% |
1% |
|
315 |
Apparel Manufacturing |
828 |
81.3 |
12% |
9% |
4% |
0% |
0% |
|
316 |
Leather and Allied Product Manufacturing |
551 |
89.7 |
48% |
35% |
11% |
2% |
0% |
|
321 |
Wood Product Manufacturing |
16,330 |
91.7 |
60% |
30% |
22% |
7% |
1% |
|
322 |
Paper Manufacturing |
4,344 |
87.9 |
38% |
28% |
8% |
1% |
0% |
|
323 |
Printing and Related Support Activities |
2,620 |
82.2 |
17% |
15% |
2% |
0% |
0% |
|
324 |
Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing |
376 |
86.7 |
27% |
22% |
5% |
1% |
0% |
|
325 |
Chemical Manufacturing |
2,611 |
85.2 |
24% |
18% |
5% |
1% |
0% |
|
326 |
Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing |
7,627 |
86.1 |
30% |
21% |
6% |
2% |
0% |
|
327 |
Nonmetallic Mineral Product Manufacturing |
5,772 |
88.4 |
41% |
26% |
10% |
4% |
1% |
|
331 |
Primary Metal Manufacturing |
13,196 |
91.3 |
58% |
34% |
19% |
5% |
1% |
|
332 |
Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing |
20,549 |
88.9 |
44% |
27% |
13% |
3% |
1% |
|
333 |
Machinery Manufacturing |
10,156 |
86.2 |
31% |
21% |
8% |
2% |
0% |
|
334 |
Computer and Electronic Product Manufacturing |
360 |
85.3 |
29% |
23% |
6% |
1% |
0% |
|
335 |
Electrical Equipment, Appliance, and Component Manufacturing |
3,889 |
86.5 |
32% |
22% |
8% |
2% |
0% |
|
336 |
Transportation Equipment Manufacturing |
7,812 |
88.4 |
41% |
24% |
12% |
4% |
1% |
|
337 |
Furniture and Related Product Manufacturing |
5,292 |
87.8 |
38% |
27% |
9% |
2% |
0% |
|
339 |
Miscellaneous Manufacturing |
2,770 |
86.8 |
35% |
24% |
8% |
3% |
0% |
1 This period encompasses the entire IMIS record for noise through 2006. The data were first inspected, and individual records with internal inconsistencies were removed. One example of an inconsistency is a record coded as a personal noise result with units other than dB or percentage dose (e.g., a value coded as a noise result with units inadvertently entered as mg/m3 would have been removed before analysis). The final dataset contained 224,339 personal noise exposure records.
2 Please note that workplace sampling is required, and the historical data displayed should not be used to justify whether or not to monitor for overexposure to noise.
2. Historically Affected Jobs in General Industry
Noise is a potential hazard for most jobs that involve abrasive or high-power machinery, impact of rapidly moving parts (product or machinery), or power tools. According to IMIS noise measurements, workers in certain occupations within specific industries are exposed to excessive noise more frequently than others. While many jobs have noise exposure, historically, some of the occupations with the most extreme exposures (listed by Standard Industrial Classification, or SIC) have included:
-
SIC 20 and 21 (food, beverages, and tobacco industry): slaughterers and meat packers.
-
SIC 22, 23, and 31 (textile, apparel, and leather industry): textile winders, shoe and leather workers and repairers, textile knitting and weaving machine operators.
-
SIC 24 (lumber and wood products industry, including logging and lumber mill operations): most occupations (except cabinetmakers).
-
SIC 25 (furniture and fixtures industry): machine feeders.
-
SIC 26 (paper and paper industry): paper goods machine operators.
-
SIC 28 through 30 (printing and publishing, chemicals and petroleum, and plastics and rubber industries): chemical equipment operators (SIC 28 and 29), laborers and freight movers (SIC 28 and 29), grinding machine operators (SIC 30), and helpers (SIC 30).
-
SIC 32 (nonmetallic minerals industry): inspectors, testers, and sorters; extruding, forming, and pressing machine operators; hoist and winch operators; unspecified "operators."
-
SIC 33 and 34 (primary metal and fabricated metal products industries): forging machine operators, grinding and lapping machine operators, and welders.
-
SIC 35 through 39 (various equipment manufacturers): milling and planing machine operators, coil winders and tapers, forging machine operators, grinding and lapping machine operators, and abrasive blasters.
3. Summary of Construction Industry Noise Exposure by Trade and Activity
Research conducted by the University of Washington provided information on noise exposures in the construction industry. This data is provided in Tables E-5 and E-6 below.
|
Trades Monitored |
Number of Measurements |
OSHA TWA Mean dBA |
OSHA TWA Percent >90 dBA |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Brick/Tile Worker |
28 |
75.2 |
8 |
|
Bricklayer |
15 |
83.8 |
4 |
|
Carpenter |
82 |
82.3 |
11 |
|
Cement Mason |
26 |
78.9 |
10 |
|
Electrician |
208 |
80.0 |
4 |
|
Insulation Worker |
22 |
74.5 |
5 |
|
Iron Worker |
59 |
82.1 |
10 |
|
Laborer |
58 |
83.3 |
14 |
|
Operating Engineer |
44 |
83.5 |
14 |
|
Sheet Metal Worker |
38 |
80.4 |
0 |
Source: Adapted from Seixas and Neitzel, 2002. (Submittal to OSHA's Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking Docket H-011G).
|
TRADE |
Average dBA for Each Task Event |
TRADE |
Average dBA for Each Task Event |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Operating work vehicle |
80.1 |
Wood framing |
91.0 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
87.8 |
Building forms |
92.9 |
|
Shop work |
88.8 |
Stripping forms |
94.8 |
|
Interior finish |
89.4 |
Welding |
94.9 |
|
Manual material handling |
89.4 |
"Other" tasks |
95.3 |
|
Layout |
90.5 |
- |
- |
|
Floor leveling |
70.4 |
Placing concrete |
87.8 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
83.3 |
Repairing concrete |
88.9 |
|
Finishing concrete |
84.4 |
Patching concrete |
92.6 |
|
Setting forms |
86.5 |
"Other" tasks |
93.1 |
|
Manual material handling |
86.5 |
Grinding |
95.2 |
|
Operating work vehicle |
79.2 |
Installing slab conduit |
91.0 |
|
Sheet metal work |
81.6 |
Installing wall conduit |
91.1 |
|
Manual material handling |
86.5 |
Installing cable tray |
91.8 |
|
Panel wiring, installing fixtures |
87.0 |
Pulling wire |
95.6 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
87.0 |
Installing trench conduit |
95.8 |
|
"Other" tasks |
90.5 |
- |
- |
|
Sheet metal work |
77.8 |
"Other" tasks |
83.4 |
|
Applying insulation by hand |
83.0 |
Manual material handling |
84.6 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
83.3 |
- |
- |
|
Operating forklift |
87.1 |
Manual materials handling |
94.3 |
|
Setting forms |
87.9 |
"Other" tasks |
94.7 |
|
Operating work vehicle |
88.5 |
Tying and placing rebar |
95.5 |
|
Erecting iron |
91.8 |
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
95.6 |
|
Grinding |
91.9 |
Welding and burning |
98.4 |
|
Rigging |
93.6 |
Laying metal deck |
99.6 |
|
Bolt up |
93.7 |
- |
- |
|
Layout |
80.1 |
Placing concrete |
91.5 |
|
Manual material handling |
82.7 |
Stripping forms |
91.7 |
|
Interior finish |
85.2 |
Building forms |
92.1 |
|
Operating forklift |
85.3 |
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
92.3 |
|
Finishing concrete |
85.3 |
Rigging |
92.6 |
|
Grouting |
86.1 |
"Other" tasks |
95.4 |
|
Wood framing |
86.5 |
Demolition |
99.3 |
|
Floor leveling |
87.5 |
Chipping concrete |
102.9 |
|
MASONRY TRADES |
|||
|
Bricking, blocking, tiling |
90.2 |
Manual material handling |
88.4 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
86.4 |
"Other" tasks |
94.4 |
|
Forklift operation |
88.5 |
Pointing, cleaning, caulking |
91.6 |
|
Grinding |
97.0 |
Weatherproofing |
84.2 |
|
Grouting, tending, mortaring |
91.4 |
Work vehicle operation |
96.3 |
|
Break, rest, lunch, cleanup |
85.7 |
Layout |
89.3 |
|
Rigging |
86.6 |
Grade checking |
89.6 |
|
"Other" tasks |
86.9 |
Welding |
91.2 |
Source: Adapted from Seixas and Neitzel, 2004.
APPENDIX F--NOISE REDUCTION RATING
Noise Reduction Ratings
When OSHA promulgated its Hearing Conservation Amendment in 1983, it incorporated the EPA labeling requirements for hearing protectors (40 CFR 211), which required manufacturers to identify the noise reduction capability of all hearing protectors on the hearing protector package. This measure is referred to as the noise reduction rating (NRR). It is a laboratory-derived numerical estimate of the attenuation achieved by the protector. It became evident that the amount of protection users were receiving in the workplace with the prescribed hearing protectors did not correlate with the attenuation indicated by the NRR. OSHA acknowledged that in most cases, this number overstated the protection afforded to workers and required the application for certain circumstances of a safety factor of 50% to the NRR, above and beyond the 7 dB subtraction called for when using A-weighted measurements. For example, consider a worker who is exposed to 98 dBA for 8 hours and whose hearing protectors have an NRR of 25 dB. We can estimate the worker’s resultant exposure using the 50% safety factor. The worker’s resultant exposure is 89 dBA in this case.
The 50% safety factor adjusts labeled NRR values for workplace conditions and is used when considering whether engineering controls are to be implemented.
Estimated dBA exposure = 98 dBA - [(25-7) × 50%] = 89 dBA
However, when assessing the adequacy of the hearing protection for hearing conservation (HC) purposes, CSHOs should only subtract 7dB from the NRR.
Exposure for PPE/ HC enforcement = 98 dBA - (25-7) = 80 dBA
Single/Double Hearing Protection
Dual hearing protection involves wearing two forms of hearing protection simultaneously (e.g. earplugs and ear muffs). The noise exposure for workers wearing dual protection may be estimated by the following method: Determine the hearing protector with the higher rated NRR (NRRh) and subtract 7 dB if using A-weighted sound level data. Add 5 dB to this field-adjusted NRR to account for the use of the second hearing protector. Subtract the remainder from the TWA. It is important to note that using such double protection will add only 5 dB of attenuation. For a more extensive discussion of how to use the NRR, see the NIOSH website. NIOSH has developed guidelines for calculating and using the NRR in various circumstances (Hearing Protector Devices ). Also see 29 CFR 1910.95 Appendix B.
Methods for Estimating HPD Attenuation – Equations and Examples
Use the following formulas to estimate the attenuation afforded to a noise-exposed employee in a work environment by muffs, plugs, or a combination of both.
-
For Single Protection (either muffs or plugs):
- Determine the manufacturer’s NRR.
- Subtract the NRR from the C-weighted TWA workplace noise level, as follows:
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBC) - NRR
If C-weighted noise level data is not available, A-weighted data can be used by subtracting a 7 dB correction factor from the NRR, as follows:
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBA) - (NRR - 7)
Example:
TWA=100 dBA, muff NRR=19 dB
Estimated Exposure = 100 - (19-7) = 88 dBA
-
For Dual Protection (ear muffs and plugs used simultaneously):
- Determine the NRR for the higher rated protector (NRRh).
- Subtract 7 dB from NRRh if using A-weighted sound level data.
- Add 5 dB to the field-adjusted NRR to account for the use of the second hearing protector.
- Subtract the remainder from the TWA as follows:
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBC) - (NRRh + 5) , or
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBA) - [(NRRh- 7) + 5]
Example:
TWA=110 dBA, plug NRR=29, and muff NRR=25 dB
Estimated Exposure = 110 - [(29 - 7) + 5] = 83 dBA
When applying the 50% safety factor for estimating field attenuation (required when considering whether engineering controls are to be implemented), the above equations are modified as follows:
-
Single Protection:
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBC) - [NRR x 50%], or
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBA) - [(NRR - 7) x 50%]
-
Dual Protection:
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBC) - [(NRRh x 50%) + 5], or
Estimated Exposure (dBA) = TWA (dBA) - {[(NRRh - 7) x 50%] + 5}
APPENDIX G--EVALUATING NOISE EXPOSURE OF WORKERS WEARING SOUND-GENERATING HEADSETS
G.1 Workers at Risk
Workers can be overexposed to noise when they wear communications headsets as part of their work. Clerical personnel, aircraft pilots and other cockpit personnel, air traffic controllers, emergency personnel, reservation clerks, receptionists, and telephone operators are just a few examples of the more than 3 million workers who can be exposed to high noise levels via communications headsets. For a person wearing a sound-generating headset, the sound/noise exists predominantly between the eardrum and the headset. Because of the amplification properties of the human ear, the sound that exists inside the ear while wearing a headset is quite different from ambient levels.
Probe microphones and similar devices allow sound levels to be measured inside the ear. In addition, there are other methods that can be used to monitor these types of exposures. CSHOs can contact the OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center, Health Response Team, for more information and assistance.
G.2 Acoustic Limited Devices
Laboratory evaluations have determined that headsets can be categorized in two basic groups:
- Those without any form of electronic limiting device.
- Those with some form of limiting device built into the headset.
Most modern telecommunication headsets use sophisticated limiting circuits. Some personal audio headsets also have this capability. Headsets with acoustic limiting devices that are functioning as designed have been shown, in both laboratory and field tests, to provide enough protection to keep worker noise exposures below OSHA permissible noise levels. In some work environments, however, headsets without limiting devices have caused worker noise exposures to exceed the levels permitted by OSHA.
For more information, see OSHA's letter of interpretation dated 4/14/1987-- Use of Walkman Radio, Tape, or CD Players and Their Effect When Hearing Protection is in Use.
APPENDIX H--ECONOMIC FEASIBLITY ANALYSIS OF NOISE ENGINEERING CONTROLS
Several sources have offered detailed methods for evaluating the feasibility of engineering controls for noise. These methods involve diverse interpretations of how the costs of noise exposure are calculated, based on the individual needs of the organization for which the method was developed. They also include various additional steps and tools to help refine the organization's priorities or to help standardize the process. This appendix reviews five possible approaches for evaluating the benefits and costs of noise control:
-
OSHA Region III
-
American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA)--Benefits and Costs of Noise Control. In: The Noise Manual (AIHA, 2003; or latest edition); in the 2003 edition, see Chapter 9, "Noise Control Engineering"
-
Additional detail: Driscoll, "The Economics of Noise Control Engineering Versus the Hearing Conservation Program"
-
Example: Colgate-Palmolive, winner, 2012 Safe-in-Sound award
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)--Buy-Quiet Roadmap
Note that other methods for performing economic feasibility analyses may be available, and CSHOs should refer to regional/national office enforcement personnel for guidance, as necessary.
H.1 OSHA Region III
Note on Costs
Dollar amounts quoted in this section are relative estimates, used as examples to demonstrate methods for determining whether implementing a hearing conservation program or engineering controls is more economical. Actual costs will vary based on factors such as location, availability of supplies, and varying cost inflation. The CSHO should investigate local costs in situations where the relative cost differential is close, as determined following this procedure.
In 2001, OSHA Region III produced an instruction on conducting economic feasibility evaluations for noise-control engineering. This instruction (Directive Number STD 104.1A) was based in part on information published in the Regulatory Impact and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis of the Hearing Conservation Amendment, OSHA Office of Regulatory Analysis, February 1983.
This section presents information adapted from the Region III instruction. The assumptions and tables contain examples of approximate costs and other related information. This information is used here to demonstrate (through examples) some simple methods that CSHOs can use when considering economic feasibility of engineering controls compared to a hearing conservation program. The numbers used in these assumptions, tables, and examples should be refined as appropriate for each inspection and locality.
H.1.1 Assumptions for an Economic Analysis
To perform an economic analysis efficiently and realistically, several assumptions need to be made:
Assumption 1: If actual life expectancy of equipment is known to the CSHO, then it should be used. If unknown, assume the life expectancy of durable-equipment engineering noise control is 10 years. Regardless of the source of the life expectancy figure, use it to determine the average cost per year (i.e., total lump sum upfront costs for equipment divided by years of life expectancy).
Assumption 2: If actual costs for an engineering control are known to the CSHO, then they should be used. If costs for an item listed in Table H.1-2 are unknown, the average cost in Table H.1-2 shall be used for cost estimating.
Assumption 3: The maintenance cost for an engineering control shall not exceed 5% of the initial cost per year over a 10-year time span (based on guidance from the Office of the President of the United States, OMB).
Assumption 4: If actual maintenance costs for an engineering control are known to the CSHO, then they should be used. If unknown, then the percentage given in Table H.1-2 shall be used for cost estimating.
Assumption 5: The least expensive control option or group of controls that will achieve a reduction of 3 dBA or more in worker exposure shall be used for determining economic feasibility.
Assumption 6: An engineering or administrative control is economically feasible if its total cost is less than or equal to the cost of a continuing effective hearing conservation program for all the workers who would benefit from the control's implementation (i.e., have a reduction in their noise exposure).
Assumption 7: If actual costs of administrative controls are known to the CSHO, then they should be used. Where administrative controls are feasible but the costs are unknown, no additional costs will be assumed for cost estimation purposes.
Assumption 8: If the actual cost of a production penalty for a control option is known to the CSHO, then it should be used. If unknown, no production penalty will be assumed for cost estimation purposes.
Assumption 9: If a proposed noise control would also address another hazard (e.g., machine guarding, local exhaust ventilation, etc. hood), then the cost of the noise control shall be deemed feasible because these other controls do not require an economic feasibility analysis.
Assumption 10: If actual hearing conservation program costs are known to the CSHO, then they should be used. If unknown, use an assumed figure of $375/worker/year (the average of the range provided in Appendix G.1.2 of this chapter). If applicable, use Table H.1-1 to adjust this unit cost based on the number of workers in the hearing conservation program at this worksite.
Assumption 11: Maintenance problems (e.g., bad bearings, steam leaks) that result in excessive workplace noise levels are cited under the engineering/administrative control paragraph; however, these are deemed economically feasible regardless of the cost.
Assumption 12: If engineering design for noise controls is done by the employer's engineering or industrial hygiene staff, then there will be no additional engineering costs applied to the control. In this case, the Table H.1-2 values will determine the costs of an engineering control.
Assumption 13: If outside or consulting engineering services are required to design and fine tune the control, then these costs must be estimated and added to Table H.1-2 values. For cost estimation, the hourly rate for a consulting acoustical engineer is assumed to be $150 (2010 dollars). The daily rate is assumed to be $1,000. Assume that the consulting engineer is local, and therefore, no travel or per diem costs need be considered. For each day in the field, it is customary for a consulting engineer to charge one additional day for report/plan preparation.
H.1.2 General Principles
An engineering control is any physical alteration in the workplace that will reduce occupational noise exposure. An administrative control is any manipulation of the worker's work schedule, procedure, or practice that will result in a reduction in the daily noise dose.
H.1.3 Examples
Note on Noise Evaluation Threshold
This example (Dusty Foundry) can also be used to demonstrate another topic: when different noise measurement thresholds are appropriate.
In this example the noise evaluations that determined the employees' exposure were intended to identify employees who needed to be included in the hearing conservation program.
Therefore, the measurements would have been made with the 80-dBA threshold (and if a citation were to be issued, the daily dose would have to be greater than or equal to 66% of the PEL).
In contrast, if the evaluation had been intended to demonstrate compliance with the PEL or the need for engineering controls, the 90-dBA threshold would have been appropriate (and if a citation were to be issued, the daily dose would have had to be greater than or equal to 132 percent of the PEL).
The following examples will serve to illustrate how and when economic feasibility determination is necessary.
-
Dusty Foundry
There are 100 production workers exposed in excess of 50% of the PEL.
-
What is the cost of a hearing conservation program per worker for this foundry? From Assumption 10 and Table H.1-1, we have:
$375 x .05 + $375 = $19 + $375 = $394
Therefore, the cost of a hearing conservation program per worker at this foundry is $394.
-
In the cleaning department, five workers polish small castings using hand-held pneumatic polishing tools. Seven additional workers at other tasks along the same wall in the cleaning department are similarly exposed to noise from the polishing tools. There are no engineering controls. The daily noise dose is 89 dBA to 93 dBA on the sampled workers. There are two shifts in this department. The polishers are side-by-side and place the castings on wooden work tables. The background noise when no one is using the pneumatic tools is 79 dBA. You determine that retrofit mufflers, barriers between adjacent polishers, and absorptive treatment to the cement block wall in front of the polishing tables will result in a noise reduction of 9 dBA to 11 dBA at the worker's ear. In this case, the retrofit mufflers and sound absorbers and barriers are expendable and replaced every year. Are these controls economically feasible, given that the 8-hour TWA is less than 100 dBA?
-
Determine the cost of the pneumatic mufflers (i.e., small air exhaust muffler for a pneumatic hand tool). From Table H.1-2, the unit cost of such a muffler is $16.00 (average of high and low cost) with no maintenance or production penalty involved. In this case, the retrofit mufflers and sound absorbers and barriers are expendable and replaced every year. Therefore:
$16.00 x 5 grinders = $80
-
Determine the cost of the absorbers and barriers. Five 4 x 4 foot areas of acoustical absorption are needed as well as three 8 x 8 foot barriers. Two workers will require 1.5 days (12 hours) to perform the installation. There would be no production penalty, and maintenance costs can be considered to be negligible. Therefore:
80 sq. ft. absorption x $6 = $480
192 sq. ft. barriers x $15 = $2,880
Installation labor: 2 workers x 12 hours x $27/hour = $648.
-
Determine the total cost of engineering controls:
Add the cost of the mufflers, acoustic absorbers, barriers, and installation.
80 + 480 + 2,880 + 648 = $4,088
-
Determine the cost of hearing conservation for all workers who would benefit from these controls:
Adjust the hearing conservation cost per worker (Table H.1-1) and multiply that cost by the number of workers (12).
12 workers x 2 shifts x $394 = $9,456
Given that the cost of engineering controls ($4,088) is less than the cost of hearing conservation ($9,456), these controls are both technically and economically feasible.
-
-
In the shakeout area, full-shift noise levels are 98 dBA to 100 dBA. Four workers are employed here for each of two shifts. Silica exposures for these workers are 3 to 4 times the PEL, given that there is no local exhaust ventilation provided. We propose a total enclosure of the shakeout that will be locally exhausted, mechanically isolated from the shaker table, and lined with some acoustically absorptive material. This control approach, if properly implemented, will reduce the noise exposures to 90 dBA and the silica exposures to one-quarter of the PEL. Given that the daily noise levels do not exceed 100 dBA, is enclosure of the shakeout economically feasible?
Because this engineering control will abate both silica and noise overexposures at the same time, an economic analysis is not necessary. This control, therefore, is both economically and technically feasible.
-
In the finishing department, two pedestal grinders were sampled for noise. Although both grinders were identical models finishing the same type of castings, one operator's exposure was 89 dBA while the other one's was 98 dBA. Further investigation revealed that the noisy grinder had defective idler bearings. Would bearing replacement be an economically feasible engineering control?
From Assumption 11, we do not need to do an economic analysis for bearing replacement on this pedestal grinder because the noise is from the defective idle bearings, which need to be replaced to keep the equipment in good working order. Therefore, this control is economically feasible and should be cited as a violation of (b)(1).
-
To abate engineering violations, Dusty Foundry must engage a consulting engineer. Consider problem 2.b and 2.c above. Dusty Foundry will need one day with the engineer on site to evaluate and prepare an abatement report. The cost for engineering will be:
$1,000 x 1 days = $1,000
$1,000 + $4,088 (cost of controls) = $5,088
Therefore, the total cost for these controls with consulting engineering assistance is $5,088, which is still less than the cost of hearing conservation ($9,456). The engineering controls are still economically feasible.
-
-
Rocking Chair Furniture Company
The company has 100 production workers exposed to daily noise exposures in excess of 50% of the PEL. (Note: If a citation will be issued, the daily dose must be greater than or equal to 66% of the PEL).
-
A large wood planer is situated in the middle of the production area. A loader and off-bearer operate the machine. It has no noise controls. The sound levels vary from 98 dBA to 118 dBA depending on the type of wood (hard versus soft) and the surface area of the wood being finished. All production workers are exposed to the noise from the machine. Administrative controls limit everybody's daily dose to less than 400%, or 100 dBA. Are engineering controls economically feasible?
-
The equipment manufacturer, contacted by phone, indicates that one engineering option is to rebuild the drive mechanism and replace the cutters with those of a helical design. According to the manufacturer's technical representative, this will greatly improve the quality of the planed finish and reduce the noise level to about 90 dBA. With the existing administrative controls, everybody's daily exposure level would be reduced to less than 84 dBA. A call to the regional service technician produced a cost figure of $10,000 per planer to retrofit, with no maintenance or production penalty involved.
Per Assumption 7, the administrative controls contribute no additional cost. The total cost is $10,000 for major modifications to one planer. Per Assumption 1, this engineering control has a life expectancy of 10 years, so the average cost per year is $1,000.
-
A second engineering option is to enclose the existing planer with a plywood shop-built structure lined with sound-absorbing fiberglass (this design has no production penalty and a life expectancy of 10 years). Three workers will work together for 10 hours to install the enclosure, for a total of 30 hours. This option reduces the workers' exposure to a similar extent as would modifying the planer as described above. From Table H.1-2, we select the lower cost of $4,000, as the enclosure can be fabricated in-plant. Table H.1-2 also indicates that the enclosure will have a 5% maintenance cost. Table H.1-2 indicates that the labor rate is $27 per hour, so the total cost will be the cost of control + maintenance at 5% over 10 years + installation labor, thus:
$4,000 + $ 2,000 + $810 = $6,810 total assumed cost.
Per Assumption 1, this engineering control has a life expectancy of 10 years, so the average cost per year is $6,810 ÷ 10 = $681.
Considering that all 100 workers will benefit from the implementation of this engineering control, the assumed cost for hearing conservation is calculated from Table H-1.1 with a 5% increase in the cost of the hearing conservation program, based on 100 workers participating:
($375 x .05) + $375 = $394 per worker per year
$394 x 100 workers = $39,400 per year for all 100 worker
Given that the engineering option cost per year is less than the cost per year of a hearing conservation program, the engineering option is economically feasible.
-
-
Consider the situation where the planer has been relocated to a room by itself. The room is treated with acoustical material to prevent reflected or reverberant noise. Both workers who operate the planer are administratively controlled to prevent their noise doses from exceeding 100 dBA. The planer is operated on the second shift only. The employer's records indicate that the hearing conservation program costs a little more than the initial estimate: an average of $419 per year per worker. Are either of the two engineering control options for the planer described in the previous paragraphs economically feasible?
The per-worker cost of hearing conservation is:
$419 x 2 = $938 per year for hearing conservation.
This cost for hearing conservation is compared to the per-year cost of the two engineering options: rebuild and upgrade the planer at an average cost per year of $1,000, or construct an enclosure around the planer within the room at an average cost per year of $681.
Since the $681 cost per year of constructing an enclosure is less than the $938 cost per year of the hearing conservation program, this engineering option is economically feasible.
-
-
Tables for Economic Analysis Examples
Tables H.1-1 and H.1-2 provide background information used in the examples for economic feasibility determinations.
|
Total Number of Workers at the Same Geographic Location |
Percent Increase per Worker per Year Over the Unit Cost |
Resulting Calculation per Worker per Year (With Unit Cost at $375) |
|---|---|---|
|
250+ |
0 |
($375 x 0) + $375 = $375 |
|
100-249 |
5 |
($375 x .05) + $375 = $394 |
|
50-99 |
8 |
($375 x .08) + $375 = $405 |
|
20-49 |
75 |
($375 x .75) + $375 = $656 |
|
0-19 |
125 |
($375 x 1.25) + $375 = $844 |
References for Table H.1-1 data were adapted from Table 7 in Regulatory Impact and Regulatory Flexibility Analysis of the Hearing Conservation Amendment, USDOL-OSHA, Office of Regulatory Analysis, February 1983. The example unit cost ($375/worker) for a hearing conservation program in 2010 dollars is the midpoint in the cost range of $350 to $400 described previously.
|
Control Option |
dBA Reduction |
Cost (in 2010 $) |
Percent Production Penalty |
Maintenance Cost per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Absorption |
3-5 |
2-10/ft2 |
None |
2% |
|
Damping materials |
2-20 |
2-6/ft2 |
None |
None |
|
Damping pad |
2-20 |
10-20/ft2 |
None |
None |
|
Damping compound |
2-20 |
180-250/5 gallon pail |
None |
None |
|
Acoustic barriers |
3-15 |
5-25/ft2 |
None |
2% |
|
Mufflers, air exhaust (small) |
5-25 |
2-30/unit |
None |
None |
|
Mufflers, air exhaust (large) |
5-25 |
10-600/unit |
None |
5% |
|
Mufflers, engine (average) |
5-25 |
300/unit |
None |
None |
|
Mufflers, engine (very large) |
5-25 |
10,000/unit |
None |
None |
|
Silencers, small fan |
5-25 |
300/unit |
None |
None |
|
Silencers, large fan |
5-25 |
3,000-25,000/unit |
None |
None |
|
Vibration mounts |
5-25 |
100-1,000/unit |
None |
1% |
|
Quiet valves |
5-25 |
500-5,000/unit |
None |
None |
|
Cab enclosure (for heavy equipment) |
5-20 |
15,000/unit |
None |
5% |
|
Enclosure for multiple workers |
5-20 |
5,000-35,000/unit |
None |
5% |
|
Enclosure for process (partial) |
3-10 |
500-3,500/unit |
0-20 |
5% |
|
Enclosure for process (total) |
3-10 |
4,000-35,000/unit |
0-20 |
5% |
|
Duct wrap/lagging |
3-5 |
5-300/100 ft |
None |
None |
|
Ceiling baffles |
Rated in Sabens: NRC of 0.4-0.5 |
2-15/ft2 |
None |
None |
Note 1: Costs presented here were updated by contacting manufacturers for pricing over the period from May 2010 to April 2012.
Note 2: Installation costs are not included. According to data from the BLS, an average labor rate of $27/hour (2010 rate) could be assumed when considering installation costs (regional rates could be more or less).
Sources: BLS, 2009a,b.
When additional information is on hand, the CSHO may also make an informed decision about using the low or high end of the cost range (instead of the average). Select the high end of the cost range for larger sizes of equipment, materials with extra thickness, situations that require high-precision or specialty parts, locations with higher costs of living, or when other factors tip the selection toward the more costly option.
H.2 AIHA--Benefits and Costs of Noise Control
General Guidelines:
General guideline 1: Most organizations will find that hearing conservation program costs average $350 to $400 per program participant per year.
General guideline 2: Workers' compensation costs for hearing loss average about 0.2% of payroll. (Workers' compensation averages about 2% of payroll; 10% percent of that is associated with hearing loss compensation.)
General guideline 3: Reducing compressed air pressure and volume used can reduce noise levels substantially and can also save on energy costs. It is almost always cost-effective. Other good opportunities for noise reduction are associated with routine maintenance and machine guarding (why not build in noise reduction at the same time?).
General guideline 4: "As a criteria for an acoustical maintenance program, each machine should typically operate within 2 dBA of the minimum sound level of which it is optimally capable."
Sources: Driscoll, 2010, 2012.
In The Noise Manual, Chapter 9, AIHA outlines a procedure for comparing the benefits and costs of noise control (Driscoll and Royster, 2003).
The AIHA chapter recognizes that employers wonder:
"What magnitude of noise reduction in the employees' TWA is possible, and is it worth doing?" That is, if an employee's TWA can be reduced by 3 dBA using noise control, should it be achieved?
The chapter encourages the reader to consider the potential magnitude of noise reduction and then prioritize efforts using a series of steps.
The first step is identifying realistic short- and long-term goals. A short-term goal could be to reduce the noise exposure of the most highly exposed workers to a level that makes it easier to protect them (e.g., with administrative controls or personal protective equipment). A long-term goal could be to reduce all noise exposure to nonhazardous levels, which can result in cost savings by eliminating the need for hearing conservation programs and additional worker compensation expenses.
To set priorities, AIHA suggests that important considerations include:
-
The number of workers affected by the noise source or sources.
-
The potential for the noise to significantly damage their hearing.
-
The characteristics of the noise, which can affect the control options. (Is it a pure tone? Impulse noise?)
-
How likely it is that the intervention will succeed in meeting the organization's goals.
-
Whether the control method will increase, decrease, or have a neutral effect on productivity.
-
The estimated cost of the control, including purchase, installation, and maintenance.
Promoting a systematic evaluation, AIHA offers various factors that an employer can assign to these considerations and then process using an equation that divides the product of these factors by the estimated cost.
H.3 Additional Detail: Driscoll--The Economics of Noise Control Engineering Versus the Hearing Conservation Program
One of the authors of The Noise Manual (AIHA, 2003) chapter, Dennis Driscoll, has outlined a method for determining the cost of a hearing conservation program in more detail. This method considers 18 costs in the annual hearing conservation program cost:
General guidelines provided by AIHA:
General guideline 1: Whenever possible, include noise control at the design phase (equipment or facilities). Considering noise exposure only at a later stage and then retrofitting existing equipment can cost more than 10 times as much as designing the noise control before construction begins. The cost of purchasing new production equipment comes into play somewhere between the two.
General guideline 2: Include maintenance expenses in the cost estimate--unless more specific information is available, assume that these can run about 5% per year (e.g., for 10 years).
Source: Driscoll and Royster, 2003.
-
Number of participants in the hearing conservation program
-
Hearing protection devices
-
Noise surveys
-
Audiometric testing
-
Audiometric follow-up and retests
-
Audiometric follow-up and retests
-
Audiometric follow-up and retests
-
Recordability determination
-
Worker training materials
-
Calibration of acoustical instrumentation
-
Calibration of audiometers
-
Worker training time
-
Worker hearing test time
-
Hearing conservation program administrative time
-
Maintenance of acoustical instrumentation
-
Lost production
-
Space allocation
-
Expense to certify CAOHC (Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation) technicians
-
Medical record retention
-
Workers' compensation
Using this method, the cost of the hearing conservation program does not include machinery (present or future).
In 2010 and 2011, approximately 100 professional industrial hygienists were given an opportunity to complete a worksheet on the costs of the HCP at their organizations. This exercise was part of a workshop on the economics of noise control engineering versus the hearing conservation program (Driscoll, 2010).
The worksheet results were quite consistent in showing that, using these 18 points as cost criteria, the majority of organizations spent $350 to $400 per year per worker in the hearing conservation program. Results for a few organizations, however, were substantially higher. The highest costs tended to be associated with fixed daily fees for services provided at multiple remote locations where few workers were employed (the highest hearing conservation program cost reported was $1,800 per worker per year). Costs were lower when these fixed fees, such as for mobile audiometry van service to remote facilities, could be averaged over a larger number of workers. However, in general, the total hearing conservation program cost was not notably different for small organizations compared with large organizations.
H.4 Example: Colgate-Palmolive--Winner of the 2012 Safe-In-Sound Award
General guidelines:
General guideline 1: Plan to complete two noise-control projects per year.
General guideline 2: Noise reduction projects often have additional benefits, such as reduced energy requirements, cleaner facilities, and improved machinery performance or service life.
Sources: Driscoll, 2010, 2012. Colgate-Palmolive, 2012.
NIOSH has partnered with the National Hearing Conservation Association (NHCA) to create an award for excellence in hearing loss prevention. This award is called the Safe-In-Sound award. Colgate-Palmolive won the 2012 Safe-In-Sound award through an extensive effort to reduce noise exposure in its facilities around the world (NIOSH, 2012).
With the assistance of a noise-control engineer and following the general principles outlined by AIHA, Colgate-Palmolive identified and prioritized noise sources. The process revealed that compressed air accounted for approximately 30% of the noise at production facilities and required approximately 15% of the energy. To help solve both problems, the company created "Noise, Energy & Maintenance" teams to help the company optimize system operation, minimize leaks, and assist workers in using compressed air appropriately. They planned to execute two noise reduction projects per year at many sites.
As of 2012, the company had completed 250 noise reduction projects across 60 facilities, investing $2 million. The results averaged approximately 6 dBA noise reduction per project (and up to 22 dBA for some projects). Noise exposure was reduced for more than 5,000 workers through these projects (the math suggests that this equates to an average cost of $400 per worker). Many of these projects also resulted in energy savings, cleaner facilities, and improved equipment life. One of Colgate-Palmolive's goals is to create a "Zero Hearing Protection" site. Because the company uses the ACGIH-TLV criteria (i.e., 85 dBA with 3 dBA doubling rate) or the local regulation, whichever is more stringent, this goal will reduce worker noise exposure to levels well below OSHA's permissible exposure limit (PEL) and action level (AL).
In an online presentation, Colgate-Palmolive provides a photojournal of noise-control projects and reports on the dBA levels before and after modifications. View this presentation here.
H.5 NASA – Buy-Quiet Roadmap
NASA developed a comprehensive program to guide quieter equipment purchases. This program, termed the "Buy-Quiet Process Roadmap," is part of the NASA EARLAB Auditory Demonstration Laboratory website.
General guidelines:
General guideline 1: The cost of a dual-ear, full-disability claim across the United States reported in The Noise Manual (Berger et al., 2003) averages approximately $66,000 in 2011 dollars (assuming a long-term average of 4.2% inflation)
General guideline 2: The net present value of the hearing conservation program and personal protective equipment (hearing-protective devices) may be set to $0 for TWAs below the AL.
Source: Nelson, 2012
The Roadmap includes a simple spreadsheet application to help calculate the cost/benefit ratio for potential noise reduction projects. A white paper explains the approach used to determine the costs of exposing a person to noise for the length of a career (Nelson, 2012).
This method uses the following factors to estimate the cost of noise exposure:
-
The TWA noise exposure (presumed constant over time).
-
The net present value (NPV) of potential disability claims at the end of 30 years.
-
The NPV of hearing aids and batteries that might be needed after retirement.
-
The NPV of the hearing conservation program and personal protective equipment during the career.
The white paper offers the following note about use of the NPV:
The economic benefit of noise control is estimated by comparing the reduction of the net present value of noise exposure to the cost of the corresponding noise-control effort.
For purposes of this paper, the discount rate for the NPV calculation is assumed to be 0% (inflation neutral). The NPV is then just the sum of the expected expenditures in today's dollars. This assumption translates in practice to the expectation that all inflated future costs will be paid with equally-inflated future dollars out of available cash accounts.
The white paper cites a 2006 study commissioned by the U.S. Navy titled Long-term Cost Benefit of Noise Control on Ships (Bowes et al., 2006). Extrapolating the cost per year and adjusting for inflation, the NPV of the hearing conservation program was determined to be $1,300 per year, or $38,000 for 30 years. This value is incorporated into NASA's cost/benefit calculations for noise-control projects.
H.6 References
Berger et al. 2003. Hearing Loss Statutes in the United States and Canada. Chapter 18, Table 18.1, in The Noise Manual. 5th Edition. American Industrial Hygiene Association. pp. 692-696.
Bowes et al. 2006. Long-Term Cost Benefit of Noise Control on Ships. Document Number CRM D0014732.A2/Final. CNA Corporation.
Colgate-Palmolive. 2012. Presentation: Safe-In-Sound Excellence Award.
Driscoll, D.P. 2010. Presentation: The Economics of Noise Control Engineering Versus the Hearing Conservation Program. Professional Conference on Industrial Hygiene (PCIH), American Board of Industrial Hygiene.
Driscoll, D.P. 2012. Personal communication with D. Driscoll and ERG. March 28.
Driscoll, D.P. and L.H. Royster. 2003. Benefits and Costs of Noise Control. In Berger et al., eds. The Noise Manual. 5th Edition. American Industrial Hygiene Association. pp. 281-9.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Buy-Quiet Process Roadmap.
Nelson, D. A. 2012. The Long-Term Cost of Noise Exposure.
NIOSH. 2012. NIOSH Update: NIOSH and NHCA present 2012 Safe-In-Sound Excellence in Hearing Loss Prevention Awards™. NIOSH Web page. February 23.
APPENDIX I--Reviewing Audiograms
OSHA requires employers conduct baseline and annual audiometry testing on workers who have daily TWA noise exposures of 85 dBA or more. Audiogram review is an important tool for assessing the effectiveness of the hearing conservation program. OSHA requires employers to establish a program to monitor annual audiograms to determine if employees exposed to noise hazards are losing their hearing over the course of employment. OSHA defines a Standard Threshold Shift (STS) as a change in the hearing threshold relative to the baseline audiogram of an average of 10 or more dB in 2,000, 3,000, and 4,000 Hz in either ear. OSHA requires employers to record hearing loss in the OSHA 300 log if there is an STS and the employee meets the definition of mild hearing impairment/loss defined as an average hearing loss in 2,000, 3,000 and 4,000 Hz greater than 25 dB from audiometric zero.
Suggested Audiograms for Program Review
-
Audiograms with a threshold shift or STS – (include audiograms that required a second test, even if the second test did not reveal a threshold shift):
-
If employee re-tested, was the re-test performed within 30 days of the original test?
-
Was the baseline revised by an audiologist, otolaryngologist, or physician?
-
Did employer/employee get appropriate notification and documentation of their STS?
-
Did the notification comply with 21-day criteria?
-
Was the worker re-fitted for hearing protective devices and re-trained as required?
-
-
If recording criteria was met, was the confirmed STS recorded on the OSHA 300 Log log?
-
If the STS was not recorded on the OSHA 300 Log, investigate the reason.
-
Red Flags:
-
Multiple STS not reported or lined-out in OSHA 300 Log.
-
Multiple statements that hearing loss is not occupational.
-
Request employer provide criteria for recordkeeping and explain all line-outs/non-recorded STS. Access to medical records for provider determination may be necessary.
-
-
-
All Revised Baselines for the past 12 months:
-
Are baselines revised by an audiologist, otolaryngologist, or physician?
-
Are most baseline revisions associated with an STS?
-
Are baselines revised for each ear separately?
-
What referral criteria are in place for referral for problem audiograms?
-
Were any employees referred to a specialist (audiologist, otolaryngologist (ENT) or other physician).
-
Red Flags:
-
Multiple determinations that STS are not related to workplace noise exposure.
-
Revised baselines without recording/reporting STS or referring employee to a specialist. Request employer provide rational for baseline revision. Access to medical records for provider determination may be necessary.
-
-
-
A random sample of annual audiograms should also be reviewed to assess the pattern of hearing loss over the course of employments.
-
Are employees experiencing multiple STS over the course of employment?
-
Reviewing and Interpreting Audiograms
Compare the most recent annual audiogram with the baseline or reference audiogram to determine if an employee has an STS. If an STS is observed, review data for intervening years to determine when the STS occurred. The baseline audiogram is usually, but not always, the first audiogram. The baseline audiogram should be clearly documented and may be different for each ear. If a persistent STS is identified, the audiogram demonstrating the initial STS is often adopted as the revised baseline for future comparisons. Revising the baseline must be done by an audiologist, otolaryngologist (ENT physician) or other trained physician.
Audiograms may be recorded as a graph, in table format, or on a paper ticket. The key frequencies for review are 2,000, 3,000, and 4,000 Hz in each ear. Results should be evaluated for each ear separately; a threshold shift can occur in one ear and not the other. There are smartphone applications that will automatically calculate STS values and perform age correction. If a smart phone application is used during an investigation, some manual calculations should also be conducted to verify the application is correctly calculating STS values.
The OSHA Office of Occupational Medicine and Nursing (OOMN) can be contacted for additional assistance in reviewing and interpreting audiograms.
Audiogram Evaluation and STS Calculations
STS Calculation without Age Correction (see Example 1 below)
-
For the most recent/current audiogram, compare the hearing thresholds at 2,000, 3,000 and 4,000 Hz to the baseline/reference audiogram values at the same frequencies.
-
Subtract the baseline hearing thresholds at 2,000, 3,000 and 4,000 Hz from the most recent/current audiogram at the same frequencies (Diff.).
-
For each ear, add the three threshold differences, then divide by 3 to get the average threshold difference in hearing loss over the three frequencies (AVG).
-
If the average of the threshold difference is less than 10 dB, the employee does not have an STS.
-
If the average of the threshold differences is greater than or equal to 10 dB, then an STS is present.
-
Example 1: STS Calculation without Age Correction
Employee is a male, age at most recent audiogram was 40 years. His baseline audiogram was recorded at age 30.

STS Calculation: Calculate the difference between the baseline and current audiogram thresholds at the three required frequencies (2000, 3000, 4000 Hz) and divide the sum by 3 for the average threshold difference. If the average difference is greater than or equal to 10 dB, an STS has occurred. In this example, an STS has occurred in the right ear.
STS Calculation with Age Correction (see Examples 2-3 below)
-
The standard allows employers to correct for presbycusis (hearing loss attributed to aging). Age-correction values can be applied to determine whether an age-corrected STS has occurred. (Note that these examples utilize the tables in Appendix F of 1910.95; as noted previously in Section IV.B.1, if age correction is to be performed then NHANES data is recommended for use instead of the tables in the noise standard. However, the procedure in this section will be similar regardless of the data utilized.)
-
Refer to the tables in 1910.95 Appendix F.
-
In the appropriate table (sex based), find the age-correction factors at 2,000, 3,000 and 4,000 Hz for:
-
The age of the employee at the time of the most recent/current audiogram and,
-
for the age of the employee at the baseline/reference audiogram (remember the baseline may be different for each ear).
-
-
Calculate the difference by subtracting the baseline correction factors from the current age correction factors. There should be 3 age-correction factors for each ear (see Figure I-1 below).
-
Subtract the calculated age-correction factors from the threshold differences (Diff.) previously calculated. These are the age-corrected thresholds.
-
Calculate the average of the age-corrected thresholds; if the average is greater than or equal to 10 dB, an age-corrected STS has occurred.
Figure I-1: Selection of age correction values (Table F-1, Male); age correction between ages 30-40 shown.

Example 2: STS Calculation with Age Correction
Same employee as in Example 1, male, currently age 40, baseline audiogram done at age 30.

STS Calculation: Compare baseline and current audiogram to determine if there is an STS. If an ear has an STS, subtract the calculated age correction values (Table F-1, see Figure 1) from the threshold difference in each frequency and divide the sum by 3 to calculate the age-corrected average. If the age-corrected average is greater than or equal to 10 dB, the employee has an age-corrected STS. In this example, an age-corrected STS has occurred in the right ear.
OSHA Recordable: NO. Although there is an age-corrected threshold shift ≥ 10 dB in the right ear, the average hearing level in the current audiogram at 2K, 3K, and 4K Hz is (15+15+20)/3 = 16.7 which is < 25 dB. If the average of 2K, 3K, and 4K Hz in the current audiogram is < 25 dB, the STS is not recordable on the 300 Log.
Example 3: STS Calculation with Age Correction and Revised Baseline
Female, age 40 at current audiogram. Baseline left ear 2010 (age 30)/Baseline right ear revised 2017 (age 37).

STS Calculation: Calculate the difference between the baseline and current audiogram thresholds at the three required frequencies (2000, 3000, 4000 Hz), and divide the sum by 3 for average difference. If the average difference is greater than or equal to 10 dB, an STS has occurred. In this example, initial calculations reveal both left (11.7 dB) and right (13.3 dB) ears have an STS without age correction.
Age-corrected STS Calculation: Calculate the differences in age-correction values between the current audiogram and the baseline audiograms. Note that the age correction value for the left ear is the difference between 30 and 40 years of age. Because the right ear baseline was updated due to an STS at age 37, the age correction value for the right ear is the difference between 37 and 40 years of age.
Subtract the age correction values (Table F-2, see Figure 2 below) from the initial threshold differences (Diff.) at each frequency. Calculate the age-corrected average of 2000, 3000, 4000 Hz. After age-correction, the left ear does NOT have an age-corrected STS, but the right ear has an age-corrected STS. This employee may have had two threshold shifts in the past 3 years.
OSHA Recordable: YES for right ear. The age-corrected STS is ≥ 10 dB AND the average the of the current audiogram thresholds at 2K, 3K, and 4K is (15+30+40)/3=28.3 dB ≥ 25 dB compared to audiometric zero.
Figure I-2: Selection of age correction values (Table F-2, Female); age correction between ages 30-40 (left ear) and ages 37-40 (right ear) shown.

OSHA Recordability Criteria
Not all STSs meet OSHA recordability criteria. In order to determine if the STS meets the criteria for occupational hearing loss, an additional calculation is required (see 29 CFR 1904.10 and Examples 2-3 above):
-
From the current audiogram, identify whether an STS has occurred for either ear (age-corrected values may be used).
-
Calculate the average current hearing thresholds in frequencies 2,000, 3,000 and 4,000 Hz for the ear(s) with an STS. Add the hearing thresholds and divide by 3.
-
If the average in these frequencies is 25 dB or more, the STS is recordable on the 300 Log.
-
If the average is less than 25 dB, then the STS is not recordable. However, all the criteria required for reporting and follow-up of an STS per 29 CFR 1910.95 still applies.
-
Figure I-3: Blank audiogram review table.

APPENDIX J--THREE WAYS TO JUMP-START A NOISE-CONTROL PROGRAM
The following slides are an excerpt from a presentation by Dennis Driscoll, P.E., during a course held at the 2011 Professional Conference on Industrial Hygiene. The slides are reprinted here with the author's permission.
This presentation provides practical suggestions for reducing excessive noise from three sources.
-
Pneumatic or compressed air sources.
-
Elevated sound levels from sources that can be reduced through maintenance for noise control.
-
Machinery noise sources that can be controlled by considering noise while improving machine guarding.
These three sources are some of the most frequent causes of excessive workplace noise. Controlling these sources can have a marked impact on the overall noise-exposure levels that workers experience.
Additionally, these three items will provide the greatest noise reduction per dollar invested, and can even have an economic payback through energy savings and life expectancy of equipment.
The Economics of Noise Control Engineering Versus the Hearing Conservation Program
Impediments and Road Blocks
-
Lack of time, background, money, and/or confidence to get started.
-
Resistance, indifference, and/or lukewarm support from above.
-
Resistance, indifference, and/or lukewarm support from below (operators/mechanics).
Topics
- Let's look at three (3) homeruns we can all manage:
-
Pneumatic or compressed air sources,
-
Maintenance for noise control, and
-
Improving machine guarding.
-
Pneumatic and Compressed Air Systems

Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
-
The usage of compressed air is often a plant-wide noise issue in manufacturing plants.
-
Compressed air can easily be responsible for 25-33% of a plant's noise problems.
-
Compressed air noise is probably the easiest source to control.
-
Better managing compressed air usage and noise can have significant financial and energy savings over time.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
Pneumatic or compressed air systems are used to:
- Operate or motivate equipment, using devices such as air cylinders, air valves, solenoids, etc.
- Air jets and nozzles, including hand-held air guns, are used to move parts/product, blow-off debris, close flaps on corrugated containers (boxes/cases), or similar service-type actions.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
Noise generated by compressed air is caused by turbulence due to the mixing of gases with widely different velocities.
Additional turbulence is created as the compressed air blows against objects, such as parts or sections of the machinery.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
The shearing action occurring in the mixing region results in excessive noise, where the sound level is proportional velocity of air flow raised to the 8th power.

Therefore, the 1st Step toward controlling compressed air noise is to reduce the air velocity to as low as practical and maintaining that setting.
Noise Reduction Resulting from
Air Pressure Adjustments
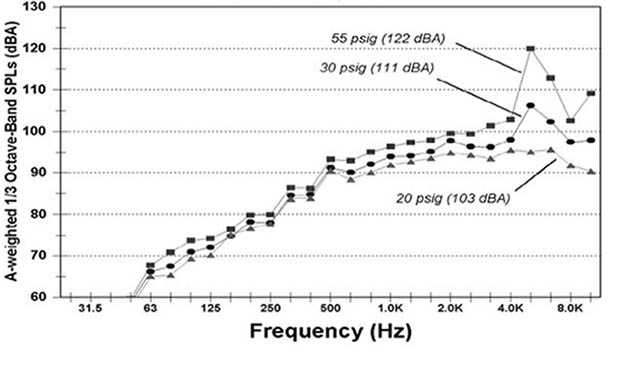
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
The 2nd Step is to treat all open-ended discharge lines and ports, including standard air jets and nozzles with commercially-available quiet-design nozzles or pneumatic silencers.
Care must be exercised to ensure the type of device used meets the service needs at the plant.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
There are two categories of devices:
- Air exhaust, and
- Service-type devices



Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
And there is an energy cost savings, too:
- For example, blowing compressed air through a 10mm open pipe at a pressure of 5 bars uses 185 Nm3/hr.
- At an average cost of $0.015 (U.S. Dollars) per 1 Nm3/hr, and an estimated use time of 40%, this equates to 704 hours of consumption per year. Therefore, the annual cost for the open pile is:
185 Nm3/hr x $0.015 x 704 hours = $1953.60.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
And there is an energy cost savings, too:
- Using a Silvent 705 quiet-design nozzle provides the same air-flow service, but only uses 95 Nm3/hr. This results in an annual cost of $1003.20. Therefore, the savings is:
| Open Pipe | Quiet Design Nozzle | Annual Savings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $1953.60 | - | $1003.20 | = | $950.40 |
| Per Nozzle!!!! |
AND, provides 20 dBA of attenuation.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
- Manufacturers of quiet-design compressed air devices:
- -Silvent, Inc.
- -Exair Corporation
- -Vortec
- -Allied Witan Company
- -McGill Air Pressure Corp.
Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
Contact any number of these manufacturers and:
- Request a free-of-charge survey and audit of all compressed air devices used at the plant.
- Recommendations and cost estimates for retrofitting all air sources.
- Calculation of the energy savings and break-even point for retrofit investment.

Pneumatic and
Compressed Air Systems
Steps for minimizing compressed air noise:
- Optimize air pressure settings for all pneumatic devices, document and maintain settings over time.
- Identify and repair compressed air leaks from sources such as valves, cracked hoses, failed seals, etc.
- Use programmable logic controllers (PLC) that integrate all digital sensors along a production line that can shut off the delivery of compressed air when the line or device is off line.
- Should Step 1-3 not be sufficient, then retrofit all compressed air devices (service and non-service type).
Acoustical Maintenance
Acoustical Maintenance
- To achieve the goal of reducing worker noise exposures sufficiently to eliminate the need for hearing protection or the HCP, it will require a combination of noise control measures and then maintaining these controls over time.

Acoustical Maintenance
-
In addition, a critical component in the long-term success of the noise control program is to vigilantly keep manufacturing equipment in optimal working condition.
- This will help minimize the noise generated, AND it will also minimize the wear and tear on equipment, which improves its life expectancy. Hence, there is a hidden cost savings that can be difficult to quantify, but needs to be at least recognized as a benefit.
Acoustical Maintenance

Acoustical Maintenance
-
Maintaining all equipment and noise controls at their optimum performance condition needs to be an on-going effort.
-
Hand in hand with general mechanical maintenance, which improves the performance and life-span of any piece of equipment, an acoustical maintenance program will help ensure the equipment remains within the noise limits intended by the company, or as the equipment should generate under optimal working conditions.
Acoustical Maintenance
-
As criteria for an acoustical maintenance program, each machine should typically operate within 2 dBA of the minimum sound level of which it is optimally capable.
-
Plus, when equipment is maintained in good working order, from a noise exposure standpoint the added benefit is that it will minimize the time workers need to spend in the direct sound field of the machine while performing any service requirements.
Acoustical Maintenance
To assist with implementing an effective acoustical maintenance program, the following elements are presented:
- Conduct an initial baseline sound level survey for each machine in good working order while operating under normal conditions. This should consist of documenting the A-weighted sound level at fixed locations for each machine or production line.
Example Noise Contour Map
Acoustical Maintenance
-
Periodically (bi-monthly, quarterly, or at least semi-annually) conduct a general sound survey of each machine, and compare the operating sound level with the baseline sound level data.
-
If noise generating elements are identified, or the sound levels indicate at least an increase over the baseline data of 2 dBA, then appropriate repair should be performed, and
Acoustical Maintenance
- Maintenance and operating personnel should be trained to observe and listen for potential noise sources outside the norm for the equipment of concern. They should become familiar with the noise generating mechanisms of each machine and with the visual inspection procedures.
Acoustical Maintenance
- When a noise-producing problem is identified during a visual and auditory inspection, the problem should be corrected immediately if it involves only a minor malfunction or adjustment, and even if the equipment appears to be operating normally. If the problem requires more extensive attention, then it should be labeled or tagged at the problem location and be scheduled for service during the next maintenance round.
Acoustical Maintenance
- Successful implementation of an acoustical maintenance program will ensure the correction of simple and often overlooked noise problems. This process alone will yield significant benefits in both the long-term life of the equipment and minimizing the noise exposure risk to employees.
Machine Guarding
If you must guard, then let's go all the way!!
Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits
Poly Carbonate Safety Enclosures

Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits

Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits

Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits

Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits


Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits
-
For all existing polycarbonate guards, tightly seal, or at least minimize, all gaps or openings between the panel edges and their frame, and between all adjacent metal frame sections.
-
For sealing polycarbonate enclosures with large openings, such as gaps between the floor and bottom edge of the machine cabinet, use a dense but flexible barrier material.
Machine Guarding and Acoustical Benefits

- Install at least some sound absorption material to at least 25% of any available surface areas inside the enclosures. The material's location in not critical, as it just needs to be inside the enclosure.
Three Significant Home Runs
-
Get a handle on pneumatic and compressed air devices and machine controls,
-
Implement an Acoustical Maintenance Program to maintain existing noise controls and keep machinery in good working order, and
-
Go all the way with machine guarding to include the acoustical benefits (pennies on the dollar).
Three Significant Home Runs

-
You have the tools to quantify the cost of a HCP, prioritize noise control projects, and to determine the return on investment toward eliminating the need for a HCP.
-
NIHL is 100% preventable.
-
I challenge you to be the key individual that makes a difference in the lives of workers at your location(s).
Dennis P. Driscoll, P.E.
Associates In Acoustics, Inc.